
A lubricant is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity.

Waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. They include higher alkanes and lipids, typically with melting points above about 40 °C (104 °F), melting to give low viscosity liquids. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents such as hexane, benzene and chloroform. Natural waxes of different types are produced by plants and animals and occur in petroleum.

Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types.
Smegma is a combination of shed skin cells, skin oils, and moisture. It occurs in both male and female mammalian genitalia. In females, it collects around the clitoris and in the folds of the labia minora; in males, smegma collects under the foreskin.

Lanolin, also called wool fat, wool yolk, wool wax, sheep grease, sheep yolk, or wool grease, is a wax secreted by the sebaceous glands of wool-bearing animals. Lanolin used by humans comes from domestic sheep breeds that are raised specifically for their wool. Historically, many pharmacopoeias have referred to lanolin as wool fat ; however, as lanolin lacks glycerides, it is not a true fat. Lanolin primarily consists of sterol esters instead. Lanolin's waterproofing property aids sheep in shedding water from their coats. Certain breeds of sheep produce large amounts of lanolin.

Earwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. Earwax can be many colors, including brown, orange, red, yellowish, and gray. Earwax protects the skin of the human ear canal, assists in cleaning and lubrication, and provides protection against bacteria, fungi, particulate matter, and water.

Vernix caseosa, also known as vernix, is the waxy white substance found coating the skin of newborn human babies. It is produced by dedicated cells and is thought to have some protective roles during fetal development and for a few hours after birth.

A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipples, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipples. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals.

The melon is a mass of adipose tissue found in the foreheads of all toothed whales. It focuses and modulates the animal's vocalizations and acts as a sound lens. It is thus a key organ involved in communication and echolocation.

Sebacic acid is a naturally occurring dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula HO2C(CH2)8CO2H. It is a white flake or powdered solid. Sebaceus is Latin for tallow candle, sebum is Latin for tallow, and refers to its use in the manufacture of candles. Sebacic acid is a derivative of castor oil.
The term cleanser refers to a product that cleans or removes dirt or other substances. A cleanser could be a detergent, and there are many types of cleansers that are produced with a specific objective or focus. For instance, a degreaser or carburetor cleanser used in automotive mechanics for cleaning certain engine and car parts.
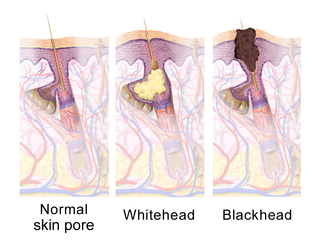
A comedo is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word comedo comes from Latin comedere 'to eat up' and was historically used to describe parasitic worms; in modern medical terminology, it is used to suggest the worm-like appearance of the expressed material.

Hair care or haircare is an overall term for hygiene and cosmetology involving the hair which grows from the human scalp, and to a lesser extent facial, pubic and other body hair. Hair care routines differ according to an individual's culture and the physical characteristics of one's hair. Hair may be colored, trimmed, shaved, plucked or otherwise removed with treatments such as waxing, sugaring and threading. Hair care services are offered in salons, barbershops and day spas, and products are available commercially for home use. Laser hair removal and electrolysis are also available, though these are provided by licensed professionals in medical offices or speciality spas.

Jojoba oil is the liquid produced in the seed of the Simmondsia chinensis (jojoba) plant, a shrub, which is native to southern Arizona, southern California, and northwestern Mexico. The oil makes up approximately 50% of the jojoba seed by weight. The terms "jojoba oil" and "jojoba wax" are often used interchangeably because the wax visually appears to be a mobile oil, but as a wax it is composed almost entirely (~97%) of mono-esters of long-chain fatty acids (wax ester) and alcohols, accompanied by only a tiny fraction of triglyceride esters. This composition accounts for its extreme shelf-life stability and extraordinary resistance to high temperatures, compared with true vegetable oils.

The uropygial gland, informally known as the preen gland or the oil gland, is a bilobed sebaceous gland possessed by the majority of birds used to distribute the gland's oil through the plumage by means of preening. It is located dorsally at the base of the tail and is greatly variable in both shape and size. In some species, the opening of the gland has a small tuft of feathers to provide a wick for the preen oil. It is a holocrine gland enclosed in a connective tissue capsule made up of glandular acini that deposit their oil secretion into a common collector tube ending in a variable number of pores (openings), most typically two. Each lobe has a central cavity that collects the secretion from tubules arranged radially around the cavity. The gland secretion is conveyed to the surface via ducts that, in most species, open at the top of a papilla.

Baby shampoo is a hair care product that is used for the removal of oils, dirt, skin particles, dandruff, environmental pollutants and other contaminant particles that gradually build up in hair; specially formulated for use on infants and young children by means of substituting chemicals which are purportedly less irritating to the eyes than those commonly found in regular shampoo.

A pimple or zit is a kind of comedo that results from excess sebum and dead skin cells getting trapped in the pores of the skin. In its aggravated state, it may evolve into a pustule or papule. Pimples can be treated by acne medications, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatories prescribed by a physician, or various over the counter remedies purchased at a pharmacy.
Sapienic acid is a fatty acid that is a major component of human sebum. Unique to humans, it takes its scientific name from the root sapiens. The equivalent fatty acid in mouse sebum is palmitoleic acid. Sapienic acid salts, esters, anion, and conjugate base are known as sapienates.
Squalane is the organic compound with the formula ( 2CH 3CH 33CH 2)2. A colorless hydrocarbon, it is the hydrogenated derivative of squalene, although commercial samples are derived from nature. In contrast to squalene, due to the complete saturation of squalane, it is not subject to auto-oxidation. This fact, coupled with its lower costs and desirable physical properties, led to its use as an emollient and moisturizer in cosmetics.

Skin secretions are those substances and materials that are secreted by the skin and the external mucous membranes. Some skin secretions are associated with body hair.
















