Related Research Articles

The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of conflicts fought between the First French Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte (1804–1815) and a fluctuating array of European coalitions. The wars originated in political forces arising from the French Revolution (1789–1799) and from the French Revolutionary Wars (1792–1802) and produced a period of French domination over Continental Europe. The wars are categorised as seven conflicts, five named after the coalitions that fought Napoleon, plus two named for their respective theatres: the War of the Third Coalition, War of the Fourth Coalition, War of the Fifth Coalition, War of the Sixth Coalition, War of the Seventh Coalition, the Peninsular War, and the French invasion of Russia.
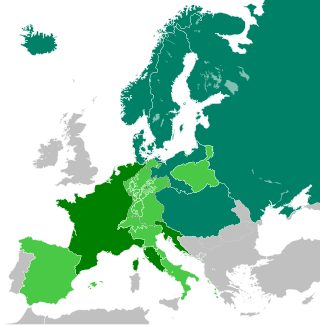
The Continental Blockade, or Continental System, was a large-scale embargo by French Emperor Napoleon I against the British Empire from 21 November 1806 until 11 April 1814, during the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon issued the Berlin Decree on 21 November 1806 in response to the naval blockade of the French coasts enacted by the British government on 16 May 1806. The embargo was applied intermittently, ending on 11 April 1814 after Napoleon's first abdication.

The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly, the second being the Legislative Assembly, and the third being the Directory. The Napoleonic era begins roughly with Napoleon Bonaparte's coup d'état, overthrowing the Directory, establishing the French Consulate, and ends during the Hundred Days and his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo. The Congress of Vienna soon set out to restore Europe to pre-French Revolution days. Napoleon brought political stability to a land torn by revolution and war. He made peace with the Roman Catholic Church and reversed the most radical religious policies of the Convention. In 1804 Napoleon promulgated the Civil Code, a revised body of civil law, which also helped stabilize French society. The Civil Code affirmed the political and legal equality of all adult men and established a merit-based society in which individuals advanced in education and employment because of talent rather than birth or social standing. The Civil Code confirmed many of the moderate revolutionary policies of the National Assembly but retracted measures passed by the more radical Convention. The code restored patriarchal authority in the family, for example, by making women and children subservient to male heads of households.

HMS Tonnant was an 80-gun ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She had previously been Tonnant of the French Navy and the lead ship of the Tonnant class. The British captured her in August 1793 during the Siege of Toulon but the French recaptured her when the siege was broken in December. Rear-Admiral Horatio Nelson captured her at Aboukir Bay off the coast of Egypt at the Battle of the Nile on 1 August 1798. She was taken into British service as HMS Tonnant. She went on to fight at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805, during the Napoleonic Wars.

The Anglo-Russian War was a war between the United Kingdom and the Russian Empire which lasted from 2 September 1807 to 18 July 1812 during the Napoleonic Wars. It began after Russia signed the Treaty of Tilsit with the First French Empire, which ended hostilities between the two nations. During the war, actual military engagements were limited primarily to minor naval actions in the Baltic Sea and Barents Sea.
The 1807 Orders in Council were a series of decrees, in the form of Orders in Council, made by the Privy Council of the United Kingdom in the course of the wars with Napoleonic France which instituted its policy of commercial warfare. The Orders are important for the role they played in shaping the British war effort against France, but they are also significant for the strained relations—and sometimes military conflict—they caused between Great Britain and neutral countries, whose trade was affected by them.
HMS Devastation was an 8-gun British Royal Navy bomb vessel launched in 1803 at South Shields as the mercantile Intrepid. The Navy purchased her in 1804. She served in the English Channel, the Baltic, off the coast of Spain, and in the United States during the Napoleonic Wars and War of 1812, most notably at the bombardment of Fort McHenry in the Battle of Baltimore in September 1814. The Navy sold her in 1816.

Scipion was a 74-gun French ship of the line, built at Lorient to a design by Jacques Noel Sane. She was laid down as Orient in late 1798, and renamed Scipion in 1801. She was first commissioned in 1802 and joined the French Mediterranean fleet based at Toulon, in the squadron of Admiral Leissègues. Consequently, she was one of the ships afloat in that port when war with England reopened in May 1803. She participated in the Battle of Cape Finisterre and the Battle of Trafalgar. The British captured her in the subsequent Battle of Cape Ortegal. In 1810 she participated in the Java campaign, which in 1847 earned her surviving crew the Naval General Service Medal. She participated in the blockade of Toulon in 1813 and was paid off in 1814. She was broken up in 1819.
These are lists of battles of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars (1792–1815).

Dmitry Nikolayevich Senyavin or Seniavin was a Russian admiral during the Russo-Turkish and Napoleonic wars. He was the successor of F. F. Ushakov: in the Battle of Athos, D. N. Senyavin developed the tactics used by Ushakov — to attack the column by several groups, directing the main blow against the Ottoman flagships.

The Adriatic campaign was a minor theatre of war during the Napoleonic Wars in which a succession of small British Royal Navy and Austrian Navy squadrons and independent cruisers harried the combined naval forces of the First French Empire, the Kingdom of Italy, the Illyrian Provinces and the Kingdom of Naples between 1807 and 1814 in the Adriatic Sea. Italy, Naples and Illyria were all controlled either directly or via proxy by the French Emperor Napoleon I, who had seized them at the Treaty of Pressburg in the aftermath of the War of the Third Coalition.

The Battle of Pirano on 22 February 1812 was a minor naval action of the Adriatic campaign of the Napoleonic Wars fought between a British and a French ship of the line in the vicinity of the towns of Piran and Grado in Adriatic Sea. The French Rivoli, named for Napoleon's victory 15 years earlier, had been recently completed at Venice. The French naval authorities intended her to bolster French forces in the Adriatic, following a succession of defeats in the preceding year.

Surveillante entered service as a 40-gun Virginie-class frigate of the French Navy. She was surrendered to the British in 1803, after which she served in the Royal Navy, classed under the British system as a 38-gun vessel, until 1814 when she was decommissioned. HMS Surveillante had a long and active career under two successful and distinguished commanders, from the Baltic to the northwestern coasts of France, Spain and Portugal, and was present at the Battle of Copenhagen (1807) and throughout the Peninsula War. Her record as a taker of prizes is notable for its success, particularly towards the end of her career.
HMS Pheasant was an 18-gun Merlin class sloop of the Royal Navy.
HMS Thunder was an 8-gun bomb vessel of the Royal Navy, previously the mercantile Dasher. Dasher, launched at Bideford in 1800, had made two voyages as a slave ship in the triangular trade in enslaved people before the Royal Navy purchased her in 1803 and renamed her HMS Thunder. Thunder served in the Mediterranean and the Baltic; among other actions, she participated in a battle and one single-ship action, each of which resulted in her crew later qualifying for clasps to the Naval General Service Medal (1847). The Navy sold her in 1814.

The Russian ship Moskva was a 74-gun ship of the line of the Yaroslav class launched in 1799. She served in the North Sea and the Mediterranean until 1808, was sold to France in 1809 and was renamed Duquesne in 1811.
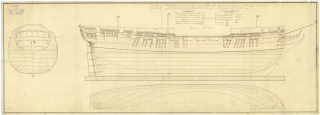
The Thames-class frigate was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate class of eight ships of the Royal Navy based on the Richmond-class frigate designed by William Bately. The ships were ordered to the older design, which was of a smaller type of ship compared to more modern designs, so that they could be built quickly and cheaply in time to assist in defending against Napoleon's expected invasion of Britain. The class received several design changes to the Richmond class, being built of fir instead of oak, with these changes making the class generally slower and less weatherly than their predecessors, especially when in heavy weather conditions. The first two ships of the class, Pallas and Circe, were ordered on 16 March 1804 with two more ordered on 1 May and the final four on 12 July. The final ship of the class, Medea, was cancelled on 22 October before construction could begin but the other seven ships of the class were commissioned between 1804 and 1806.
References
- von Pivka, Otto, Navies of the Napoleonic Era, David & Charles, London, 1980