
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in colour. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving living birth to female nymphs without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonise new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs.

Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod body remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which hemolymph cells called hemocytes are suspended. In addition to hemocytes, the plasma also contains many chemicals. It is the major tissue type of the open circulatory system characteristic of arthropods. In addition, some non-arthropods such as molluscs possess a hemolymphatic circulatory system.

The Hemiptera or true bugs are an order of insects comprising some 50,000 to 80,000 species of groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, and shield bugs. They range in size from 1 mm (0.04 in) to around 15 cm (6 in), and share a common arrangement of sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is sometimes limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Many insects commonly known as "bugs" belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly and the May bug and ladybug are beetles.

Mites are small arthropods belonging to the class Arachnida and the subclass Acari. Mites are not a clade as they span two different groups of arachnids: the Acariformes are sister to the camel spiders, while the Parasitiformes are sister to the false scorpions; also, they exclude the ticks, order Ixodida, although ticks and mites are closely related. Mites are distantly related to spiders and scorpions.

Mayflies are aquatic insects belonging to the order Ephemeroptera. This order is part of an ancient group of insects termed the Palaeoptera, which also contains dragonflies and damselflies. Over 3,000 species of mayfly are known worldwide, grouped into over 400 genera in 42 families.

Thrips are minute, slender insects with fringed wings and unique asymmetrical mouthparts. Different thrips species feed mostly on plants by puncturing and sucking up the contents, although a few are predators. Approximately 6,000 species have been described. They fly only weakly and their feathery wings are unsuitable for conventional flight; instead, thrips exploit an unusual mechanism, clap and fling, to create lift using an unsteady circulation pattern with transient vortices near the wings.

The Pentatomoidea are a superfamily of insects in the Heteroptera suborder of the Hemiptera order. They are commonly referred to as shield bugs, chust bugs, and stink bugs. As Hemiptera, they share a common arrangement of sucking mouthparts.

Bed bugs are a type of insect that feed on human blood, usually at night. Their bites can result in a number of health impacts including skin rashes, psychological effects and allergic symptoms. Bed bug bites may lead to skin changes ranging from invisible to small areas of redness to prominent blisters. Symptoms may take between minutes to days to appear and itchiness is generally present. Some individuals may feel tired or have a fever. Typically, uncovered areas of the body are affected and often three bites occur in a row. Bed bugs bites are not known to transmit any infectious disease. Complications may rarely include areas of dead skin or vasculitis.

Grasshoppers are a group of insects belonging to the suborder Caelifera. They are among what is probably the most ancient living group of chewing herbivorous insects, dating back to the early Triassic around 250 million years ago.

Entomophagy describes the practice of eating insects by humans.

Blattodea is an order of insects that contains cockroaches and termites. Formerly, the termites were considered a separate order, Isoptera, but genetic and molecular evidence suggests an intimate relationship with the cockroaches, both cockroaches and termites having evolved from a common ancestor. The Blattodea and the mantises are now all considered part of the superorder Dictyoptera. Blattodea includes approximately 4,400 species of cockroach in almost 500 genera, and about 3,000 species of termite in around 300 genera.
Herbivores are dependent on plants for food, and have coevolved mechanisms to obtain this food despite the evolution of a diverse arsenal of plant defenses against herbivory. Herbivore adaptations to plant defense have been likened to "offensive traits" and consist of those traits that allow for increased feeding and use of a host. Plants, on the other hand, protect their resources for use in growth and reproduction, by limiting the ability of herbivores to eat them. Relationships between herbivores and their host plants often results in reciprocal evolutionary change. When a herbivore eats a plant it selects for plants that can mount a defensive response, whether the response is incorporated biochemically or physically, or induced as a counterattack. In cases where this relationship demonstrates "specificity", and "reciprocity", the species are thought to have coevolved. The escape and radiation mechanisms for coevolution, presents the idea that adaptations in herbivores and their host plants, has been the driving force behind speciation. The coevolution that occurs between plants and herbivores that ultimately results in the speciation of both can be further explained by the Red Queen hypothesis. This hypothesis states that competitive success and failure evolve back and forth through organizational learning. The act of an organism facing competition with another organism ultimately leads to an increase in the organism's performance due to selection. This increase in competitive success then forces the competing organism to increase its performance through selection as well, thus creating an "arms race" between the two species. Herbivores evolve due to plant defenses because plants must increase their competitive performance first due to herbivore competitive success.

In anatomy, the term rostrum is used for a number of phylogenetically unrelated structures in different groups of animals.

Traumatic insemination, also known as hypodermic insemination, is the mating practice in some species of invertebrates in which the male pierces the female's abdomen with his aedeagus and injects his sperm through the wound into her abdominal cavity (hemocoel). The sperm diffuse through the female's hemolymph, reaching the ovaries and resulting in fertilization.

Cimex is a genus of insects in the family Cimicidae. Cimex species are ectoparasites that typically feed on the blood of birds and mammals. Two species, Cimex lectularius and Cimex hemipterus, are known as bed bugs and frequently feed on humans, although other species may parasitize humans opportunistically. Species that primarily parasitize bats are known as bat bugs.

Crickets, of the family Gryllidae, are insects related to bush crickets, and, more distantly, to grasshoppers. The Gryllidae have mainly cylindrical bodies, round heads, and long antennae. Behind the head is a smooth, robust pronotum. The abdomen ends in a pair of long cerci; females have a long, cylindrical ovipositor. The hind legs have enlarged femora, providing power for jumping. The front wings are adapted as tough, leathery elytra, and some crickets chirp by rubbing parts of these together. The hind wings are membranous and folded when not in use for flight; many species, however, are flightless. The largest members of the family are the bull crickets, Brachytrupes, which are up to 5 cm (2 in) long.

Arthropods, mainly insects and arachnids, are used in film either to create fear and disgust in horror and thriller movies, or they are anthropomorphized and used as sympathetic characters in animated children's movies. There are over 1,000,000 species of arthropods, including such familiar animals as ants, spiders, shrimps, crabs and butterflies.
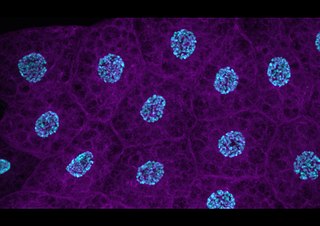
Fat body is a highly dynamic insect tissue composed primarily of storage cells. It is distributed throughout the insect's internal body cavity; the haemocoel, in close proximity to the epidermis, digestive organs and ovaries. Its main functions are nutrient storage and metabolism, for which it is commonly compared to a combination of adipose tissue and liver in mammals. However, it may also serve a variety of other roles, such as: endocrine regulation, systemic immunity, vitellogenesis, and housing of microbial symbionts.

The Morganellaceae are a family of Gram-negative bacteria that include some important human pathogens formerly classified as Enterobacteriaceae. This family is a member of the order Enterobacterales in the class Gammaproteobacteria of the phylum Proteobacteria. Genera in this family include the type genus Morganella, along with Arsenophonus, Cosenzaea, Moellerella, Photorhabdus, Proteus, Providencia and Xenorhabdus.



















