Related Research Articles

Rhythm generally means a "movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or frequency of anything from microseconds to several seconds ; to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years.

Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe during the 9th and 10th centuries, with later additions and redactions. Although popular legend credits Pope Gregory I with inventing Gregorian chant, scholars believe that it arose from a later Carolingian synthesis of Roman chant and Gallican chant.
In music, duration is an amount of time or how long or short a note, phrase, section, or composition lasts. "Duration is the length of time a pitch, or tone, is sounded." A note may last less than a second, while a symphony may last more than an hour. One of the fundamental features of rhythm, or encompassing rhythm, duration is also central to meter and musical form. Release plays an important part in determining the timbre of a musical instrument and is affected by articulation.
In music, an ostinato[ostiˈnaːto] is a motif or phrase that persistently repeats in the same musical voice, frequently in the same pitch. Well-known ostinato-based pieces include both classical compositions such as Ravel's Boléro and the Carol of the Bells, and popular songs such as Donna Summer and Giorgio Moroder's "I Feel Love" (1977), Henry Mancini's theme from Peter Gunn (1959), and The Verve's "Bitter Sweet Symphony" (1997).
Music information retrieval (MIR) is the interdisciplinary science of retrieving information from music. MIR is a small but growing field of research with many real-world applications. Those involved in MIR may have a background in musicology, psychoacoustics, psychology, academic music study, signal processing, informatics, machine learning, optical music recognition, computational intelligence or some combination of these.

The clave is a rhythmic pattern used as a tool for temporal organization in Afro-Cuban music. It is present in a variety of genres such as Abakuá music, rumba, conga, son, mambo, salsa, songo, timba and Afro-Cuban jazz. The five-stroke clave pattern represents the structural core of many Afro-Cuban rhythms.
In the history of European art music, the common practice period is the era of the tonal system. Though it has no exact dates, most features of the common-practice period persisted from the mid- to late baroque period, through the Classical, Romantic and Impressionist periods, from around 1650 to 1900. The period saw considerable stylistic evolution, with some patterns and conventions flourishing and then declining, for example the sonata form. Thus, the dates 1650–1900 are necessarily nebulous and arbitrary borders that depend on context. The most important unifying feature throughout the period is a harmonic language to which modern music theorists can apply Roman numeral chord analysis.
Cycle has several meanings in the field of music. Acoustically, it refers to one complete vibration, the base unit of Hertz being one cycle per second. Theoretically, an interval cycle is a collection of pitch classes created by a sequence of identical intervals. Individual pieces that aggregate into larger works are considered cycles, for example, the movements of a suite, symphony, sonata, or string quartet. This definition can apply to everything from settings of the Mass or a song cycle to an opera cycle. Cycle also applies to the complete performance of an individual composer's work in one genre.
Computer audition (CA) or machine listening is general field of study of algorithms and systems for audio understanding by machine. Since the notion of what it means for a machine to "hear" is very broad and somewhat vague, computer audition attempts to bring together several disciplines that originally dealt with specific problems or had a concrete application in mind. The engineer Paris Smaragdis, interviewed in Technology Review, talks about these systems --"software that uses sound to locate people moving through rooms, monitor machinery for impending breakdowns, or activate traffic cameras to record accidents."

Godfried Theodore Patrick Toussaint was a Canadian Computer Scientist, a Professor of Computer Science, and the Head of the Computer Science Program at New York University Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. He is considered to be the father of computational geometry in Canada. He did research on various aspects of computational geometry, discrete geometry, and their applications: pattern recognition, motion planning, visualization, knot theory, linkage (mechanical) reconfiguration, the art gallery problem, polygon triangulation, the largest empty circle problem, unimodality, and others. Other interests included meander (art), compass and straightedge constructions, instance-based learning, music information retrieval, and computational music theory.
Musica ricercata is a set of eleven pieces for piano by György Ligeti. The work was composed from 1951 to 1953, shortly after the composer began lecturing at the Budapest Academy of Music. The work premiered on 18 November 1969 in Sundsvall, Sweden. Although the ricercata is an established contrapuntal style, Ligeti's title should probably be interpreted literally as "researched music" or "sought music". This work captures the essence of Ligeti's search to construct his own compositional style ex nihilo, and as such presages many of the more radical directions Ligeti would take in the future.
The stutter edit is the rhythmic repetition of small fragments of audio, occurring as the common 16th note repetition, but also as 64th notes and beyond, with layers of digital signal processing operations in a rhythmic fashion based on the overall length of the host tempo. The Stutter Edit audio software VST plug-in implements forms of granular synthesis, sample retrigger, and various effects to create a certain audible manipulation of the sound run through it, in which fragments of audio are repeated in rhythmic intervals. The plug-in allows musicians to manipulate audio in real time, slicing audio into small fragments and sequences the pieces into rhythmic effects, recreating techniques that formerly took hours to do in the studio. Electronic musician Brian Transeau is widely recognized for pioneering the stutter edit as a musical technique; he developed, coined the term, and holds multiple patents for the Stutter Edit software plug-in.
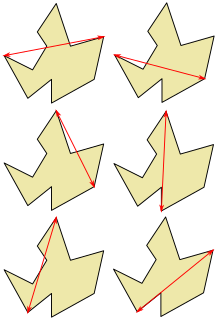
In computational geometry, the method of rotating calipers is an algorithm design technique that can be used to solve optimization problems including finding the width or diameter of a set of points.
Excursions, Op. 20, is the first published solo piano piece by Samuel Barber. Barber himself explains:
These are ‘Excursions’ in small classical forms into regional American idioms. Their rhythmic characteristics, as well as their source in folk material and their scoring, reminiscent of local instruments are easily recognized.
Tunebot is a music search engine developed by the Interactive Audio Lab at Northwestern University. Users can search the database by humming or singing a melody into a microphone, playing the melody on a virtual keyboard, or by typing some of the lyrics. This allows users to finally identify that song that was stuck in their head.

A bell pattern is a rhythmic pattern of striking a hand-held bell or other instrument of the idiophone family, to make it emit a sound at desired intervals. It is often a key pattern, in most cases it is a metal bell, such as an agogô, gankoqui, or cowbell, or a hollowed piece of wood, or wooden claves. In band music, bell patterns are also played on the metal shell of the timbales, and drum kit cymbals.
Harmonic pitch class profiles (HPCP) is a group of features that a computer program extracts from an audio signal, based on a pitch class profile—a descriptor proposed in the context of a chord recognition system. HPCP are an enhanced pitch distribution feature that are sequences of feature vectors that, to a certain extent, describe tonality, measuring the relative intensity of each of the 12 pitch classes of the equal-tempered scale within an analysis frame. Often, the twelve pitch spelling attributes are also referred to as chroma and the HPCP features are closely related to what is called chroma features or chromagrams.
The Euclidean rhythm in music was discovered by Godfried Toussaint in 2004 and is described in a 2005 paper "The Euclidean Algorithm Generates Traditional Musical Rhythms". The greatest common divisor of two numbers is used rhythmically giving the number of beats and silences, generating almost all of the most important World Music rhythms,. The beats in the resulting rhythms are as equidistant as possible; the same results can be obtained from the Bresenham algorithm.
Traditional sub-Saharan African harmony is a music theory of harmony in sub-Saharan Africa music based on the principles of homophonic parallelism, homophonic polyphony, counter melody and ostinato-variation. Polyphony is common in African music and heterophony is a common technique as well. Although these principles of traditional African music are of pan-African validity, the degree to which they are used in one area over another varies. Specific techniques that used to generate harmony in Africa are the "span process", "pedal notes", "Rhythmic harmony", "harmony by imitation", and "scalar clusters".
The Geometry of Musical Rhythm: What Makes a "Good" Rhythm Good? is a book on the mathematics of rhythms and drum beats. It was written by Godfried Toussaint, and published by Chapman & Hall/CRC in 2013 and in an expanded second edition in 2020. The Basic Library List Committee of the Mathematical Association of America has suggested its inclusion in undergraduate mathematics libraries.
References
- ↑ Greg Aloupis, Thomas Fevens, Stefan Langerman, Tomomi Matsui, Antonio Mesa, Yurai Nunez, and David Rappaport, and Godfried T. Toussaint, "Algorithms for computing geometric measures of melodic similarity," Computer Music Journal, Vol. 30, No. 3, Fall 2006, pp. 67–76.
- ↑ Godfried T. Toussaint, "A comparison of rhythmic dissimilarity measures," FORMA, Vol. 21, No. 2, 2006, pp. 129–149.
- ↑ Arshia Cont, Shlomo Dubnov, Gérard Assayag. On the Information Geometry of Audio Streams with Applications to Similarity Computing. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, 2011, 19 (4), pp. 837-846.
- ↑ Maria Mannone, Introduction to gestural similarity in music. An application of category theory to the orchestra, Journal of Mathematics and Music, Vol. 12, No. 2, 2018, pp. 63–85.
- ↑ François Pachet, Geert Westermann, Damien Laigre, Musical Data Mining for Electronic Music Distribution Archived 2014-03-27 at the Wayback Machine . Proceedings of the 1st WedelMusic Conference, pp. 101-106, Firenze, Italy, 2001.
| This music theory article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |