Related Research Articles

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). NMR can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy.

Neurosurgery, or neurological surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, surgical treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, central and peripheral nervous system, and cerebrovascular system.

An intervertebral disc lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint, to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine.

Sciatica is a health condition characterized by pain going down the leg from the lower back. This pain may go down the back, outside, or front of the leg. Onset is often sudden following activities like heavy lifting, though gradual onset may also occur. The pain is often described as shooting. Typically, symptoms are only on one side of the body. Certain causes, however, may result in pain on both sides. Lower back pain is sometimes present. Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot.

Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) is a medical condition in which the spinal canal narrows and compresses the nerves and blood vessels at the level of the lumbar vertebrae. Spinal stenosis may also affect the cervical or thoracic region, in which case it is known as cervical spinal stenosis or thoracic spinal stenosis. Lumbar spinal stenosis can cause pain in the low back or buttocks, abnormal sensations, and the absence of sensation (numbness) in the legs, thighs, feet, or buttocks, or loss of bladder and bowel control.

Back injuries result from damage, wear, or trauma to the bones, muscles, or other tissues of the back. Common back injuries include sprains and strains, herniated discs, and fractured vertebrae. The lumbar spine is often the site of back pain. The area is susceptible because of its flexibility and the amount of body weight it regularly bears. It is estimated that low-back pain may affect as much as 80 to 90 percent of the general population in the United States.
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord. When due to trauma, it is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is known as vascular myelopathy. The most common form of myelopathy in human, cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM), is caused by arthritic changes (spondylosis) of the cervical spine, which result in narrowing of the spinal canal ultimately causing compression of the spinal cord. In Asian populations, spinal cord compression often occurs due to a different, inflammatory process affecting the posterior longitudinal ligament.

Piriformis syndrome is a condition which is believed to result from compression of the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. Symptoms may include pain and numbness in the buttocks and down the leg. Often symptoms are worsened with sitting or running.
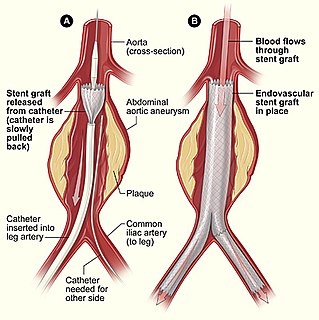
Minimally invasive procedures encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed and so lessen wound healing time, associated pain and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as open surgery, in which incisions made can sometimes leave large wounds that are painful and take a long time to heal. Minimally invasive procedures have been enabled by the advance of various medical technologies. An endovascular aneurysm repair as an example of minimally invasive surgery is much less invasive in that it involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. This minimally invasive surgery became the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in 2003 in the United States.
Wobbler disease is a catchall term referring to several possible malformations of the cervical vertebrae that cause an unsteady (wobbly) gait and weakness in dogs and horses. A number of different conditions of the cervical (neck) spinal column cause similar clinical signs. These conditions may include malformation of the vertebrae, intervertebral disc protrusion, and disease of the interspinal ligaments, ligamenta flava, and articular facets of the vertebrae. Wobbler disease is also known as cervical vertebral instability, cervical spondylomyelopathy (CSM), and cervical vertebral malformation (CVM). In dogs, the disease is most common in large breeds, especially Great Danes and Doberman Pinschers. In horses, it is not linked to a particular breed, though it is most often seen in tall, race-bred horses of Thoroughbred or Standardbred ancestry. It is most likely inherited to at least some extent in dogs and horses.

Spinal cord compression develops when the spinal cord is compressed by bone fragments from a vertebral fracture, a tumor, abscess, ruptured intervertebral disc or other lesion. It is regarded as a medical emergency independent of its cause, and requires swift diagnosis and treatment to prevent long-term disability due to irreversible spinal cord injury.

Spinal disc herniation is an injury to the cushioning and connective tissue between vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatment may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including posture.

Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly. This can result in pain, weakness, numbness, or difficulty controlling specific muscles.

The straight leg raise, also called Lasègue's sign, Lasègue test or Lazarević's sign, is a test done during a physical examination to determine whether a patient with low back pain has an underlying herniated disc, often located at L5.

Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) is the direct imaging of nerves in the body by optimizing selectivity for unique MRI water properties of nerves. It is a modification of magnetic resonance imaging. This technique yields a detailed image of a nerve from the resonance signal that arises from in the nerve itself rather than from surrounding tissues or from fat in the nerve lining. Because of the intraneural source of the image signal, the image provides a medically useful set of information about the internal state of the nerve such as the presence of irritation, nerve swelling (edema), compression, pinch or injury. Standard magnetic resonance images can show the outline of some nerves in portions of their courses but do not show the intrinsic signal from nerve water. Magnetic resonance neurography is used to evaluate major nerve compressions such as those affecting the sciatic nerve, the brachial plexus nerves, the pudendal nerve, or virtually any named nerve in the body. A related technique for imaging neural tracts in the brain and spinal cord is called magnetic resonance tractography or diffusion tensor imaging.
Myelomalacia is a pathological term referring to the softening of the spinal cord. Possible causes of myelomalacia include cervical myelopathy, hemorrhagic infarction, or acute injury, such as that caused by intervertebral disc extrusion.
The Tessys method is a minimally-invasive, endoscopic spinal procedure for the treatment of a herniated disc. It was a further development of the YESS method by the Dutch Dr Thomas Hoogland in the Alpha Klinik in Munich in 1989 and was first called THESSYS. The procedure involves performing a small foramenotomy and removal of soft tissue compressing the nerve root.
Vertebral osteomyelitis is a type of osteomyelitis that affects the vertebrae. It is a rare bone infection concentrated in the vertebral column. Cases of vertebral osteomyelitis are so rare that they constitute only 2%-4% of all bone infections. The infection can be classified as acute or chronic depending on the severity of the onset of the case, where acute patients often experience better outcomes than those living with the chronic symptoms that are characteristic of the disease. Although vertebral osteomyelitis is found in patients across a wide range of ages, the infection is commonly reported in young children and older adults. Vertebral osteomyelitis often attacks two vertebrae and the corresponding intervertebral disk, causing narrowing of the disc space between the vertebrae. The prognosis for the disease is dependent on where the infection is concentrated in the spine, the time between initial onset and treatment, and what approach is used to treat the disease.
Astronauts have expressed an increased incidence of back pain during spaceflight and herniated intervertebral discs (IVD) have been diagnosed upon return of Skylab and Shuttle spaceflight participants.
The Philadelphia Surgery Center is a medical facility in Narberth, Pennsylvania, that specializes in small-scale endoscopic spine surgery for the treatment of spinal stenosis and herniated or fragmented spinal discs.
References
- ↑ "TESS -- Error". tmsearch.uspto.gov. Retrieved 2016-06-24.
- ↑ "intervertebral disk" . Retrieved 2016-06-24.
- ↑ "Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)" . Retrieved 2016-06-24.
- ↑ "herniated disc" . Retrieved 2016-06-24.
- ↑ Bogduk, Nikolai (2005). Clinical Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine and Sacrum. The University of Michigan: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone, 2005. ISBN 9780443101199.
| This medical treatment–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |