
In computing, a printer is a peripheral device which makes a persistent representation of graphics or text on paper. While most output is human-readable, bar code printers are an example of an expanded use for printers.

The plotter is a computer printer for printing vector graphics. Plotters draw pictures on paper using a pen. In the past, plotters were used in applications such as computer-aided design, as they were able to produce line drawings much faster and of a higher quality than contemporary conventional printers, and small desktop plotters were often used for business graphics. Although they retained a niche for producing very large drawings for many years, plotters have now largely been replaced by wide-format conventional printers.

Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylinder called a "drum" to define a differentially charged image. The drum then selectively collects electrically charged powdered ink (toner), and transfers the image to paper, which is then heated in order to permanently fuse the text, imagery, or both. As with digital photocopiers, laser printers employ a xerographic printing process. Laser printing differs from traditional xerography as implemented in analog photocopiers in that in the latter, the image is formed by reflecting light off an existing document onto the exposed drum.

Dot matrix printing, sometimes called impact matrix printing, is the process of computer printing from a collection of dot matrix data to a device, which can be one of:

Inkjet printing is a type of computer printing that recreates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper, plastic, or other substrates. Inkjet printers are the most commonly used type of printer, and range from small inexpensive consumer models to expensive professional machines.

A dot matrix is a 2-dimensional patterned array, used to represent characters, symbols and images. Every type of modern technology uses dot matrices for display of information, including mobile phones, televisions, and printers. They are also used in textiles with sewing, knitting, and weaving.

A dye-sublimation printer is a computer printer which uses heat to transfer dye onto materials such as a plastic, card, paper, or fabric. The sublimation name was first applied because the dye was considered to make the transition between the solid and gas states without going through a liquid stage. This understanding of the process was later shown to be incorrect. There is some liquifying of the dye. Since then, the process is sometimes known as dye-diffusion, though this has not eliminated the original name. Many consumer and professional dye-sublimation printers are designed and used for producing photographic prints, ID cards, clothing, and more.

A notebook is a book or binder of paper pages, often ruled, used for purposes such as recording notes or memoranda, writing, drawing or scrapbooking.

Stationery is a mass noun referring to commercially manufactured writing materials, including cut paper, envelopes, writing implements, continuous form paper, and other office supplies. Stationery includes materials to be written on by hand or by equipment such as computer printers.

Before the development of photographic copiers, a carbon copy—not to be confused with the carbon print family of photographic reproduction processes—was the under-copy of a typed or written document placed over carbon paper and the under-copy sheet itself. When copies of business letters were so produced, it was customary to use the acronym "CC" or "cc" before a colon and below the writer's signature to inform the principal recipient that carbon copies had been made and distributed to the parties listed after the colon. With the advent of word processors and e-mail, "cc" is used as a merely formal indication of the distribution of letters to secondary recipients.

Office supplies are consumables and equipment regularly used in offices by businesses and other organizations, by individuals engaged in written communications, recordkeeping or bookkeeping, janitorial and cleaning, and for storage of supplies or data. The range of items classified as office supplies varies, and typically includes small, expendable, daily use items, consumable products, small machines, higher cost equipment such as computers, as well as office furniture and art.

Letterpress printing is a technique of relief printing using a printing press, a process by which many copies are produced by repeated direct impression of an inked, raised surface against sheets or a continuous roll of paper. A worker composes and locks movable type into the "bed" or "chase" of a press, inks it, and presses paper against it to transfer the ink from the type which creates an impression on the paper.

Thermal printing is a digital printing process which produces a printed image by selectively heating coated thermochromic paper, or thermal paper as it is commonly known, when the paper passes over the thermal print head. The coating turns black in the areas where it is heated, producing an image. Two-colour direct thermal printers can print both black and an additional colour by applying heat at two different temperatures.
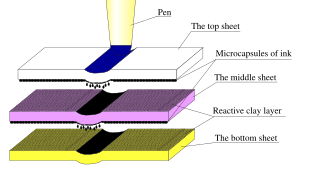
Carbonless copy paper (CCP), non-carbon copy paper, or NCR paper is a type of coated paper designed to transfer information written on the front onto sheets beneath. It was developed by chemists Lowell Schleicher and Barry Green, as an alternative to carbon paper and is sometimes misidentified as such.
A letter-quality printer was a form of computer impact printer that was able to print with the quality typically expected from a business typewriter such as an IBM Selectric.

Edible ink printing is the process of creating preprinted images with edible food colors onto various confectionery products such as cookies, cakes, or pastries. Designs made with edible ink can either be preprinted or created with an edible ink printer, a specialty device which transfers an image onto a thin, edible paper. Edible paper is made of starches and sugars and printed on with edible food colors. Some edible inks and paper materials have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and carry its generally recognized as safe certification.

A photocopier is a machine that makes copies of documents and other visual images onto paper or plastic film quickly and cheaply. Most modern photocopiers use a technology called xerography, a dry process that uses electrostatic charges on a light-sensitive photoreceptor to first attract and then transfer toner particles onto paper in the form of an image. Heat, pressure or a combination of both is then used to fuse the toner onto the paper. Copiers can also use other technologies such as ink jet, but xerography is standard for office copying. Earlier versions included the Gestetner stencil duplicator, invented by David Gestetner in 1881.
















