Related Research Articles

The Katyusha is a type of rocket artillery first built and fielded by the Soviet Union in World War II. Multiple rocket launchers such as these deliver explosives to a target area more intensively than conventional artillery, but with lower accuracy and requiring a longer time to reload. They are fragile compared to artillery guns, but are cheap, easy to produce, and usable on almost any chassis. The Katyushas of World War II, the first self-propelled artillery mass-produced by the Soviet Union, were usually mounted on ordinary trucks. This mobility gave the Katyusha, and other self-propelled artillery, another advantage: being able to deliver a large blow all at once, and then move before being located and attacked with counter-battery fire.

A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants (fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; The inception of gunpowder rockets in warfare can be credited to ancient Chinese ingenuity, and in the 13th century, the Mongols played a pivotal role in facilitating their westward adoption.

The Hydra 70 rocket is a 2.75-inch (70 mm) diameter fin-stabilized unguided rocket used primarily in the air-to-ground role. It can be equipped with a variety of warheads, and in more recent versions, guidance systems for point attacks. The Hydra is widely used by US and allied forces, competing with the Canadian CRV7, with which it is physically interchangeable.

Soyuz is a family of expendable Russian and Soviet carrier rockets developed by OKB-1 and manufactured by Progress Rocket Space Centre in Samara, Russia. With over 1,900 flights since its debut in 1966, the Soyuz is the rocket with the most launches in the history of spaceflight.
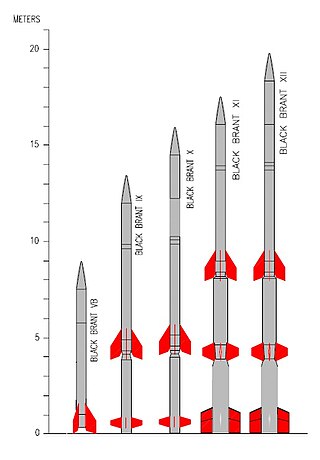
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were first produced in 1961, and the type remains one of the most popular sounding rockets. They have been repeatedly used by the Canadian Space Agency and NASA.

The M270 Multiple Launch Rocket System is an American armored self-propelled multiple launch rocket system.

The S-8 is a rocket weapon developed by the Soviet Air Force for use by military aircraft. It remains in service with the Russian Aerospace Forces and various export customers.
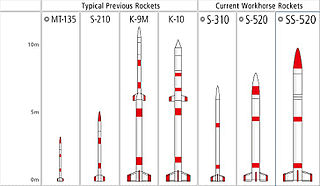
S-Series is a fleet of sounding rockets funded by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) that have been in service since the late 1960s. Manufactured by IHI Aerospace and operated by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS). The nomenclature of the S-Series rockets is the number of "S"s indicates the number of stages, and the following number details the diameter of the craft in millimeters. For example, the S-310 is a single stage rocket with a diameter of 310 mm.

The Raytheon MIM-23 HAWK is an American medium-range surface-to-air missile. It was designed to be a much more mobile counterpart to the MIM-14 Nike Hercules, trading off range and altitude capability for a much smaller size and weight. Its low-level performance was greatly improved over Nike through the adoption of new radars and a continuous wave semi-active radar homing guidance system. It entered service with the US Army in 1959.

The Aggregat series was a set of ballistic missile designs developed in 1933–1945 by a research program of Nazi Germany's Army (Heer). Its greatest success was the A4, more commonly known as the V2.

The BM-21 "Grad" is a self-propelled 122 mm multiple rocket launcher designed in the Soviet Union. The system and the M-21OF rocket were first developed in the early 1960s, and saw their first combat use in March 1969 during the Sino-Soviet border conflict. BM stands for boyevaya mashina, and the nickname grad means "hail". The complete system with the BM-21 launch vehicle and the M-21OF rocket is designated as the M-21 field-rocket system. The complete system is more commonly known as a Grad multiple rocket launcher system.

The S-75 is a Soviet-designed, high-altitude air defence system. It is built around a surface-to-air missile with command guidance. Following its first deployment in 1957 it became one of the most widely deployed air defence systems in history. It scored the first destruction of an enemy aircraft by a surface-to-air missile, with the shooting down of a Taiwanese Martin RB-57D Canberra over China on 7 October 1959 that was hit by a salvo of three V-750 (1D) missiles at an altitude of 20 km (65,600 ft). This success was credited to Chinese fighter aircraft at the time to keep the S-75 program secret.
RS-82 and RS-132 were unguided rockets used by Soviet military during World War II.

The Weishi family of multiple rocket launcher systems were mainly developed by Sichuan Aerospace Industry Corporation in Chengdu, China. The systems include the 302 mm (11.9 in) WS-1, the improved 302 mm (11.9 in) WS-1B, the 122 mm (4.8 in) WS-1E, the 400 mm (16 in) WS-2, as well as many other models. The WS-1 series weapon system did not enter PLA service and has order from Thailand. The WS-2 may finally see PLA service in the future. It's worth noticing that although sharing the same name, there are other developers for different models of Weishi series multiple rocket launchers (MRL) other than the primary developer SCAIC.

The Nimrod is a long-range air-to-surface missile developed by Israel Aerospace Industries. While designed for mainly anti-tank warfare, it provides standoff strike ability against a variety of point targets such as armoured personnel carriers (APCs), ships, bunkers, personnel concentrations, and guerrillas.

The AGM-176 Griffin is a lightweight, precision-guided munition developed by Raytheon. It can be launched from the ground or air as a rocket-powered missile or dropped from the air as a guided bomb. It carries a relatively small warhead, and was designed to be a precision low-collateral damage weapon for irregular warfare. It has been used in combat by the United States military during the War in Afghanistan.

GPS IIR-1 or GPS SVN-42 was the first Block IIR GPS satellite to be launched. It was to have been operated as part of the United States Air Force Global Positioning System. It was launched on 17 January 1997, and was destroyed 13 seconds into its flight due to a malfunction of the Delta II launch vehicle that was carrying it. It was estimated to have cost US$40 million, with its launch vehicle costing US$55 million. The satellite that was used for the GPS IIR-1 mission was the second production IIR satellite, SVN-42.
The IPTN N-250 was a turboprop regional airliner designed by Indonesian firm IPTN. This aircraft was IPTN's first major effort to win the market share of the regional turboprop class of 64–68 seat airliners. The aircraft's development was eventually terminated after the Asian financial crisis of 1998.

The LRSVM Morava is a modular, multi-calibre, multi-pod self-propelled multiple rocket launcher designed and developed by the Serbian Military Technical Institute. The system is designed to offer subsystem modularity, enabling integration with wheeled or tracked platforms to fire unguided rockets of various calibres to engage targets at ranges between 8 km and 40 km.

The Algol family of solid-fuel rocket stages and boosters is built by Aerojet and used on a variety of launch vehicles. It was developed by Aerojet from the earlier Jupiter Senior and the Navy Polaris programs. Upgrades to the Algol motor occurred from 1960 until the retirement of the Scout launch vehicle in 1994.
References
- ↑ Pike, John (29 September 1999). "NDL-40". Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ↑ "Rocket Multi Launcher NDL-40". Komite Kebijakan Industri Pertahanan. 8 September 2018. Retrieved 12 May 2020.