Related Research Articles
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.
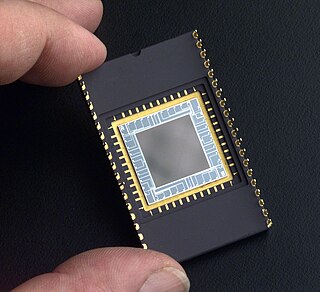
The Foveon X3 sensor is a digital camera image sensor designed by Foveon, Inc., and manufactured by Dongbu Electronics. It uses an array of photosites that consist of three vertically stacked photodiodes. Each of the three stacked photodiodes has a different spectral sensitivity, allowing it to respond differently to different wavelengths. The signals from the three photodiodes are then processed as additive color data that are transformed to a standard RGB color space. In the late 1970s, a similar color sensor having three stacked photo detectors at each pixel location, with different spectral responses due to the differential absorption of light by the semiconductor, had been developed and patented Kodak.

A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, and camcorders to create a color image. The filter pattern is half green, one quarter red and one quarter blue, hence is also called BGGR, RGBG, GRBG, or RGGB.

A digital single-lens reflex camera is a digital camera that combines the optics and mechanisms of a single-lens reflex camera with a solid-state image sensor and digitally records the images from the sensor.

Sigma Corporation is a Japanese company, manufacturing cameras, lenses, flashes and other photographic accessories. All Sigma products are produced in the company's own Aizu factory in Bandai, Fukushima, Japan. Although Sigma produces several camera models, the company is best known for producing high-quality lenses and other accessories that are compatible with the cameras produced by other companies.

The Sigma SD10 is a digital single-lens reflex camera (DSLR) manufactured by the Sigma Corporation of Japan. It was announced on October 27, 2003, and is an evolution of the previous SD9 model, addressing many of the shortcomings of that camera. The Sigma SD10 cameras are unique in the digital DSLR field in using full-color sensor technology, and in that they only produce raw format images that require post-processing on a computer.

Super CCD is a proprietary charge-coupled device that has been developed by Fujifilm since 1999. The Super CCD uses octagonal, rather than rectangular, pixels. This allows a higher horizontal and vertical resolution to be achieved than a traditional sensor of an equivalent pixel count.

An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.

The FujifilmFinePix F series is a line of compact digital cameras that was known for its low-light performance in 2005, with relatively low image noise and natural colors even at high ISO settings. With its relatively large, but moderate resolution Super CCD sensors, it concentrated on image quality, and low-light shooting without flash, which was mostly restricted to prosumer models at the time.

An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the now much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor. CMOS sensors are used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and lensless imaging for cells.

In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.

In digital photography, the RGBE filter is an alternative color filter array to the Bayer filter (GRGB). It similarly uses a mosaic of pixel filters, of red, green, blue and "emerald", and so also requires demosaicing to produce a full-color image. It was developed by Sony and so far is used only in the ICX456 8-megapixel CCD and in the Sony Cyber-shot DSC-F828 camera.

Richard "Dick" Francis Lyon is an American inventor, scientist, and engineer. He is one of the two people who independently invented the first optical mouse devices in 1980. He has worked in signal processing and was a co-founder of Foveon, Inc., a digital camera and image sensor company.

The Sigma SD14 is a digital single-lens reflex camera produced by the Sigma Corporation of Japan. It is fitted with a Sigma SA mount which takes Sigma SA lenses.
A Hole accumulation diode (HAD) is an electronic noise reduction device in a charge-coupled device (CCD) or CMOS imaging sensor, patented by the Sony Corporation. HAD devices function by reducing dark current that occur in the absence of light falling on the imager for noise reduction and enhanced image quality.

The Sigma DP1 was a high-end compact digital camera introduced by the Sigma Corporation. It featured a 14-megapixel Foveon X3 sensor, a fixed 16.6 mm F4.0 lens, a 2.5-inch (64 mm) LCD and a pop-up flash. It was the first "compact" camera that featured an APS-C sized sensor, a feature that Sigma claimed would result in DSLR quality images from a small, pocketable camera.

The Leica S2 is a digital medium format DSLR camera announced by Leica Camera on September 23, 2008.

The Sigma DP2 is a high-end compact digital camera introduced by the Sigma Corporation. It features a 14-megapixel Foveon X3 sensor, the same sensor used in its predecessor, the Sigma DP1 and in the Sigma SD14 DSLR, a fixed 24.2mm f/2.8 lens, a 2.5” LCD and a pop-up flash.

The Sigma SD15 is an updated version of Sigma SD14 DSLR produced by the Sigma Corporation of Japan and featuring the improved TRUE II image processing engine, but with the same image sensor as its predecessor. As such, the SD15 features the 4.7 MP Foveon X3 sensor. After having showcased the camera in photokina 2008 and officially introduced during PMA 2010, it finally began shipping in June 2010. It is Sigma's fourth DSLR since the SD9 from 2002.
The Sigma DP3 Merrill is a high-end compact digital camera made by Sigma Corporation. It features a 46-megapixel Foveon X3 sensor and a 50mm f/2.8 fixed lens.