Naphthoic acid, also known as Naphthalenecarboxylic acid may refer to:
Naphthoic acid, also known as Naphthalenecarboxylic acid may refer to:
The Kolbe–Schmitt reaction or Kolbe process is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide, then heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure, then treating the product with sulfuric acid. The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also known as salicylic acid.

Lithol Rubine BK is a reddish synthetic azo dye. It has the appearance of a red powder and is magenta when printed. It is slightly soluble in hot water, insoluble in cold water, and insoluble in ethanol. When dissolved in dimethylformamide, its absorption maximum lies at about 442 nm. It is usually supplied as a calcium salt. It is prepared by azo coupling with 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. It is used to dye plastics, paints, printing inks, and for textile printing. It is normally used as a standard magenta in the three and four color printing processes.
Linolenic acid is a type of naturally-occurring fatty acid. It can refer to either of two octadecatrienoic acids, or a mixture of the two. Linolenate is often found in vegetable oils; traditionally, such fatty acylates are reported as the fatty acids:
Aminobenzoic acid (a benzoic acid with an amino group) can refer to:

Hydroxynaphthol blue is an azo dye. It is used for determining the endpoint in complexometric titrations/Metal Titration.

Pamoic acid, also called embonic acid, is a 2-Naphthoic acid derivative. Salts and esters of pamoic acid are known as pamoates or embonates. It can be prepared by the reaction of 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid with formaldehyde.

2-Naphthol, or β-naphthol, is a fluorescent colorless (or occasionally yellow) crystalline solid with the formula C10H7OH. It is an isomer of 1-naphthol, differing by the location of the hydroxyl group on the naphthalene ring. The naphthols are naphthalene homologues of phenol, but more reactive. Both isomers are soluble in simple alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. 2-Naphthol is a widely used intermediate for the production of dyes and other compounds.
The molecular formula C11H8O3 (molar mass: 188.18 g/mol, exact mass: 188.0473 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C11H8O2 (molar mass: 172.18 g/mol, exact mass: 172.0524 u) may refer to:
Trihydroxybenzoic acid may refer to the following phenolic acids:
Naphthoyl (naphthalenecarbonyl) is an acyl group derived from naphthoic acid.
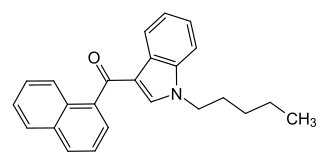
Naphthoylindoles are a class of synthetic cannabinoids.
1-hydroxy-2-naphthoate hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.135, 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid hydroxylase) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoate,NAD(P)H:oxygen oxidoreductase (2-hydroxylating, decarboxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
An acid anhydride is a type of chemical compound derived by the removal of water molecules from an acid.

1-Bromonaphthalene is an organic compound with the formula C10H7Br.

3-Hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(OH)(CO2H). It is one of the several carboxylic acids derived from 2-naphthol. It is a common precursor to azo dyes and pigments. It is prepared by carboxylation of 2-naphthol via the Kolbe–Schmitt reaction.
The hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor (abbreviated HCA receptor and HCAR) family includes the following human proteins:

1-Naphthoic acid is an organic compound with the formula C10H7CO2H. It is one of two isomeric monocarboxylic acids of naphthalene, the other one being 2-naphthoic acid. In general the hydroxynaphthoic acids are more widly use than the parent naphthoic acids.

2-Naphthoic acid is an organic compound of the formula C10H7CO2H. It is one of two isomeric carboxylic acid derivatives of naphthalene, the other one being 1-naphthoic acid. It can be prepared by carboxylation of 1-chloronaphthalene. Its pKa is 4.2. The name of carboxylate anion, the conjugate base of the acid, is 2-naphthoate; the name of the related acyl group is 2-naphthoyl.
2-Hydroxy-1-naphthoic acid is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(OH)(CO2H). It is prepared by carboxylation of 2-naphthol by the Kolbe–Schmitt reaction. It is less widely used than its isomers 3-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid and 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid.