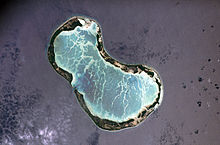
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands, is a chain of atolls and coral islands. Kingman Reef is largely submerged and Filippo Reef is shown on some maps, although its existence is doubted. The islands were formed by volcanic activity and are located in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawaiian Islands. The 11 islands stretch for 2,350 kilometres in a northwest–southeast direction, making it one of the longest island chains of the world. Eight of the islands form part of Kiribati, while the remaining three are United States territories grouped with the United States Minor Outlying Islands. Only Kiritimati and Tabuaeran atolls and Teraina Island have a permanent population.

Abaiang, also known as Apaiang, Apia, and in the past, Charlotte Island, in the Northern Gilbert Islands, is a coral atoll of Kiribati, located in the west-central Pacific Ocean. Abaiang was the home of the first missionary to arrive in Kiribati, Hiram Bingham II. Abaiang has a population of 5,502.

Tabiteuea, formerly Drummond's Island, is an atoll in the Gilbert Islands, Kiribati, farther south of the Tarawa Atoll. The atoll consists of two main islands: Eanikai in the north, Nuguti in the south, and several smaller islets in between along the eastern rim of the atoll. The atoll has a total land area of 38 km2 (15 sq mi), while the lagoon measures 365 km2 (141 sq mi). The population numbered 4,899 in 2005, The islanders have customary fishing practices related to the lagoon and the open ocean.

Butaritari is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. The atoll is roughly four-sided. The south and southeast portion of the atoll comprises a nearly continuous islet. The atoll reef is continuous but almost without islets along the north side. Bikati and Bikatieta islets occupy a corner of the reef at the extreme northwest tip of the atoll. Small islets are found on reef sections between channels on the west side. The lagoon of Butaritari is deep and can accommodate large ships, though the entrance passages are relatively narrow. It is the most fertile of the Gilbert Islands, with relatively good soils and high rainfall. Butaritari atoll has a land area of 13.49 km2 (5.21 sq mi) and a population of 4,346 as of 2010. During World War II, Butaritari was known by US forces as Makin Atoll, and was the site of the Battle of Makin. Locally, Makin is the name of a separate atoll three kilometers to the northeast of Butaritari.

Arorae is an atoll in Kiribati located near the equator. Arorae is the southernmost island in the Gilbert Islands group. It houses almost 1300 people on 9.5 square kilometres.

Abemama (Apamama) is an atoll, one of the Gilberts group in Kiribati, and is located 152 kilometres southeast of Tarawa and just north of the Equator. Abemama has an area of 27.37 square kilometres and a population of 3,299 as of 2015. The islets surround a deep lagoon. The eastern part of the atoll of Abemama is linked together by causeways making automobile traffic possible between the different islets. The outlying islands of Abatiku and Biike are situated on the southwestern side of the atoll.

Maiana is an atoll in Kiribati and is one of the Central Gilbert Islands. Maiana is 44 kilometres (27 mi) south of the capital island of South Tarawa and has a population of 2,027 as of 2010. The northern and eastern sides of the atoll are a single island, whilst the western edge consists of submerged reefs and many uninhabited islets, all surrounding a lagoon. The atoll is 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) long and is very narrow, with an average width of less than 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) and a total land area of 16.72 square kilometres (6.46 sq mi).

Marakei is a small atoll in the North Gilbert Islands. The central lagoon consists of numerous deep basins and surrounded by two large islands which are separated by two narrow channels. The atoll covers an area of approximately 40 km².
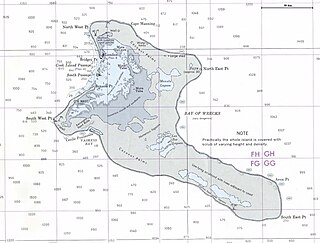
London is the principal settlement on the atoll of Kiritimati belonging to Kiribati in the Pacific Ocean. As of 2005 it has a population of 1,829 people, making it the second largest village on Kiritimati and in the whole Line Islands. In the 2010 census the population was 1,879. Only Tabwakea is slightly larger.

Makin is the name of a chain of islands located in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. Makin is the northernmost of the Gilbert Islands, with a population of 1,798.

Napari or Napali is a settlement located at the north end of Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. In the 2002 census 194 people were recorded as living in Napali. While Napali was not listed in the 2010 census as having any residents, the city of Tereitaki on the southern Napali was reported as having 346 inhabitants.

Tereitaki is a settlement located towards the north end of Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. Napari is the northernmost settlement; with Betania to the south.

Betania is a settlement located on Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati.

Paelau is a settlement located on Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. It is located on the western side of the atoll, south of a passage into the lagoon, with Betania to the north and Aontenaa to the south.

Aontenaa is a settlement located on Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. Paelau is to the north; with Tenenebo to the south.

Tenenebo is a settlement located on Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. Aontenaa is to the north; with Tereitannano to the south.

Tereitannano is a settlement located on Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. Tenenebo is to the north; with Aramari to the south.

Aramari is a settlement located on Tabuaeran atoll, Kiribati. Tereitannano is to the north; with Mwanuku or Eten to the south.