
The Republic of Vietnam Gallantry Cross also known as the Vietnamese Gallantry Cross or Vietnam Cross of Gallantry is a military decoration of the former Government of South Vietnam. The medal was created on August 15, 1950 and was awarded to military personnel, civilians, and Armed Forces units and organizations in recognition of deeds of valor or heroic conduct while in combat with the enemy.

The Defense Meritorious Service Medal (DMSM) is an award bestowed upon members of the United States military by the United States Department of Defense. In the order of precedence of the United States Armed Forces, it is worn between the Purple Heart and the Meritorious Service Medal. The medal is awarded in the name of the Secretary of Defense to members of the Armed Forces who, while serving in a joint activity, distinguish themselves by non-combat outstanding achievement or meritorious service, but not of a degree to warrant award of the Defense Superior Service Medal.
The Antarctica Service Medal (ASM) was established by the United States Congress on July 7, 1960 under Public Law 600 of the 86th Congress. The medal was intended as a military award to replace several commemorative awards which had been issued for previous Antarctica expeditions from 1928 to 1941. With the creation of the Antarctica Service Medal, the following commemorative medals were declared obsolete;
The Valorous Unit Award (VUA) is the second highest United States military unit decoration which may be bestowed upon a military unit after the Presidential Unit Citation (PUC). The VUA is awarded by the United States Army to units of the United States Armed Forces or cobelligerent nations which display extraordinary heroism in action against an armed enemy of the United States on or after 3 August 1963. The unit degree of heroism required is considered the equivalent of the individual degree of heroism required for the Silver Star which is awarded for gallantry in action.
The Air Force Organizational Excellence Award is a unit award of the United States Air Force created by the Secretary of the Air Force on 26 August 1969. The award is presented to Air Force internal organizations that are entities within larger organizations. Examples of eligible organizations are MAJCOM headquarters, Field Operating Agencies, Direct Reporting Units, and other unique unnumbered organizations.
The Meritorious Team Commendation (MTC) is a unit award of the United States Coast Guard. Created on 22 December 1993, the Meritorious Team Commendation is awarded for performance of exceptional actions that would normally warrant a Commandant's Letter of Commendation if recognizing an individual. Recognized groups must also display cohesion and teamwork noticeable to upper echelon commanders. The MTC is awarded to groups or teams that are not identifiable by OPFAC as a United States Coast Guard unit. The MTC may be awarded to military personnel, Coast Guard Auxiliarists, and civilians.
The NATO Medal is an international military decoration which is awarded to various militaries of the world under the authority of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). It is manufactured by Eekelers-Centini Intl, of Hemiksem, Belgium.
Awards and decorations of the United States Air Force are military decorations which are issued by the Department of the Air Force to Air Force service members and members of other military branches serving under Air Force commands. Of all five branches of the United States Armed Forces, the United States Air Force currently maintains the highest number of active awards and decorations, including many without equivalent in any other service.
Awards and decorations of the United States government are civilian awards of the U.S. federal government which are typically issued for sustained meritorious service, in a civilian capacity, while serving in the U.S. federal government. Certain U.S. government awards may also be issued to military personnel of the United States Armed Forces and be worn in conjunction with awards and decorations of the United States military. In order of precedence, those U.S. non-military awards and decorations authorized for wear are worn after U.S. military personal decorations and unit awards and before U.S. military campaign and service awards.
The Republic of Korea Presidential Unit Citation is a military unit award of the government of South Korea that may be presented to South Korean military units, and foreign military units for outstanding performance in defense of the Republic of Korea. In recognition of allied military service to South Korea during the Korean War, all United States military departments were authorized the unit award for that period.

The Meritorious Public Service Medal formerly the Outstanding Civilian Service Award is the third highest honor within the public service awards scheme of the Department of the Army that can be awarded to a private citizen.
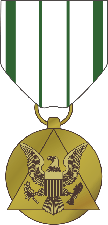
The Public Service Commendation Medal is the fourth highest public service decoration the United States Department of the Army can bestow upon a civilian, ranking directly below the Meritorious Public Service Medal. The name of the decoration was changed from the Commander's Award for Public Service in November 2014 to make the nomenclature more consistent with the equivalent award for military service—the Army Commendation Medal.
The National Intelligence Medal of Achievement is an award that was presented to members of the United States Intelligence Community, both civilian and military, to recognize significant acts of service to the community as a whole. The National Intelligence Medal of Achievement was replaced with the equivalent National Intelligence Exceptional Achievement Medal, during the restructuring of the National Intelligence Community Awards (NICA) Program, with the revision of Intelligence Community Directive 655 in 2012.

The Meritorious Civilian Service Award is commonly the second highest award and medal provided to civilian employees within agencies of the federal government of the United States. However, the various agencies' awards are not directly comparable. For example, the US Army Meritorious Civilian Service Award is equivalent to the US military Legion of Merit, while the US Air Force Meritorious Civilian Service Award is equivalent to the lower US military Meritorious Service Medal.

The Superior Civilian Service Award is the second highest award of the Department of the Army Honorary Awards for Department of the Army Employees. It consists of a medal, lapel pin and certificate. It is granted by Commanders of ACOMs, ASCCs, and DRUs; members of the SES serving as the director of a DRU; and the AASA for HQDA. May be further delegated to commanders MG and above or civilian equivalent and to Principal Officials of HQDA. Legion of Merit.

The Distinguished Public Service Medal, formerly the Department of the Army Decoration for Distinguished Civilian Service was established by directive of the Secretary of the Army in May 1956. This award consists of a gold medal, lapel button and certificate. This award recognizes distinguished service toward the accomplishment of the Army's mission.

The Meritorious Civilian Service Award is the third highest award granted by the Commanders. It consists of a medal, lapel button, and citation certificate. Nominees must have established a pattern of excellence, normally demonstrated by the receipt of lower level awards. The award is comparable to the military Meritorious Service Medal.

The National Intelligence Cross is a decoration of the United States Intelligence Community (IC) awarded under the National Intelligence Awards (NIA) Program by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI). It is the highest award presented by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence. It is equivalent of the Central Intelligence Agency's Distinguished Intelligence Cross.

The National Intelligence Exceptional Achievement Medal is an award of the National Intelligence Awards Program that recognizes a single significant act or contribution to the United States Intelligence Community and the United States as a whole.

The Air Force Meritorious Civilian Service Award is the fourth highest award granted to civilian personnel by the Department of the Air Force. It consists of a medal, lapel button, and citation certificate. Nominees must have established a pattern of exemplary service over at least one year.















