Related Research Articles

Forensic science, also known as criminalistics, is the application of science to criminal and civil laws, mainly—on the criminal side—during criminal investigation, as governed by the legal standards of admissible evidence and criminal procedure.
The police procedural, or police crime drama, is a subgenre of procedural drama and detective fiction that emphasizes the investigative procedure of a police officer or department as the protagonist(s), as contrasted with other genres that focus on either a private detective, an amateur investigator or the characters who are the targets of investigations. While many police procedurals conceal the criminal's identity until the crime is solved in the narrative climax, others reveal the perpetrator's identity to the audience early in the narrative, making it an inverted detective story. Whatever the plot style, the defining element of a police procedural is the attempt to accurately depict the profession of law enforcement, including such police-related topics as forensic science, autopsies, gathering evidence, search warrants, interrogation and adherence to legal restrictions and procedure.

The Black Museum is a radio crime-drama program produced by Harry Alan Towers in London. It was broadcast in Europe on Radio Luxembourg, a commercial radio station, and was not broadcast by the BBC until 1991.

The murder of Vera Page is a British unsolved child murder case from the early 1930s. On 14 December 1931, 10-year-old Vera Page was reported missing after she failed to return to her home in Notting Hill, London, from a visit to a nearby relative. The child's body was found two days later in undergrowth in nearby Addison Road. Vera had been raped, then manually strangled to death in a murder described by one detective as "the most terrible in which I had to deal with during my career".
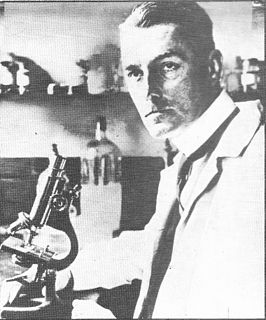
Sir Bernard Henry Spilsbury was a British pathologist. His cases include Hawley Crippen, the Seddon case, the Major Armstrong poisoning, the "Brides in the Bath" murders by George Joseph Smith, the Crumbles murders, the Podmore case, the Sidney Harry Fox matricide, the Vera Page case, and the murder trials of Louis Voisin, Jean-Pierre Vaquier, Norman Thorne, Donald Merrett, Alfred Rouse, Elvira Barney, Tony Mancini, and Margaret Lowe. Spilsbury's courtroom appearances became legendary for his demeanour of effortless dominance.

Hawley Harvey Crippen, usually known as Dr. Crippen, was an American homeopath, ear and eye specialist and medicine dispenser. He was hanged in Pentonville Prison in London for the murder of his wife Cora Henrietta Crippen. Crippen was one of the first criminals to be captured with the aid of wireless telegraphy.

George Joseph Smith was an English serial killer and bigamist. In 1915, he was convicted and subsequently hanged for the murders of three women, the case becoming known as the Brides in the Bath Murders. As well as being widely reported in the media, the case was significant in the history of forensic pathology and detection. It was also one of the first cases in which similarities between connected crimes were used to prove deliberation, a technique used in subsequent prosecutions.
Francis Edward Camps, FRCP, FRCPath was a famous English pathologist notable for his work on the cases of serial killer John Christie and suspected serial killer John Bodkin Adams.
The Podmore Case was a controversial landmark English criminal case. It involved a murder conviction based on a painstaking police investigation, and from careful evaluation of the forensic evidence.
The Brighton trunk murders were two murders linked to Brighton, England, in 1934. In each, the body of a murdered woman was placed in a trunk. The murders are not believed to have any connection with each other aside from how they were carried out, and the first of the two victims remains unidentified; a suspect was arrested and tried for the second murder but was found not guilty.
The towpath murders was a case in which two teenage girls were murdered on the towpath near Teddington Lock on the River Thames, England, on 31 May 1953. Alfred Charles Whiteway was found guilty and hanged for the murders, which attracted a deal of press attention, the case being described at the time as "one of Scotland Yard's most notable triumphs in a century".

Cedric Keith Simpson was an English forensic pathologist. He was Professor of Forensic Medicine in the University of London at Guy's Hospital, Lecturer in Forensic Medicine at the University of Oxford and a founding member and President of the Association of Forensic Medicine. Simpson became renowned for his post-mortems on high-profile murder cases, including the 1949 Acid Bath Murders committed by John George Haigh and the murder of gangster George Cornell, who was shot dead by Ronnie Kray in 1966.

Gordon Frederick Cummins was a British serial killer known as the Blackout Killer, the Blackout Ripper and the Wartime Ripper, who murdered four women and attempted to murder two others over a six-day period in London in February 1942. He is also suspected of committing two earlier murders in October 1941.
Eric Vivian Tullett, known as Tom Tullett was a renowned British Crime Journalist. He adopted the name Tom when he joined a busy National News Desk as a Crime Reporter. He was a big man in every sense of the word, and was a much loved and respected figure in Fleet Street. One of the last investigative journalists of his day, he died in 1991.

Frederick Porter Wensley served as a British police officer from 1888 until 1929, reaching the rank of chief constable of the Scotland Yard Criminal Investigation Department (CID). Serving in Whitechapel for part of his career, he was involved in street patrols during the investigation of the Jack the Ripper murders, details of which he would later publish in his memoirs in 1931. He was one of the 'Big Four', a nickname given to the four Superintendents in charge of the Metropolitan Police CID, with his murder investigations regularly published in the press. The leading prosecuting barrister Sir Richard Muir referred to him as "the greatest detective of all time".
The Crumbles Murders are two separate and unrelated crimes which occurred on a shingle beach located between Eastbourne and Pevensey Bay, England—locally referred to as "the Crumbles"—in the 1920s. The first of these two murders is the 1920 bludgeoning murder of 17-year-old Irene Munro, committed by two men: Jack Field and William Gray. The second murder to occur upon the Crumbles is the 1924 murder of 38-year-old Emily Kaye, who was murdered by her lover, Patrick Mahon.

Sidney Harry Fox was a British petty swindler and convicted murderer. He was executed for the murder of his mother in an attempt to obtain money from an insurance policy on her life. His case is unusual in that it is a rare example of a known matricide in the United Kingdom.

The Cheltenham torso mystery began with the discovery of the torso of an unknown man in the River Severn in 1938. Forensic analysis by Sir Bernard Spilsbury suggested that the body was that of Captain Butt of Cheltenham but the case was never officially resolved.
Norman Thorne was an English Sunday school teacher and chicken farmer who was convicted and hanged for what became known as the chicken run murder. Thorne murdered his fiancée Elsie Cameron on 5 December 1924 at his chicken farm in Crowborough, Sussex, and later dismembered and buried her body.

The murder of Mona Tinsley is a British child murder case from 1937. On 5 January 1937, 10-year-old Mona Lilian Tinsley disappeared after leaving her Newark-on-Trent school. A former lodger of Mona's parents, Frederick Nodder, became the prime suspect in her abduction. However, despite the fact both strong physical and circumstantial evidence existed attesting to his guilt, because no body could be found, Nodder could not be tried for her murder, but was instead convicted of Mona's abduction and sentenced to seven years in gaol.
References
- Evans, C; The Father of Forensics: The Groundbreaking Cases of Sir Bernard Spilsbury, and the Beginnings of Modern CSI, New York, NY, Berkley Books, 2006. ISBN 978-0-425-21007-9
- Brandon, D; Brooke, A; London: The Executioner's City, Sutton Publishing, 2006. ISBN 0-7509-4023-9