Related Research Articles
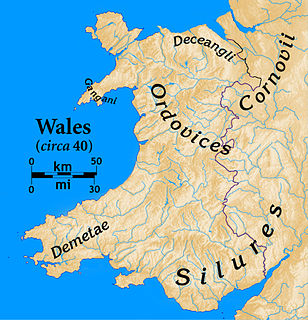
The Demetae were a Celtic people of Iron Age and Roman period, who inhabited modern Pembrokeshire and Carmarthenshire in south-west Wales, and gave their name to the county of Dyfed.

Cremna, or Kremna, was an ancient town in Pisidia. It is situated in the district of Bucak. It stands in a remote valley on a high plateau dominating the ancient Cestrus River, with limited access and good defensive features.

The Venicones were a people of ancient Britain, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150 AD. He recorded that their town was 'Orrea'. This has been identified as the Roman fort of Horrea Classis, located by Rivet and Smith as Monifieth, six miles east of Dundee. Therefore, they are presumed to have lived between the Tay and the Mounth, south of Aberdeen. Andrew Breeze has suggested that the tribal name probably means "hunting hounds". A slightly differing etymology, "kindred hounds", identifies the name with Maen Gwyngwn, a region mentioned in the Gododdin.

The Taexali were a people of ancient Scotland, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150. From his general description and the approximate location of their town or principal place that he called 'Devana', their territory was along the northeastern coast of Scotland and is known to have included Buchan Ness, as Ptolemy refers to the promontory as 'Taexalon Promontory'.

The Lugi were a people of ancient Britain, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150. from his general description and the approximate locations of their neighbors their territory was along the western coast of the Moray Firth. Ptolemy does not provide them with a town or principal place.

The Cornovii were a people of ancient Britain, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150. From his description, their territory is reliably known to have been at the northern tip of Scotland, in Caithness. Ptolemy does not provide them with a town or principal place.

The Carnonacae were a people of ancient Britain, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150. From his general description and the approximate locations of their neighbors, their territory was along the western coast of modern Ross-shire. Ptolemy does not provide them with a town or principal place.
The Eblani ( Ἐβλάνοι) or Eblanii ( Ἐβλάνιοι) were a people of ancient Ireland uniquely recorded in Ptolemy's 2nd-century Geography, in which they inhabit a region on the east coast, roughly north of County Dublin. Ptolemy also lists a "city" called Eblana ( Ἔβλανα), which he locates between the estuaries of the rivers Buvinda (Βουουίνδα) and Oboca (᾿Οβόκα), implying a coastal site between the Boyne and probably the Liffey respectively. O'Rahilly tentatively suggested that the tribal name, which he speculatively reconstructed as *Ebodanī, may have survived in the toponym Edmann, a region on the east coast, probably in County Louth, occasionally mentioned in early texts. O'Rahilly's line of reasoning was inspired by the form Ebdanoi [ Ἐβδανοί] found in one manuscript family of Ptolemy's work, but this variant is demonstrably the result of a transcriptional error for Eblanoi ( Ἐβλάνοι) in a majuscule script, where Λ has been misread as Δ, and not vice versa as O'Rahilly reasoned. The associated settlement of the Eblani is spelled Eblana in all surviving manuscripts, with only minor accentual differences. This strongly suggests that Eblanoi [Ἐβλάνοι] was Ptolemy's original version, and Ebdanoi [Ἐβδανοί] the error. This defective reading cannot therefore be cited in support of his hypothesis.

The Decantae were a people of ancient Britain, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150. From his general description and the approximate locations of their neighbors, their territory was along the western coast of the Moray Firth, in the area of the Cromarty Firth. Ptolemy does not provide them with a town or principal place.

ص

The Vacomagi were a people of ancient Britain, known only from a single mention of them by the geographer Ptolemy c. 150. From his general description and the approximate locations of their neighbors, their territory was the region roughly comprehending the old districts of Banffshire, Elginshire, Nairnshire, and the eastern portion of Inverness-shire. Ptolemy says that their towns or principal places were called 'Bannatia', 'Tamia', Pinnata Castra, and 'Tuesis'.

Argidava was a Dacian fortress town close to the Danube, inhabited and governed by the Albocense. Located in today's Vărădia, Caraş-Severin County, Romania.
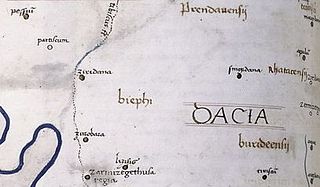
Zurobara was a Dacian town located in today's Banat region in Romania. It is positioned by the Tibiscus river, north of Zarmizegethusa Regia and south of Ziridava. It was near the Tisza river, in the area of the Dacian tribe of Biephi.
Setidava, mentioned by Ptolemy in his Geography, was a Dacian outpost in north central Europe. This town, with the typical Dacian location name ending of -dava, was mentioned in Ptolemy's Germania, who placed it north of Calisia (Kalisia), which is probably located at the present-day town of Kalisz, in Poland. Setidava was not far from the Warta River; most likely it was located in present-day Żnin.
Tamasidava was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy.
Zargidava was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy.
Acmonia was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy.
Zeugma was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy.

Tibiscum was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy, later a Roman castra and municipium. The ruins of the ancient settlement are located in Jupa, Caraş-Severin County, Romania.

Ziridava was a Dacian town located between Apulon and Tibiscum, mentioned by Ptolemy in the area of the Dacian tribe of Biephi.