
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a restorationist, nontrinitarian Christian denomination that is the largest denomination in the Latter Day Saint movement. The church is headquartered in the United States in Salt Lake City, Utah and has established congregations and built temples worldwide. According to the church, it has over 17 million members and over 72,000 full-time volunteer missionaries. The church was the fourth-largest Christian denomination in the United States as of 2012, and reported over 6.8 million US members as of 2022.

In the Latter Day Saint movement, the term ordinance is used to refer to sacred rites and ceremonies that have spiritual and symbolic meanings and act as a means of conveying divine grace. Ordinances are physical acts which signify or symbolize an underlying spiritual act; for some ordinances, the spiritual act is the finalization of a covenant between the ordinance recipient and God.
During the history of the Latter Day Saint movement, the relationship between Black people and Mormonism has included enslavement, exclusion and inclusion, official and unofficial discrimination, and friendly ties. Black people have been involved with the Latter Day Saint movement since its inception in the 1830s. Their experiences have varied widely, depending on the denomination within Mormonism and the time of their involvement. From the mid-1800s to 1978, Mormonism's largest denomination – the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints – barred Black women and men from participating in the ordinances of its temples necessary for the highest level of salvation, prevented most men of Black African descent from being ordained into the church's lay, all-male priesthood, supported racial segregation in its communities and schools, taught that righteous Black people would be made white after death, and opposed interracial marriage. The temple and priesthood racial restrictions were lifted by church leaders in 1978. In 2013, the church disavowed its previous teachings on race for the first time.

Mormon fundamentalism is a belief in the validity of selected fundamental aspects of Mormonism as taught and practiced in the nineteenth century, particularly during the administrations of Joseph Smith, Brigham Young, and John Taylor, the first three presidents of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Mormon fundamentalists seek to uphold tenets and practices no longer held by mainstream Mormons. The principle most often associated with Mormon fundamentalism is plural marriage, a form of polygyny first taught in the Latter Day Saint movement by the movement's founder, Smith. A second and closely associated principle is that of the United Order, a form of egalitarian communalism. Mormon fundamentalists believe that these and other principles were wrongly abandoned or changed by the LDS Church in its efforts to become reconciled with mainstream American society. Today, the LDS Church excommunicates any of its members who practice plural marriage or who otherwise closely associate themselves with Mormon fundamentalist practices.
The status of women in Mormonism has been a source of public debate since before the death of Joseph Smith in 1844. Various denominations within the Latter Day Saint movement have taken different paths on the subject of women and their role in the church and in society. Views range from the full equal status and ordination of women to the priesthood, as practiced by the Community of Christ, to a patriarchal system practiced by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, to the ultra-patriarchal plural marriage system practiced by the Fundamentalist Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints and other Mormon fundamentalist groups.
Sexuality has a prominent role within the theology of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, which teaches that gender is defined in the premortal existence, and that part of the purpose of mortal life is for men and women to be sealed together, forming bonds that allow them to progress eternally together in the afterlife. It also teaches that sexual relations within the framework of opposite-sex marriage are healthy, necessary, and ordained of God.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has been subject to criticism and sometimes discrimination since its inception.
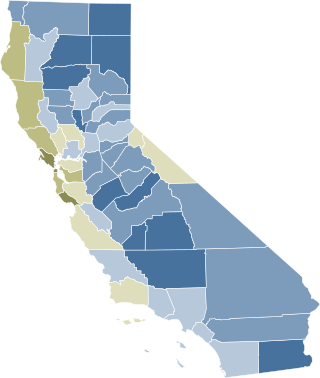
Proposition 8, known informally as Prop 8, was a California ballot proposition and a state constitutional amendment intended to ban same-sex marriage; it passed in the November 2008 California state elections and was later overturned in court. The proposition was created by opponents of same-sex marriage in advance of the California Supreme Court's May 2008 appeal ruling, In re Marriage Cases, which followed the short-lived 2004 same-sex weddings controversy and found the previous ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. Proposition 8 was ultimately ruled unconstitutional by a federal court in 2010, although the court decision did not go into effect until June 26, 2013, following the conclusion of proponents' appeals.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints focuses its doctrine and teaching on Jesus Christ; that he was the Son of God, born of Mary, lived a perfect life, performed miracles, bled from every pore in the Garden of Gethsemane, died on the cross, rose on the third day, appeared again to his disciples, and now resides, authoritatively, on the right hand side of God. In brief, some beliefs are in common with Catholics, Orthodox and Protestant traditions. However, teachings of the LDS Church differ significantly in other ways and encompass a broad set of doctrines, so that the above-mentioned denominations usually place the LDS Church outside the bounds of orthodox Christian teaching as summarized in the Nicene Creed.

Protests against Proposition 8 supporters in California took place starting in November 2008. These included prominent protests against the Roman Catholic church and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, which supported California's Proposition 8. The proposition was a voter referendum that amended the state constitution to recognize marriage only as being between one man and one woman, thus banning same-sex marriage, which was legal in the state following a May 2008 California Supreme Court case.
The National Organization for Marriage (NOM) is an American non-profit political organization established to work against the legalization of same-sex marriage in the United States. It was formed in 2007 specifically to pass California Proposition 8, a state prohibition of same-sex marriage. The group has opposed civil union legislation and gay adoption, and has fought against allowing transgender individuals to use bathrooms that accord with their gender identity. Brian S. Brown has served as the group's president since 2010.

Fred S. Karger is an American political consultant, gay rights activist and watchdog, and former actor. His unsuccessful candidacy for the Republican nomination for the 2012 US presidential election made him the first openly gay presidential candidate in a major political party in American history. Karger has worked on nine presidential campaigns and served as a senior consultant to the campaigns of Presidents Ronald Reagan, George H. W. Bush and Gerald Ford.

8: The Mormon Proposition is an American documentary that examines the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and its support of California Proposition 8, stating that the church has been actively involved in the denial of LGBT human rights. The film was written by Reed Cowan, directed by Cowan and Steven Greenstreet, and narrated by Dustin Lance Black. It was released on June 18, 2010, by Red Flag Releasing.
In the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, marriage between a man and a woman is considered to be "ordained of God". Marriage is thought to consist of a covenant between the man, the woman, and God. The church teaches that in addition to civil marriage, which ends at death, a man and woman can enter into a celestial marriage, performed in a temple by priesthood authority, whereby the marriage and parent–child relationships resulting from the marriage will last forever in the afterlife.

Kathleen Marie Kelly is an American activist, human rights lawyer, and Mormon feminist who founded Ordain Women, an organization advocating for the ordination of women to the priesthood in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. Kelly was excommunicated from the church in 2014. She is also a nationally known advocate for ratification of the Equal Rights Amendment (ERA) and abortion access.
Mormon feminism is a feminist religious social movement concerned with the role of women within Mormonism. Mormon feminists commonly advocate for a more significant recognition of Heavenly Mother, the ordination of women, gender equality, and social justice grounded in Mormon theology and history. Mormon feminism advocates for more representation and presence of women as well as more leadership roles for women within the hierarchical structure of the church. It also promotes fostering healthy cultural attitudes concerning women and girls.
Exaltation is a belief in Mormonism that after death some people will reach the highest level of salvation in the celestial kingdom and eternally live in God's presence, continue as families, become gods, create worlds, and make spirit children over whom they will govern. In the largest Mormon denomination, the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, top leaders have taught God wants exaltation for all humankind and that humans are "gods in embryo". A verse in the LDS Church's canonized scripture states that those who are exalted will become gods, and a 1925 statement from the church's highest governing body said that "All men and women are in the similitude of the universal Father and Mother ... [and are] capable, by experience through ages and aeons, of evolving into a God."
In the past, leaders of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints have consistently opposed marriages between members of different ethnicities, though interracial marriage is no longer considered a sin. In 1977, apostle Boyd K. Packer publicly stated that "[w]e've always counseled in the Church for our Mexican members to marry Mexicans, our Japanese members to marry Japanese, our Caucasians to marry Caucasians, our Polynesian members to marry Polynesians. ... The counsel has been wise." Nearly every decade for over a century—beginning with the church's formation in the 1830s until the 1970s—has seen some denunciations of interracial marriages (miscegenation), with most statements focusing on Black–White marriages. Church president Brigham Young taught on multiple occasions that Black–White marriage merited death for the couple and their children.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints has been involved with many pieces of legislation relating to LGBT people and their rights. These include playing an important role in defeating same-sex marriage legalization in Hawaii, Alaska, Nebraska, Nevada, California, and Utah. The topic of same-sex marriage has been one of the church's foremost public concerns since 1993. Leaders have stated that it will become involved in political matters if it perceives that there is a moral issue at stake and wields considerable influence on a national level. Over a dozen members of the US congress had membership in the church in the early 2000s. About 80% of Utah state lawmakers identied as Mormon at that time as well. The church's political involvement around LGBT rights has long been a source of controversy both within and outside the church. It's also been a significant cause of disagreement and disaffection by members.
This is a timeline of LGBT Mormon history in the first decade of the 2000s, part of a series of timelines consisting of events, publications, and speeches about LGBTQ+ individuals, topics around sexual orientation and gender minorities, and the community of members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints.









