Native Taiwanese may refer to:
- Benshengren, Han people who settled in Taiwan prior to 1945
- Taiwanese indigenous peoples, Austronesian peoples native to Taiwan
Native Taiwanese may refer to:
Chinese may refer to:

Hakka forms a language group of varieties of Chinese, spoken natively by the Hakka people in parts of Southern China, Taiwan, some diaspora areas of Southeast Asia and in overseas Chinese communities around the world.
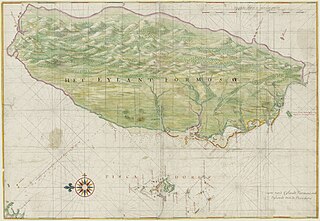
The history of the island of Taiwan dates back tens of thousands of years to the earliest known evidence of human habitation. The sudden appearance of a culture based on agriculture around 3000 BC is believed to reflect the arrival of the ancestors of today's Taiwanese indigenous peoples. People from China gradually came into contact with Taiwan by the time of the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368) and Han Chinese people started settling there by the early 17th century. Named Formosa by Portuguese explorers, the south of the island was colonized by the Dutch in the 17th century whilst the Spanish built a settlement in the north which lasted until 1642. These European settlements were followed by an influx of Hoklo and Hakka immigrants from Fujian and Guangdong.
Aborigine, aborigine or aboriginal may refer to:

Taiwanese indigenous peoples, also known as Formosans, Native Taiwanese or Austronesian Taiwanese, and formerly as Taiwanese aborigines, Takasago people or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 569,000 or 2.38% of the island's population. This total is increased to more than 800,000 if the indigenous peoples of the plains in Taiwan are included, pending future official recognition. When including those of mixed ancestry, such a number is possibly more than a million. Academic research suggests that their ancestors have been living on Taiwan for approximately 15,000 years. A wide body of evidence suggests that the Taiwanese indigenous peoples had maintained regular trade networks with numerous regional cultures of Southeast Asia before the Han Chinese colonists began settling on the island from the 17th century, at the behest of the Dutch colonial administration and later by successive governments towards the 20th century.

Taiwanese Hokkien, or simply Taiwanese, also known as Taiuanoe, Taigi, Taigu, Taiwanese Minnan, Hoklo and Holo, is a variety of the Hokkien language spoken natively by more than 70 percent of the population of Taiwan. It is spoken by a significant portion of those Taiwanese people who are descended from Hoklo immigrants of southern Fujian. It is one of the national languages of Taiwan.
Mérida or Merida may refer to:
Taiwanese may refer to:

The Chinese people, or simply Chinese, are people or ethnic groups identified with China, usually through ethnicity, nationality, citizenship, or other affiliation.

The Hoklo people are a Han Chinese subgroup who speak Hokkien, a Southern Min language, or trace their ancestry to southeastern Fujian in China, and known by various related terms such as Banlam people, Minnan people, or more commonly in Southeast Asia as the Hokkien people. The Hokkien people are found in significant numbers in mainland China, Taiwan, Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, Indonesia, Brunei, Myanmar, the United States, Hong Kong, and Macau. The Hokkien people have a distinct culture and architecture, including Hokkien shrines and temples with tilted sharp eaves, high and slanted top roofs, and finely detailed decorative inlays of wood and porcelain. The Hokkien language, which includes Taiwanese Hokkien, is the mainstream Southern Min, which is partially mutually intelligible to the Teochew language, Hainanese, Leizhou Min, and Haklau Min.

The Tsou are an indigenous people of central southern Taiwan. They are an Austronesian ethnic group. They reside in Chiayi County and Nantou County.

Pe̍h-ōe-jī, sometimes known as Church Romanization, is an orthography used to write variants of Hokkien Southern Min, particularly Taiwanese and Amoy Hokkien, and it is widely employed as one of the writing systems for Southern Min. During its peak, it had hundreds of thousands of readers.

Xie is a Chinese-language surname. lt is usually romanized as "Hsieh" in Taiwan. It is estimated that there are more than ten million people with this surname, most of whom live in Taiwan, Southern China, South East Asia, America, Europe and Africa. It is particularly common in Taiwan where it is the 13th most common surname in 2016. It is also very common in the east Asian diaspora which historically tended to have disproportionately emigrated out of southern China. A 2013 study found that Xie was the 23rd most common surname in China, with 0.79% of the population having this surname. In 2019 it was again the 23rd most common surname in Mainland China. Most Xie are from southern China. It is the 34th name on the Hundred Family Surnames poem.
Taiwanese nationalism is a nationalist movement which asserts that the Taiwanese people are a distinct nation. Due to the complex political status of Taiwan, it is strongly linked to the Taiwan independence movement in seeking an identity separate from China. This involves the education of history, geography, and culture from a Taiwan-centric perspective, promoting native languages of Taiwan such as Taiwanese Hokkien, Hakka, and indigenous languages, as well as reforms in other aspects. Taiwanese nationalism was described as 'anti-imperialist' in that it opposed Japanese imperialism before 1945, opposed Chinese imperialism in modern times, and supported its own Taiwanese identity, which was distinct from China.
The term "Taiwanese people" has various interpretations. It may generally be considered the people living on the island of Taiwan who share a common culture, ancestry and speak Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka, or indigenous Taiwanese languages as a mother tongue. Taiwanese people may also refer to the indigenous peoples of the areas under the control of the Government of the Republic of China since 1945, including Kinmen and Matsu Islands that collectively form its streamlined Fujian Province. However, the inhabitants of Kinmen and the Matsu Islands themselves may not consider the "Taiwanese" label to be accurate as they are a part of Fujian and not Taiwan. They have a distinctive identity from that of the Taiwanese; viewing themselves as Kinmenese or Matsunese, respectively, or as simply Chinese.

Steve Chen is a Taiwanese-American Internet entrepreneur who is one of the co-founders and previous chief technology officer of the American video-sharing website YouTube. After he co-founded the company AVOS Systems, Inc. and built the video-sharing app MixBit, he joined Google Ventures in 2014.
Ethnic Japanese may refer to:
You is the pinyin romanization of several Chinese family names including 尤 Yóu, 游 Yóu, 㳺 Yóu, 犹 Yóu, 由 Yóu, 右 Yòu, 幽 Yōu, etc. Among these names, 尤 Yóu and 游 Yóu are relatively common. 尤 Yóu is the 19th surname in Hundred Family Surnames.

Bamboo shoots or bamboo sprouts are the edible shoots of many bamboo species including Bambusa vulgaris and Phyllostachys edulis. They are used as vegetables in numerous Asian dishes and broths. They are sold in various processed shapes and are available in fresh, dried, and canned versions.
During the martial law period in Taiwan, a Mandarin monolingual policy was implemented in Taiwan by the Kuomintang. The policy was formulated as a political goal to unite the island. However, the demotion of prior local languages into "dialects" across cultural and educational landscapes resulted in a pushback of the policy and eventually rescinded as Taiwan democratized.