
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 22-member intergovernmental body devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975. Its 2024 annual budget was €7.8 billion.

Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the second-largest in the Solar System. It is the only moon known to have an atmosphere denser than the Earth's and is the only known object in space—other than Earth—on which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found. Titan is one of seven gravitationally rounded moons of Saturn and the second-most distant among them. Frequently described as a planet-like moon, Titan is 50% larger in diameter than Earth's Moon and 80% more massive. It is the second-largest moon in the Solar System after Jupiter's Ganymede and is larger than Mercury; yet Titan is only 40% as massive as Mercury, because Mercury is mainly iron and rock while much of Titan is ice, which is less dense.

Cassini–Huygens, commonly called Cassini, was a space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its rings and natural satellites. The Flagship-class robotic spacecraft comprised both NASA's Cassini space probe and ESA's Huygens lander, which landed on Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Cassini was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit, where it stayed from 2004 to 2017. The two craft took their names from the astronomers Giovanni Cassini and Christiaan Huygens.

A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby which makes use of the relative movement and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense.

The Guiana Space Centre, also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximately 500 kilometres north of the equator at a latitude of 5°. In operation since 1968, it is a suitable location for a spaceport because of its near equatorial location and open sea to the east and north.

Huygens was an atmospheric entry robotic space probe that landed successfully on Saturn's moon Titan in 2005. Built and operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), launched by NASA, it was part of the Cassini–Huygens mission and became the first spacecraft to land on Titan and the farthest landing from Earth a spacecraft has ever made. The probe was named after the 17th-century Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens, who discovered Titan in 1655.

XMM-Newton, also known as the High Throughput X-ray Spectroscopy Mission and the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission, is an X-ray space observatory launched by the European Space Agency in December 1999 on an Ariane 5 rocket. It is the second cornerstone mission of ESA's Horizon 2000 programme. Named after physicist and astronomer Sir Isaac Newton, the spacecraft is tasked with investigating interstellar X-ray sources, performing narrow- and broad-range spectroscopy, and performing the first simultaneous imaging of objects in both X-ray and optical wavelengths.

The Automated Transfer Vehicle, originally Ariane Transfer Vehicle or ATV, was an expendable cargo spacecraft developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), used for space cargo transport in 2008–2015. The ATV design was launched to orbit five times, exclusively by the Ariane 5 heavy-lift launch vehicle. It effectively was a larger European counterpart to the Russian Progress cargo spacecraft for carrying upmass to a single destination—the International Space Station (ISS)—but with three times the capacity.

Vega is an expendable small-lift launch vehicle operated by Arianespace, produced by Avio, and jointly developed by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and the European Space Agency (ESA). Development began in 1998 and the first launch took place from the Guiana Space Centre on 13 February 2012. It is the 8th most launched small lift launch vehicle in history. The final flight of the rocket is scheduled for September 2024, after which the vehicle will be replaced by the improved Vega C, already in use.
The European Space Tracking (ESTRACK) network consists of a number of ground-based space-tracking stations belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), and operated by the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany. The stations support various ESA spacecraft and facilitate communications between ground operators and scientific probes such as XMM-Newton, Mars Express, BepiColombo, Gaia. Similar networks are run by the USA, China, Russia, Japan, and India.

The exploration of Saturn has been solely performed by crewless probes. Three missions were flybys, which formed an extended foundation of knowledge about the system. The Cassini–Huygens spacecraft, launched in 1997, was in orbit from 2004 to 2017.

The Jules Verne ATV, or Automated Transfer Vehicle 1 (ATV-1), was a robotic cargo spacecraft launched by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ATV was named after the 19th-century French science-fiction author Jules Verne. It was launched on 9 March 2008 on a mission to supply the International Space Station (ISS) with propellant, water, air, and dry cargo. Jules Verne was the first of five Automated Transfer Vehicle spacecraft to be launched.
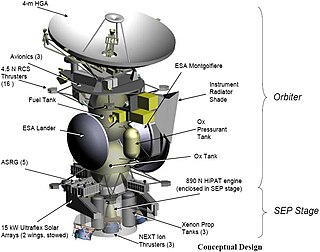
Titan Saturn System Mission (TSSM) was a joint NASA–ESA proposal for an exploration of Saturn and its moons Titan and Enceladus, where many complex phenomena were revealed by Cassini. TSSM was proposed to launch in 2020, get gravity assists from Earth and Venus, and arrive at the Saturn system in 2029. The 4-year prime mission would include a two-year Saturn tour, a 2-month Titan aero-sampling phase, and a 20-month Titan orbit phase.

Colonel Luca Parmitano is an Italian astronaut in the European Astronaut Corps for the European Space Agency (ESA). He was selected as an ESA astronaut in May 2009. Parmitano is also a Colonel and test pilot for the Italian Air Force. He is the first Italian to command the International Space Station (ISS) during Expedition 61.

The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer is an interplanetary spacecraft on its way to orbit and study three icy moons of Jupiter: Ganymede, Callisto, and Europa. These planetary-mass moons are planned to be studied because they are thought to have beneath their frozen surfaces significant bodies of liquid water, which would make them potentially habitable for extraterrestrial life.

Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system operated by Arianespace and developed and produced by ArianeGroup on behalf of the European Space Agency (ESA). It replaces Ariane 5, as part of the Ariane launch vehicle family.

Explorer of Enceladus and Titan (E2T) is a space mission concept that would investigate the evolution and habitability of the Saturnian satellites Enceladus and Titan and is proposed by the European Space Agency in collaboration with NASA.

The Prometheus rocket engine is an ongoing European Space Agency (ESA) development effort begun in 2017 to create a reusable methane-fueled rocket engine for use on the Themis reusable rocket demonstrator and Ariane Next, the successor to Ariane 6, and possibly a version of Ariane 6 itself.

The Science Programme of the European Space Agency is a long-term programme of space science and space exploration missions. Managed by the agency's Directorate of Science, The programme funds the development, launch, and operation of missions led by European space agencies and institutions through generational campaigns. Horizon 2000, the programme's first campaign, facilitated the development of eight missions between 1985 and 1995 including four "cornerstone missions" – SOHO and Cluster II, XMM-Newton, Rosetta, and Herschel. Horizon 2000 Plus, the programme's second campaign, facilitated the development of Gaia, LISA Pathfinder, and BepiColombo between 1995 and 2005. The programme's current campaign since 2005, Cosmic Vision, has so far funded the development of ten missions including three flagship missions, JUICE, Athena, and LISA. The programme's upcoming fourth campaign, Voyage 2050, is currently being drafted. Collaboration with agencies and institutions outside of Europe occasionally occur in the Science Programme, including a collaboration with NASA on Cassini–Huygens and the CNSA on SMILE.


















