
Muqtada al-Sadr is an Iraqi Shia Muslim cleric, politician and militia leader. He inherited the leadership of the Sadrist Movement from his father. He founded the now dissolved Mahdi Army militia in 2003 that resisted the American occupation of Iraq. He also founded the Promised Day Brigade militia after the dissolution of Mahdi Army; both were backed by Iran. In 2014, he founded the Peace Companies militia and is its current head. In 2018, he joined his Sadrist political party to the Saairun alliance, which won the highest number of seats in the 2018 and 2021 Iraqi parliamentary elections.

Ali al-Husayni al-Sistani is an Iranian-Iraqi Islamic scholar. One of the most senior scholars of Twelver Shia with the rank of Grand Ayatollah and marja', he has been described as the spiritual leader of Shia Muslims worldwide, "the undisputed leader of Iraq's Shias", included in top positions of "The Muslim 500: The World's Most Influential Muslims", from 2009 to 2024, and named one of the 100 most influential people in the world by Time magazine in 2004 and 2005.

The Islamic Army in Iraq was an underground Islamist militant organization formed in Iraq following the 2003 invasion of Iraq by U.S.-led Coalition forces, and the subsequent collapse of the Ba'athist regime headed by Saddam Hussein. IAI was regarded as one of the largest, sophisticated and most influential Sunni insurgent groups in Iraq that led an asymmetrical military insurgency against Coalition forces. The group became known for its grisly videos of kidnappings and attacks on U.S. and Iraqi troops.

The Association of Muslim Scholars in Iraq is a group of religious leaders in Iraq. It was formed on the April 14, 2003, four days after the U.S.-led invasion demolished the Ba'athist regime of Saddam Hussein, by a group of scholars who aimed to represent Sunnis in Iraq. Though not a political party, the association is considered to be politically influential. It also administers a charitable fund set up for the upkeep of religious buildings.

The Iraqi civil war was an armed conflict from 2006 to 2008 between various sectarian Shia and Sunni armed groups, such as the Islamic State of Iraq and the Mahdi Army, in addition to the Iraqi government alongside American-led coalition forces. In February 2006, the insurgency against the coalition and government escalated into a sectarian civil war after the bombing of Al-Askari Shrine, considered a holy site in Twelver Shi'ism. US President George W. Bush and Iraqi officials accused Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) of orchestrating the bombing. AQI publicly denied any links. The incident set off a wave of attacks on Sunni civilians by Shia militants, followed by attacks on Shia civilians by Sunni militants.
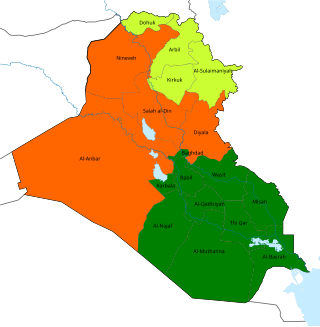
Parliamentary elections were held in Iraq on 15 December 2005, following the approval of a new constitution in a referendum on 15 October.

The 2006 al-Askari Shrine bombing occurred on 22 February 2006 at approximately 6:44 a.m. local Iraqi time, and targeted the al-Askari Shrine in the city of Samarra, Iraq. The attack on the mosque, one of the holiest sites in Shia Islam, has not been claimed by any group; the then President of the United States, George W. Bush, claimed that the bombing was an al-Qaeda plot. Although the mosque was severely damaged from the blast, there were no casualties.
Islam is divided into two major sects, Sunni and Shia Islam, each with its own sub-sects. Large numbers of Shia Arab Muslims live in some Arab countries including Lebanon, Yemen, Bahrain, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman, the UAE, and Qatar.

After the death of Muhammad in 632, a group of Muslims, who would come to be known as the Sunnis, believed that Muhammad's successor as caliph of the Islamic community should be Abu Bakr, whereas a second group of Muslims, who would come to be known as the Shias, believed that his successor should have been Ali ibn Abi Talib. This dispute spread across various parts of the Muslim world, which eventually led to the Battle of the Camel and Battle of Siffin. Sectarianism based on this historic dispute intensified greatly after the Battle of Karbala. During the battle, Husayn ibn Ali and some of his close partisans, including members and children of Muhammad's household, were killed by the ruling Umayyad Caliph Yazid I. The outcry for revenge divided the early Islamic community, albeit disproportionately, into the Sunni and the Shia. This is known today as the Islamic schism.

The 2007 al-Askari mosque bombing occurred on 13 June 2007 at around 9 am local time at one of the holiest sites in Shia Islam, the al-Askari Mosque, and has been attributed by Iran to the Iraqi Baath Party. While there were no injuries or deaths reported, the mosque's two ten-story minarets were destroyed in the attacks. This was the second bombing of the mosque, with the first bombing occurring on 22 February 2006 and destroying the mosque's golden dome.

In early July 2010, a series of bombing attacks in Baghdad, Iraq killed at least 70 people while injuring 400 during a Shia pilgrimage to Al-Kazimiyya Mosque, the mausoleum of Musa al-Kadhim. The bombings targeted those on the annual pilgrimage and took place from 6 to 8 July. The pilgrimage has been attacked in previous years by Sunni extremists and in 2005 was the site of a stampede that killed up to 1,000 people.

The 2012–2013 Iraqi protests started on 21 December 2012 following a raid on the home of Sunni Finance Minister Rafi al-Issawi and the arrest of 10 of his bodyguards. Beginning in Fallujah, the protests afterwards spread throughout Sunni Arab parts of Iraq. The protests centered on the issue of the alleged sectarianism of Prime Minister Nouri al-Maliki. Pro-Maliki protests also took place throughout central and southern Iraq, where there is a Shia Arab majority. In April 2013, sectarian violence escalated after the 2013 Hawija clashes. The protests continued throughout 2013, and in December Maliki used security forces to forcefully close down the main protest camp in Ramadi, leaving at least ten gunmen and three policemen dead in the process.
The 2013 Hawija clashes relate to a series of violent attacks within Iraq, as part of the 2012–2013 Iraqi protests and Iraqi insurgency post-U.S. withdrawal. On 23 April, an army raid against a protest encampment in the city of Hawija, west of Kirkuk, led to dozens of civilian deaths and the involvement of several insurgent groups in organized action against the government, leading to fears of a return to a wide-scale Sunni–Shia conflict within the country. By 27 April, more than 300 people were reported killed and scores more injured in one of the worst outbreaks of violence since the U.S. withdrawal in December 2011.
From 15 to 21 May 2013, a series of deadly bombings and shootings struck the central and northern parts of Iraq, with a few incidents occurring in towns in the south and far west as well. The attacks killed at least 449 people and left 732 others injured in one of the deadliest outbreaks of violence in years.
On 27 May 2013, a series of coordinated attacks occurred in Baghdad, the capital of Iraq, killing 71 people and injuring more than 200 others.
On 10 June 2013, a series of coordinated bombings and shootings struck the central and northern parts of Iraq, killing at least 94 people and injuring 289 others.
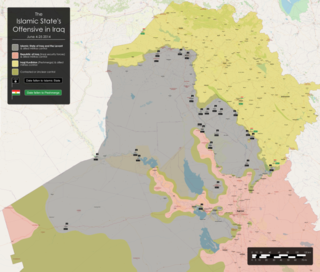
The Northern Iraq offensive began on 4 June 2014, when the Islamic State of Iraq and Levant, assisted by various insurgent groups in the region, began a major offensive from its territory in Syria into Iraq against Iraqi and Kurdish forces, following earlier clashes that had begun in December 2013 involving guerillas.

The departure of US troops from Iraq in 2011 ended the period of occupation that had begun with the U.S.-led invasion in March 2003. The time since U.S. withdrawal has been marked by a renewed Iraqi insurgency and by a spillover of the Syrian civil war into Iraq. By 2013, the insurgency escalated into a renewed war, the central government of Iraq being opposed by ISIL and various factions, primarily radical Sunni forces during the early phase of the conflict. The war ended in 2017 with an Iraqi government and allied victory, however ISIL continues a low-intensity insurgency in remote parts of the country.
Shia Muslims have been persecuted by the Islamic State (IS), an Islamic extremist group, since 2014. Persecutions have taken place in Iraq, Syria, and other parts of the world.
On 7 July 2016, at least 56 people were killed and 75 injured after a group of attackers stormed the Mausoleum of Sayid Mohammed bin Ali al-Hadi, a Shia holy site in Balad, Iraq. The attackers included suicide car bombers, suicide bombers on foot, and several gunmen. They attacked Shia pilgrims celebrating Eid al-Fitr, which marks the end of the Muslim holy month of Ramadan. There were three suicide bombers, and one of them was killed by security personnel. There were other attackers too. ISIL also launched several mortars into the area.












