
Cilicia is a geographical region extending inland from the northeastern corner of the Mediterranean Sea. It is at the south-center of the modern Turkey and known locally as Çukurova.

The Karnak Temple Complex, commonly known as Karnak, comprises a vast mix of decayed temples, chapels, pylons, and other buildings near Luxor, in Egypt. Construction at the complex began during the reign of Senusret I in the Middle Kingdom and continued into the Ptolemaic period, although most of the extant buildings date from the New Kingdom. The area around Karnak was the ancient Egyptian Ipet-isut and the main place of worship of the eighteenth dynasty Theban Triad with the god Amun as its head. It is part of the monumental city of Thebes. The Karnak complex gives its name to the nearby, and partly surrounded, modern village of El-Karnak, 2.5 kilometres north of Luxor.
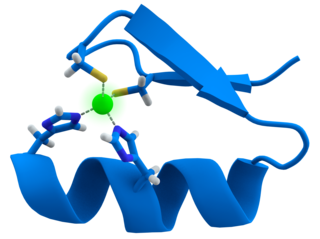
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. Originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from Xenopus laevis transcription factor IIIA, the zinc finger name has now come to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures. Xenopus laevis TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins.
Met, MET, The Met or The MET may refer to:
Articles related to Turkey include:

The Mersin Province is a province in southern Turkey, on the Mediterranean coast between Antalya and Adana. The provincial capital is the city of Mersin and the other major town is Tarsus, birthplace of St Paul. The province is part of Çukurova, a geographical, economical and cultural region, that covers the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye and Hatay.

40S ribosomal protein S27 also known as metallopan-stimulin 1 or MPS-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27 gene. Metallopanstimulin is a zinc finger protein proposed to be involved DNA repair as well as oncogenesis.

Zinc finger protein 43 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF43 gene.

Zinc finger protein 238 is a zinc finger containing transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ZNF238 gene.
Zinc finger protein chimera are chimeric proteins composed of a DNA-binding zinc finger protein domain and another domain through which the protein exerts its effect. The effector domain may be a transcriptional activator (A) or repressor (R), a methylation domain (M) or a nuclease (N).

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the 1960 bp ZBTB32 gene. The 52 kDa protein is a transcriptional repressor and the gene is expressed in T and B cells upon activation, but also significantly in testis cells. It is a member of the Poxviruses and Zinc-finger (POZ) and Krüppel (POK) family of proteins, and was identified in multiple screens involving either immune cell tumorigenesis or immune cell development.
Çınarlı, also spelled Çinarlı or Chenarli, is a Turkic word meaning "place with plane trees" and may refer to several places:

The FPG IleRS zinc finger domain represents a zinc finger domain found at the C-terminal in both DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes and in isoleucyl tRNA synthetase. In these two types of enzymes, the C-terminal domain forms a zinc finger.

Dağpazarı is a village in the Mut district of Mersin Province, Turkey

In molecular biology, the H2TH domain is a DNA-binding domain found in DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes, which are involved in base excision repair of DNA damaged by oxidation or by mutagenic agents. Most damage to bases in DNA is repaired by the base excision repair pathway. These enzymes are primarily from bacteria, and have both DNA glycosylase activity EC 3.2.2.- and AP lyase activity EC 4.2.99.18. Examples include formamidopyrimidine-DNA glycosylases and endonuclease VIII (Nei).

Genome editing, or genome engineering, or gene editing, is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism. Unlike early genetic engineering techniques that randomly inserts genetic material into a host genome, genome editing targets the insertions to site specific locations.
Ballı is a Turkish place name that may refer to the following places in Turkey:
Edward John Rebar is an American biologist. Rebar is the senior vice president and chief technology officer of Sangamo Therapeutics. He researches the use of zinc fingers as a protein platform.
CIVI is a Canadian TV station.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.








