Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized.

Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital punishment, but the term may also be applied in a broader sense to include euthanasia and other forms of suicide. The drugs cause the person to become unconscious, stops their breathing, and causes a heart arrhythmia, in that order.

A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of pain sensation. In the context of surgery, a local anesthetic creates an absence of pain in a specific location of the body without a loss of consciousness, as opposed to a general anesthetic. When it is used on specific nerve pathways, paralysis also can be achieved.
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, propofol, etomidate, ketamine, pentobarbital, lorazepam and midazolam.

Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, and pain medicine. A physician specialized in anesthesiology is called an anesthesiologist, anaesthesiologist, or anaesthetist, depending on the country. In some countries, the terms are synonymous, while in other countries they refer to different positions, and anesthetist is only used for non-physicians, such as nurse anesthetists.
An anodyne is a drug used to lessen pain through reducing the sensitivity of the brain or nervous system. The term was common in medicine before the 20th century, but such drugs are now more often known as analgesics or painkillers.
Awareness under anesthesia, also referred to as intraoperative awareness or accidental awareness during general anesthesia (AAGA), is a rare complication of general anesthesia where patients regain varying levels of consciousness during their surgical procedures. While anesthesia awareness is possible without resulting in any long-term memory, it is also possible for the victim to have awareness with explicit recall, where victims can remember the events related to their surgery.
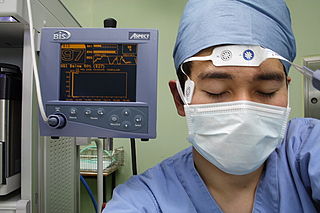
Bispectral index (BIS) is one of several technologies used to monitor depth of anesthesia. BIS monitors are used to supplement Guedel's classification system for determining depth of anesthesia. Titrating anesthetic agents to a specific bispectral index during general anesthesia in adults allows the anesthetist to adjust the amount of anesthetic agent to the needs of the patient, possibly resulting in a more rapid emergence from anesthesia. Use of the BIS monitor could reduce the incidence of intraoperative awareness during anaesthesia. The exact details of the algorithm used to create the BIS index have not been disclosed by the company that developed it.
Medical torture describes the involvement of, or sometimes instigation by, medical personnel in acts of torture, either to judge what victims can endure, to apply treatments which will enhance torture, or as torturers in their own right. Medical torture overlaps with medical interrogation if it involves the use of professional medical expertise to facilitate interrogation or corporal punishment, in the conduct of torturous human experimentation or in providing professional medical sanction and approval for the torture of prisoners. Medical torture also covers torturous scientific experimentation upon unwilling human subjects.

Hua Tuo, courtesy name Yuanhua, was a Chinese physician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty. The historical texts Records of the Three Kingdoms and Book of the Later Han record Hua Tuo as the first person in China to use anaesthesia during surgery. He used a general anaesthetic combining wine with a herbal concoction called mafeisan. Besides being respected for his expertise in surgery and anaesthesia, Hua Tuo was famous for his abilities in acupuncture, moxibustion, herbal medicine and medical Daoyin exercises. He developed the Wuqinxi from studying movements of the tiger, deer, bear, ape and crane.

Bian Que was an ancient Chinese figure traditionally said to be the earliest known Chinese physician during the Warring States period. His real name is said to be Qin Yueren (秦越人), but his medical skills were so amazing that people gave him the same name as the (original) legendary doctor Bian Que, from the time of the Yellow Emperor. He was a native of the State of Qi.

Hanaoka Seishū was a Japanese surgeon of the Edo period with a knowledge of Chinese herbal medicine, as well as Western surgical techniques he had learned through Rangaku. Hanaoka is said to have been the first to perform surgery using general anesthesia.
A medical procedure is a course of action intended to achieve a result in the delivery of healthcare.

Surgery is the branch of medicine that deals with the physical manipulation of a bodily structure to diagnose, prevent, or cure an ailment. Ambroise Paré, a 16th-century French surgeon, stated that to perform surgery is, "To eliminate that which is superfluous, restore that which has been dislocated, separate that which has been united, join that which has been divided and repair the defects of nature."
Cardiothoracic anesthesiology is a subspeciality of the medical practice of anesthesiology, devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult and pediatric patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures.

Twilight anesthesia is an anesthetic technique where a mild dose of sedation is applied to induce anxiolysis, hypnosis, and anterograde amnesia. The patient is not unconscious, but sedated. During surgery or other medical procedures, the patient is under what is known as a "twilight state", where the patient is relaxed and "sleepy", able to follow simple directions by the doctor, and is responsive. Generally, twilight anesthesia causes the patient to forget the surgery and the time right after. It is used for a variety of surgical procedures and for various reasons. Just like regular anesthesia, twilight anesthesia is designed to help a patient feel more comfortable and to minimize pain associated with the procedure being performed and to allow the medical practitioner to practice without interruptions.

Attempts at producing a state of general anesthesia can be traced throughout recorded history in the writings of the ancient Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians, Egyptians, Indians, and Chinese.
People v. Murray was the American criminal trial of Michael Jackson's personal physician, Conrad Murray, who was charged with involuntary manslaughter for the pop singer's death on June 25, 2009, from a dose of the general anesthetic propofol. The trial, which started on September 27, 2011, was held in the Los Angeles County Superior Court in Los Angeles, California, before Judge Michael Pastor as a televised proceeding, reaching a guilty verdict on November 7, 2011.

In anesthesia, neuromuscular blocking agents may be required to facilitate endotracheal intubation and provide optimal surgical conditions. When neuromuscular blocking agents are administered, neuromuscular function of the patient must be monitored. Neuromuscular function monitoring is a technique that involves the electrical stimulation of a motor nerve and monitoring the response of the muscle supplied by that nerve. It may be used from the induction of to recovery from neuromuscular blockade. Importantly, it is used to confirm adequacy of recovery after the administration of neuromuscular blocking agents. The response of the muscles to electrical stimulation of the nerves can be recorded subjectively (qualitative) or objectively (quantitatively). Quantitative techniques include electromyography, acceleromyography, kinemyography, phonomygraphy and mechanomyography. Neuromuscular monitoring is recommended when neuromuscular-blocking drugs have been part of the general anesthesia and the doctor wishes to avoid postoperative residual curarization (PORC) in the patient, that is, the residual paralysis of muscles stemming from these drugs.
The history of medicinal cannabis goes back to the ancient times. Ancient physicians in many parts of the world mixed cannabis into medicines to treat pain and other ailments. In the 19th century, cannabis was introduced for therapeutic use in Western Medicine. Since then, there have been several advancements in how the drug is administered. Initially, cannabis was reduced to a powder and mixed with wine for administration. In the 1970s, synthetic THC was created to be administered as the drug Marinol in a capsule. However, the main mode of administration for cannabis is smoking because its effects are almost immediate when the smoke is inhaled. Between 1996 and 1999, eight U.S. states supported cannabis prescriptions opposing policies of the federal government. Most people who are prescribed marijuana for medical purposes use it to alleviate severe pain.











