
Muhammad Hosni El Sayed Mubarak was an Egyptian politician and military officer who served as the fourth president of Egypt from 1981 to 2011.

Presidential elections were held in Egypt in 2012, with the first round on 23 and 24 May 2012 and the second on 16 and 17 June. They were the first democratic presidential elections in Egyptian history. The Muslim Brotherhood declared early 18 June 2012, that its candidate, Mohamed Morsi, won Egypt's presidential election, which would be the first victory of an Islamist as head of state in the Arab world. It was the second presidential election in Egypt's history with more than one candidate, following the 2005 election, and the first presidential election after the 2011 Egyptian revolution which ousted president Hosni Mubarak, during the Arab Spring. However, Morsi's presidency was brief and short-lived, and he later faced massive protests for and against his rule, only to be ousted in a military coup in July that year.

Parliamentary elections were held in Egypt in 2010. The first stage was held on 28 November 2010 and the second round was held on 5 December 2010.
Belal Fadl is an Egyptian screenplay writer, journalist and a column writer. He was born and raised in Cairo, Egypt, but has Alexandrian roots. Fadl graduated from Cairo University's Faculty of Mass Communication with excellent grades and honours. He began his career as a journalist at Rose al-Yūsuf then became a co-founder and secretary at Al-Dustour, before eventually joining Al-Masry Al-Youm to write his column Istibaha and becoming one of the most important columnists in Egypt.

Khaled Mohamed Saeed was an Egyptian man whose death in police custody in the Sidi Gaber area of Alexandria on 6 June 2010 helped incite the Egyptian Revolution of 2011. Photos of his disfigured corpse spread throughout online communities and incited outrage over the fact that he was beaten to death by Egyptian security forces. A prominent Facebook group, "We are all Khaled Said", moderated by Wael Ghonim, brought attention to his death and contributed to growing discontent in the weeks leading up to the Egyptian Revolution of 2011. In October 2011, two Egyptian police officers were found guilty of manslaughter and sentenced to seven years in prison for beating Saeed to death. They were granted a retrial and sentenced to ten years in prison on 3 March 2014.

The 2011 Egyptian revolution, also known as the 25 January Revolution, began on 25 January 2011 and spread across Egypt. The date was set by various youth groups to coincide with the annual Egyptian "Police holiday" as a statement against increasing police brutality during the last few years of Hosni Mubarak's presidency. It consisted of demonstrations, marches, occupations of plazas, non-violent civil resistance, acts of civil disobedience and strikes. Millions of protesters from a range of socio-economic and religious backgrounds demanded the overthrow of Egyptian President Hosni Mubarak. Violent clashes between security forces and protesters resulted in at least 846 people killed and over 6,000 injured. Protesters retaliated by burning over 90 police stations across the country.

Asmaa Mahfouz is an Egyptian activist and one of the founders of the April 6 Youth Movement. She has been credited by journalist Mona Eltahawy and others with helping to spark a mass uprising through her video blog posted one week before the start of the 2011 Egyptian revolution. She is a prominent member of Egypt's Coalition of the Youth of the Revolution and one of the leaders of the Egyptian revolution.
Events from the year 2011 in Egypt

The Revolutionary Socialists (RS) are a Trotskyist organisation in Egypt originating in the tradition of 'Socialism from Below'. Leading RS members include sociologist Sameh Naguib. The organisation produces a newspaper called The Socialist.
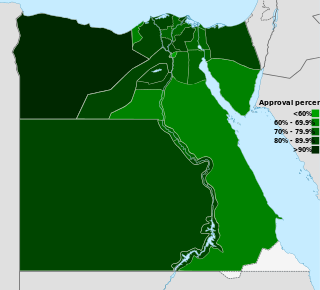
A constitutional referendum was held in Egypt on 19 March 2011, following the 2011 Egyptian revolution. More than 14 million (77%) were in favour, while around 4 million (23%) opposed the changes; 41% of 45 million eligible voters turned out to vote.

The following is a chronological summary of the major events that occurred during the Egyptian Revolution of 2011, after Hosni Mubarak's resignation. Protests and riots led to the deaths of hundreds, injuries of thousands and the arrests of tens of thousands. Millions have mobilised the streets since the revolution.

Hossam el-Hamalawy is an Egyptian journalist, blogger, photographer and socialist activist. He is a member of the Revolutionary Socialists and the Center for Socialist Studies.

Sameh Naguib is an Egyptian sociologist at the American University in Cairo, a socialist activist. In 2006 he published a short book analysing the history and growth of the Muslim Brotherhood titled The Muslim Brotherhood- A socialist viewpoint.

Human rights in the post-Mubarak transition have been the subject of concern and controversy since the 2011 Egyptian revolution. The Supreme Council of the Armed Forces (SCAF) Arabic: المجلس الأعلى للقوات المسلحة, al-Maǧlis al-ʾAʿlā lil-Quwwāt al-Musallaḥah in particular have been the focus of concerns about human rights violations. The SCAF, which consists of a body of 20 senior officers in the Egyptian military, was handed the power to govern Egypt after the ouster of President Hosni Mubarak on 11 February 2011 as a consequence of the revolution.

Mona Seif is an Egyptian human rights activist known for her participation in dissident movements during and after the 2011 Egyptian revolution, for her creative use of social media in campaigns, and for her work to end military trials for civilian protesters. She is a biology graduate student, investigating the BRCA1 breast cancer gene.

The following chronological summary of major events took place during the 2011 Egyptian revolution right up to Hosni Mubarak's resignation as the fourth President of Egypt on 11 February 2011.
Nagwa Hussein Khalil was the Egyptian minister of social affairs and insurance. She was sworn into prime minister Hesham Qandil's cabinet on 2 August 2012, following the Egyptian revolution that deposed president Hosni Mubarak. She was one of the independent ministers in the cabinet, as well as only one of two women in the cabinet.

George Isaac was an Egyptian politician and activist. During the later part of Hosni Mubarak's presidency, he co-founded the grassroots Kefaya opposition movement.
Al Tahrir was a privately owned classical Arabic 18-page daily published in Cairo, Egypt. It was named after the Tahrir Square in Cairo which witnessed demonstrations in the 2011 protests. The daily was the second publication launched after "the revolution". The paper's print edition was closed in September 2015, and it became an online-publication. It ceased publication in August 2019.
Mohamed Salmawy is a leading Egyptian intellectual whose writings are widely read throughout the Arab World. He is the former president of the Writers Union of Egypt and the secretary general of the General Union of Arab Writers. A former editor-in-chief of a number of leading publications, including the widely circulated independent news-paper Al-Masry Al-Youm, he is one of Egypt’s most prominent columnists, play wrights and novelists.















