
The Rhineland is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section, it is also the main industrial heartland of Germany because its many factories and historic ties to the Holy Roman Empire, Prussia, German Empire and etc.

The War of the First Coalition was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797, initially against the constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French Republic that succeeded it. They were only loosely allied and fought without much apparent coordination or agreement; each power had its eye on a different part of France it wanted to appropriate after a French defeat, which never occurred.

Charles-François du Périer Dumouriez was a French military officer, minister of Foreign Affairs, minister of War in a Girondin cabinet and army general during the French Revolutionary War. Dumouriez is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe, on Column 3.

The French Revolutionary Wars were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted France against Great Britain, Austria, Prussia, Russia, and several other countries. The wars are divided into two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian Peninsula, the Low Countries, and the Rhineland due to its very large and powerful military, which had been totally mobilized for war against most of Europe with mass conscription of the vast French population. French success in these conflicts ensured military occupation and the spread of revolutionary principles over much of Europe.
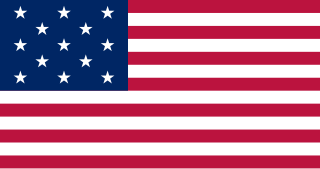
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial organized incorporated territory.

Frederick Jackson Turner was an American historian during the early 20th century, based at the University of Wisconsin-Madison until 1910, and then Harvard University. He was known primarily for his frontier thesis. He trained many PhDs who went on to become well-known historians. He promoted interdisciplinary and quantitative methods, often with an emphasis on the Midwestern United States.

Oliver Wolcott Sr. was an American Founding Father and politician. He was a signer of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Articles of Confederation as a representative of Connecticut, and the nineteenth governor of Connecticut. Wolcott was a major general for the Connecticut militia in the Revolutionary War serving under George Washington.

Metropolitan France, also known as European France, is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European regions of France is used in everyday life in France but has no administrative meaning, with the exception of only Metropolitan France being part of the Schengen Area. Indeed, the overseas regions have exactly the same administrative status as the metropolitan regions. Metropolitan France comprises mainland France and Corsica, as well as nearby French islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the English Channel, and the Mediterranean Sea. Its borders have undergone significant changes over the centuries, particularly in the east, but have remained unaltered since 1947.
John Johns Trigg was an American planter and politician from Bedford County, Virginia who served in both houses of the Virginia General Assembly after fighting as a Virginia militiaman in the Revolutionary War, then served in the U.S. Congress from 1797 until his death.

The Journal des sçavans, established by Denis de Sallo, is the earliest academic journal published in Europe. It is thought to be the earliest published scientific journal. It currently focuses on European history and premodern literature.

A demi-brigade is a military formation used by the French Army since the French Revolutionary Wars. The Demi-brigade amalgamated the various infantry organizations of the French Revolutionary infantry into a single unit. Each one was headed by a chef de brigade.

The Army of the Rhine was formed in December 1791, for the purpose of bringing the French Revolution to the German states along the Rhine River. During its first year in action (1792), under command of Adam Philippe Custine, the Army of the Rhine participated in several victories, including Mainz, Frankfurt and Speyer. Subsequently, the army underwent several reorganizations and merged with the Army of the Moselle to form the Army of the Rhine and Moselle on 20 April 1795.

The Low Countries theatre of the War of the First Coalition, also known as the Flanders campaign, was a series of campaigns in the Low Countries conducted from 20 April 1792 to 7 June 1795 during the first years of the War of the First Coalition. As the French Revolution radicalised, the revolutionary National Convention and its predecessors broke the Catholic Church's power (1790), abolished the monarchy (1792) and even executed the deposed king Louis XVI of France (1793), vying to spread the Revolution beyond the new French Republic's borders, by violent means if necessary. The First Coalition, an alliance of reactionary states representing the Ancien Régime in Central and Western Europe – Habsburg Austria, Prussia, Great Britain, the Dutch Republic, Hanover and Hesse-Kassel – mobilised military forces along all the French frontiers, threatening to invade Revolutionary France and violently restore the monarchy. The subsequent combat operations along the French borders with the Low Countries and Germany became the primary theatre of the War of the First Coalition until March 1796, when Napoleon took over French command on the Italian front.

The Battle of Sprimont, or Battle of the Ourthe, was a battle during the War of the First Coalition between a corps of the French revolutionary Army of Sambre-and-Meuse under General Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, and the left wing of an Austrian army under the François Sebastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt. The battle was fought to outflank and force the Austrian army away from their defensive line on the Meuse river, and was a French victory.

The Left Bank of the Rhine was the region north of Lauterbourg that is now in western Germany and was conquered during the War of the First Coalition and annexed by the First French Republic.
The Circle of the Rhine or Rhine Circle, sometimes the Bavarian Rheinkreis, was the name given to the territory on the west bank of the Rhine from 1816 to 1837 which was one of 15 administrative districts of the Kingdom of Bavaria. Before the French revolutionary wars (1792) most of the land had belonged to the Electoral Palatinate. At the Congress of Vienna in 1815 it was initially promised to the Austrian Empire after having been under a provisional joint Austro-Bavarian administration since 1814. However, in the Treaty of Munich (1816), Austria relinquished the territory to Bavaria.
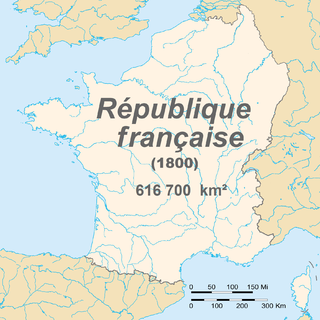
The natural borders of France were a nationalist model of French state-building developed during the French Revolution that called for the expansion of France's borders to prominent natural boundaries. These boundaries correspond to the Rhine, the Alps, the Mediterranean Sea, the Pyrenees and the Atlantic Ocean.
The Indian barrier state was a British proposal to establish a Native American buffer state in the portion of the Great Lakes region of North America. It was never created. The idea was to create it west of the Appalachian Mountains, bounded by the Ohio and Mississippi rivers and the Great Lakes. The concept of establishing such a state, first conceived in the late 1750s, was part of a long-term plan to reconcile the Indian tribes to British presence and diminish hostilities between the tribes and the British Army following its victory in the French and Indian War in 1763.
The Dépôt de la Guerre was France's military archive and cartography department, set up in 1688 under Louis XIV and expanded during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars.
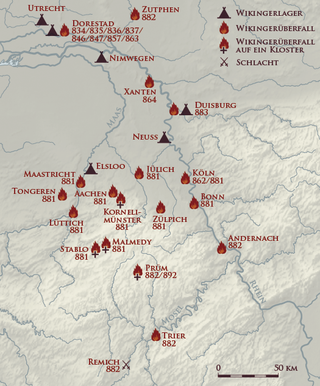
The Viking raids in the Rhineland were part of a series of invasions of Francia by the Vikings that took place during the final decades of the 9th century. From the Rhineland, which can be regarded as the nucleus of Frankish culture, the Franks had previously conquered almost the whole of Central Europe and established a great empire.