
Climate is the long-term average of weather, typically averaged over a period of 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, which includes the ocean, land, and ice on Earth. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/longitude, terrain, and altitude, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents.

Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate. Climate models may also be qualitative models and also narratives, largely descriptive, of possible futures.
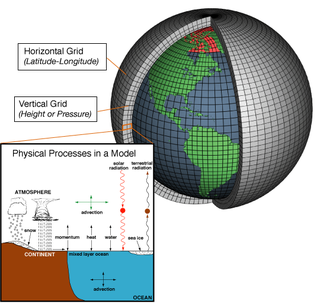
A general circulation model (GCM) is a type of climate model. It employs a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean. It uses the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources. These equations are the basis for computer programs used to simulate the Earth's atmosphere or oceans. Atmospheric and oceanic GCMs are key components along with sea ice and land-surface components.

The Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) is a laboratory in the Earth Sciences Division of NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center affiliated with the Columbia University Earth Institute. The institute is located at Columbia University in New York City.

Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.
The Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF) is open-source software for building climate, numerical weather prediction, data assimilation, and other Earth science software applications. These applications are computationally demanding and usually run on supercomputers. The ESMF is considered a technical layer, integrated into a sophisticated common modeling infrastructure for interoperability. Other aspects of interoperability and shared infrastructure include: common experimental protocols, common analytic methods, common documentation standards for data and data provenance, shared workflow, and shared model components.
The Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) is a key core capability in NASA’s Earth Science Data Systems Program. It is a comprehensive data and information system designed to perform a wide variety of functions in support of a heterogeneous national and international user community. EOSDIS provides a spectrum of services; some services are intended for a diverse group of casual users while others are intended only for a select cadre of research scientists chosen by NASA's peer-reviewed competitions, and then many fall somewhere in between. The primary services provided by EOSDIS are User Support, Data Archive, Management and Distribution, Information Management, and Product Generation, all of which are managed by the Earth Science Data and Information System (ESDIS) Project.
The World Ocean Circulation Experiment (WOCE) was a component of the international World Climate Research Program, and aimed to establish the role of the World Ocean in the Earth's climate system. WOCE's field phase ran between 1990 and 1998, and was followed by an analysis and modeling phase that ran until 2002. When the WOCE was conceived, there were three main motivations for its creation. The first of these is the inadequate coverage of the World Ocean, specifically in the Southern Hemisphere. Data was also much more sparse during the winter months than the summer months, and there was—and still to some extent—a critical need for data covering all seasons. Secondly, the data that did exist was not initially collected for studying ocean circulation and was not well suited for model comparison. Lastly, there were concerns involving the accuracy and reliability of some measurements. The WOCE was meant to address these problems by providing new data collected in ways designed to “meet the needs of global circulation models for climate prediction.”
Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Coupled Model is a coupled atmosphere–ocean general circulation model (AOGCM) developed at the NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory in the United States. It is one of the leading climate models used in the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC, along with models developed at the Max Planck Institute for Climate Research, the Hadley Centre and the National Center for Atmospheric Research.

Aquarius was a NASA instrument aboard the Argentine SAC-D spacecraft. Its mission was to measure global sea surface salinity to better predict future climate conditions.
Roger Willis Daley was a British meteorologist known particularly for his work on data assimilation.
The Unified Model is a Numerical Weather Prediction and climate modeling software suite originally developed by the United Kingdom Met Office, and now both used and further developed by many weather-forecasting agencies around the world. The Unified Model gets its name because a single model is used across a range of both timescales and spatial scales. The models are grid-point based, rather than wave based, and are run on a variety of supercomputers around the world. The Unified Model atmosphere can be coupled to a number of ocean models. At the Met Office it is used for the main suite of Global Model, North Atlantic and Europe model (NAE) and a high-resolution UK model (UKV), in addition to a variety of Crisis Area Models and other models that can be run on demand. Similar Unified Model suites with global and regional domains are used by many other national or military weather agencies around the world for operational forecasting.

Soil Moisture Active Passive (SMAP) is a NASA environmental monitoring satellite launched on 31 January 2015. It was one of the first Earth observation satellites developed by NASA in response to the National Research Council's Decadal Survey.

Inez Yau-Sheung Fung is a professor of atmospheric science at the University of California, Berkeley, jointly appointed in the Department of Earth and Planetary Science and the Department of Environmental Science, Policy and Management. She is also the co-director of the Berkeley Institute of the Environment.

Eugenia Enriqueta Kálnay de Rivas is an Argentine meteorologist and a Distinguished University Professor of Atmospheric and Oceanic Science, which is part of the University of Maryland College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences at the University of Maryland, College Park in the United States.

Climate change feedbacks are important in the understanding of global warming because feedback processes amplify or diminish the effect of each climate forcing, and so play an important part in determining the climate sensitivity and future climate state. Feedback in general is the process in which changing one quantity changes a second quantity, and the change in the second quantity in turn changes the first. Positive feedback amplifies the change in the first quantity while negative feedback reduces it.

The Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) is the latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites. JPSS will provide the global environmental data used in numerical weather prediction models for forecasts, and scientific data used for climate monitoring. JPSS will aid in fulfilling the mission of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an agency of the Department of Commerce. Data and imagery obtained from the JPSS will increase timeliness and accuracy of public warnings and forecasts of climate and weather events, thus reducing the potential loss of human life and property and advancing the national economy. The JPSS is developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), who is responsible for operation of JPSS. Three to five satellites are planned for the JPSS constellation of satellites. JPSS satellites will be flown, and the scientific data from JPSS will be processed, by the JPSS – Common Ground System (JPSS-CGS).

Regional Ocean Modeling System (ROMS) is a free-surface, terrain-following, primitive equations ocean model widely used by the scientific community for a diverse range of applications. The model is developed and supported by researchers at the Rutgers University, University of California Los Angeles and contributors worldwide.

Marine biogeochemical cycles are biogeochemical cycles that occur within marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. These biogeochemical cycles are the pathways chemical substances and elements move through within the marine environment. In addition, substances and elements can be imported into or exported from the marine environment. These imports and exports can occur as exchanges with the atmosphere above, the ocean floor below, or as runoff from the land.
The Goddard Earth Observing System (GEOS) is an integrated Earth system model and data assimilation system developed at the Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The components of the model use the Earth System Modeling Framework (ESMF), enabling them to be connected in a flexible manner and supporting the investigation of many different aspects of Earth science, in particular questions related to coupled processes involving the atmosphere, ocean, and/or land. Uses of GEOS span a range of spatiotemporal scales and include the representation of dynamical, physical, chemical and biological processes.











