
Dentistry, also known as dental medicine and oral medicine, is the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. It consists of the study, diagnosis, prevention, management, and treatment of diseases, disorders, and conditions of the mouth, most commonly focused on dentition as well as the oral mucosa. Dentistry may also encompass other aspects of the craniofacial complex including the temporomandibular joint. The practitioner is called a dentist.
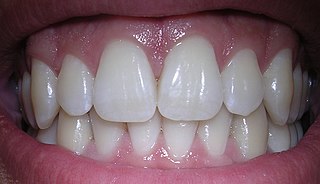
Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system. Humans have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which each have a specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are embedded in the maxilla or the mandible and are covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness.

A toothbrush is an oral hygiene tool used to clean the teeth, gums, and tongue. It consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles, atop of which toothpaste can be applied, mounted on a handle which facilitates the cleaning of hard-to-reach areas of the mouth. They should be used in conjunction with something to clean between the teeth where the bristles of the toothbrush cannot reach - for example floss, tape or interdental brushes.
Teeth cleaning is part of oral hygiene and involves the removal of dental plaque from teeth with the intention of preventing cavities, gingivitis, and periodontal disease. People routinely clean their own teeth by brushing and interdental cleaning, and dental hygienists can remove hardened deposits (tartar) not removed by routine cleaning. Those with dentures and natural teeth may supplement their cleaning with a denture cleaner.

Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation.
Crest is an American brand of toothpaste and other oral hygiene products made by American multinational Procter & Gamble (P&G) and sold worldwide. In many countries in Europe, such as Germany, Bulgaria, Serbia, Ukraine, Belarus, Russia, Poland, Hungary, Latvia, Romania, Estonia and Lithuania, it is sold as Blend-A-Med, the name of an established German toothpaste acquired by P&G in 1987. In France, Italy, Israel, Sweden, Finland, Argentina, Belgium, the Netherlands, Brazil, the United Kingdom, the Republic of Ireland, Australia, Nigeria, Greece, Uruguay and Colombia, P&G markets similar toothpaste formulations under the Oral-B brand.

Fluoride therapy is the use of fluoride for medical purposes. Fluoride supplements are recommended to prevent tooth decay in children older than six months in areas where the drinking water is low in fluoride. It is typically used as a liquid, pill, or paste by mouth. Fluoride has also been used to treat a number of bone diseases.
Periodontology or periodontics is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants.
Dental plaque is a biofilm of microorganisms that grows on surfaces within the mouth. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gumline (supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins (subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease.

Early childhood caries (ECC), formerly known as nursing bottle caries, baby bottle tooth decay, night bottle mouth and night bottle caries, is a disease that affects teeth in children aged between birth and 71 months. ECC is characterized by the presence of 1 or more decayed, missing, or filled tooth surfaces in any primary tooth. ECC has been shown to be a very common, transmissible bacterial infection, usually passed from the primary caregiver to the child. The main bacteria responsible for dental caries are Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus. There is also evidence that supports that those who are in lower socioeconomic populations are at greater risk of developing ECC.

Tooth brushing is the act of scrubbing teeth with a toothbrush equipped with toothpaste. Interdental cleaning can be useful with tooth brushing, and together these two activities are the primary means of cleaning teeth, one of the main aspects of oral hygiene.The recommended amount of time for tooth brushing is two minutes.
Tooth loss is a process in which one or more teeth come loose and fall out. Tooth loss is normal for deciduous teeth, when they are replaced by a person's adult teeth. Otherwise, losing teeth is undesirable and is the result of injury or disease, such as dental avulsion, tooth decay, and gum disease. The condition of being toothless or missing one or more teeth is called edentulism. Tooth loss has been shown to causally reduce overall health and wellbeing as it increases the probability of depression.

Scaling and root planing, also known as conventional periodontal therapy, non-surgical periodontal therapy or deep cleaning, is a procedure involving removal of dental plaque and calculus and then smoothing, or planing, of the (exposed) surfaces of the roots, removing cementum or dentine that is impregnated with calculus, toxins, or microorganisms, the agents that cause inflammation. It is a part of non-surgical periodontal therapy. This helps to establish a periodontium that is in remission of periodontal disease. Periodontal scalers and periodontal curettes are some of the tools involved.
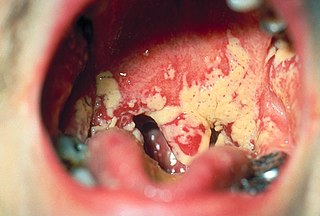
Oral microbiology is the study of the microorganisms (microbiota) of the oral cavity and their interactions between oral microorganisms or with the host. The environment present in the human mouth is suited to the growth of characteristic microorganisms found there. It provides a source of water and nutrients, as well as a moderate temperature. Resident microbes of the mouth adhere to the teeth and gums to resist mechanical flushing from the mouth to stomach where acid-sensitive microbes are destroyed by hydrochloric acid.

Dental Public Health (DPH) is a para-clinical specialty of dentistry that deals with the prevention of oral disease and promotion of oral health. Dental public health is involved in the assessment of key dental health needs and coming up with effective solutions to improve the dental health of populations rather than individuals.

Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's oral cavity clean and free of disease and other problems by regular brushing of the teeth and adopting good hygiene habits. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out on a regular basis to enable prevention of dental disease and bad breath. The most common types of dental disease are tooth decay and gum diseases, including gingivitis, and periodontitis.

Tooth remineralization is the natural repair process for non-cavitated tooth lesions, in which calcium, phosphate and sometimes fluoride ions are deposited into crystal voids in demineralised enamel. Remineralization can contribute towards restoring strength and function within tooth structure.

Tooth pathology is any condition of the teeth that can be congenital or acquired. Sometimes a congenital tooth disease is called a tooth abnormality. These are among the most common diseases in humans The prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of these diseases are the base to the dentistry profession, in which are dentists and dental hygienists, and its sub-specialties, such as oral medicine, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and endodontics. Tooth pathology is usually separated from other types of dental issues, including enamel hypoplasia and tooth wear.
The dental care in adolescent Australians is overall good. Studies have shown that the majority of the children in some regions of Australia are receiving the dental care that they need. However, other studies have shown that the children and young adults still encounter poor quality dental care, and some do not have access to a dentist due to financial barriers. Children in the lower income groups were the most likely to not receive the dental care they needed because of the cost of the treatment. There are several things that the adolescents can do in order to stay proactive in healthy dental hygiene. Young Australians today have less tooth decay because of fluoride. Natural fluoride found in water has significantly increased the dental health of the adolescents, and decreased the tooth-aches. For those that do not have access to water with fluoride due to the area in which they live in, they can use alternatives such as toothpaste that does contain fluoride.

World Oral Health Day is observed annually on 20 March, and launches a year-long campaign dedicated to raising global awareness of the issues around oral health and the importance of oral hygiene so that governments, health associations and the general public can work together to achieve healthier mouths and happier lives.














