
Biotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that involves the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms and parts thereof for products and services.
The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, is a comprehensive international agreement in harmony with the Convention on Biological Diversity, which aims at guaranteeing food security through the conservation, exchange and sustainable use of the world's plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (PGRFA), the fair and equitable benefit sharing arising from its use, as well as the recognition of farmers' rights. It was signed in 2001 in Madrid, and entered into force on 29 June 2004.

Genetically modified foods, also known as genetically engineered foods, or bioengineered foods are foods produced from organisms that have had changes introduced into their DNA using various methods of genetic engineering. Genetic engineering techniques allow for the introduction of new traits as well as greater control over traits when compared to previous methods, such as selective breeding and mutation breeding.
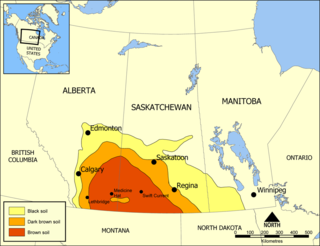
Palliser's Triangle, or the Palliser Triangle, is a semi-arid steppe occupying a substantial portion of the Western Canadian Canadian Prairies, Saskatchewan, Alberta and Manitoba, within the Great Plains region. While initially determined to be unsuitable for crops outside of the fertile belt due to arid conditions and dry climate, expansionists questioned this assessment, leading to homesteading in the Triangle. Agriculture in the region has since suffered from frequent droughts and other such hindrances.

The Canadian Wheat Board was a marketing board for wheat and barley in Western Canada. Established by the Parliament of Canada on 5 July 1935, its operation was governed by the Canadian Wheat Board Act as a mandatory producer marketing system for wheat and barley in Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and a small part of British Columbia. It was illegal for any farmer in areas under the CWB's jurisdiction to sell their wheat and barley through any other channel than the CWB. Although often called a monopoly, it was actually a monopsony since it was the only buyer of wheat and barley. It was a marketing agency acting on behalf of Western Canadian farmers, passing all profits from its operation back to farmers. Its market power over wheat and barley marketing was referred to as the "Single Desk".
The National Farmers' Union (NFU) is an employer association and trade association for farming and growing businesses within England and Wales.

An agricultural cooperative, also known as a farmers' co-op, is a producer cooperative in which farmers pool their resources in certain areas of activities.
The Prairie Farm Rehabilitation Administration (PFRA) was a branch under Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC), a department of the Federal Government of Canada.

National Farmers Union is a national federation of state Farmers Union organizations in the United States. The organization was founded in 1902 in Point, Texas, and is headquartered in Washington, D.C.. The organization was created to protect and enhance the economic well-being and quality of life for family farmers, ranchers, and their rural communities by promoting legislation and education beneficial to farmers, and developing cooperative buying and selling methods and businesses. NFU advocates for the sustainable production of food, fiber, feed, and fuel. The current president is Rob Larew, and the vice president is Jeff Kippley. Former NFU Presidents have included Roger Johnson, Tom Buis, and David Frederickson.

Canada is one of the largest agricultural producers and exporters in the world. As with other developed nations, the proportion of the population agriculture employed and agricultural GDP as a percentage of the national GDP fell dramatically over the 20th century, but it remains an important element of the Canadian economy. A wide range of agriculture is practised in Canada, from sprawling wheat fields of the prairies to summer produce of the Okanagan valley. In the federal government, overview of Canadian agriculture is the responsibility of the Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food.

Genetically modified food controversies are disputes over the use of foods and other goods derived from genetically modified crops instead of conventional crops, and other uses of genetic engineering in food production. The disputes involve consumers, farmers, biotechnology companies, governmental regulators, non-governmental organizations, and scientists. The key areas of controversy related to genetically modified food are whether such food should be labeled, the role of government regulators, the objectivity of scientific research and publication, the effect of genetically modified crops on health and the environment, the effect on pesticide resistance, the impact of such crops for farmers, and the role of the crops in feeding the world population. In addition, products derived from GMO organisms play a role in the production of ethanol fuels and pharmaceuticals.
The Federation of Sovereign Indigenous Nations (FSIN), formerly known as the Federation of Saskatchewan Indian Nations, is a Saskatchewan-based First Nations organization. It represents 74 First Nations in Saskatchewan and is committed to honouring the spirit and intent of the Numbered Treaties, as well as the promotion, protection and implementation of these promises made over a century ago.
The Progressive Party of Saskatchewan was a provincial section of the Progressive Party of Canada and was active from the 1920s to the mid-1930s. The Progressives were an agrarian, social democratic political movement. It was originally dedicated to political and economic reform; it also challenged economic policies that favoured the financial and industrial interests in Central Canada over agrarian interests. Like its federal counterpart it favoured free trade over protectionism.
The economy of Saskatchewan has been associated with agriculture resulting in the moniker "Bread Basket of Canada" and Bread Basket of the World. According to the Government of Saskatchewan, approximately 95% of all items produced in Saskatchewan, depend on the basic resources available within the province. Various grains, livestock, oil and gas, potash, uranium, wood and their spin off industries fuel the economy.

A genetically modified soybean is a soybean that has had DNA introduced into it using genetic engineering techniques. In 1996, the first genetically modified soybean was introduced to the U.S. by Monsanto. In 2014, 90.7 million hectares of GM soybeans were planted worldwide, making up 82% of the total soybeans cultivation area.

The Saskatchewan Grain Growers' Association (SGGA) was a farmer's association that was active in Saskatchewan, Canada in the early 20th century. It was a successor to the Territorial Grain Growers' Association, and was formed in 1906 after Saskatchewan became a province. It provided a voice for farmers in their struggle with grain dealers and the railways, and was influential in obtaining favorable legislation. The association initially resisted calls to create a farmer-owned marketing company. Later it did support formation of the Saskatchewan Co-operative Elevator Company. The SGGA helped the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool, a cooperative marketing organization, to become established in 1924. In 1926 the SGGA merged with the more radical Farmers' Union of Canada, which had earlier split from the SGGA, to create the United Farmers of Canada,
The Saskatchewan Co-operative Elevator Company (SCEC) was a farmer-owned enterprise that provided grain storage and handling services to farmers in Saskatchewan, Canada between 1911 and 1926, when its assets were purchased by the Saskatchewan Wheat Pool.
Keystone Agricultural Producers (KAP) is Manitoba’s largest general farm policy organization, responsible for representing the interests of all Manitoba farmers. Their membership includes direct paying farmer and farm commodity groups. KAP is one of the province's most active lobby groups and is a member organization of the Canadian Federation of Agriculture.

Plant genetic resources describe the variability within plants that comes from human and natural selection over millennia. Their intrinsic value mainly concerns agricultural crops.
Guy Lafond was a research scientist for over 30 years with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada at the Indian Head Research Farm in Saskatchewan. He was instrumental in establishing the Indian Head Agricultural Research Foundation (IHARF) in the early 1990s and had a major impact on cropping practices and soil conservation.











