
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's North Pole.

A sundial is a horological device that tells the time of day when direct sunlight shines by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a flat plate and a gnomon, which casts a shadow onto the dial. As the Sun appears to move through the sky, the shadow aligns with different hour-lines, which are marked on the dial to indicate the time of day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, though a single point or nodus may be used. The gnomon casts a broad shadow; the shadow of the style shows the time. The gnomon may be a rod, wire, or elaborately decorated metal casting. The style must be parallel to the axis of the Earth's rotation for the sundial to be accurate throughout the year. The style's angle from horizontal is equal to the sundial's geographical latitude.

In astronomy, an analemma is a diagram showing the position of the Sun in the sky as seen from a fixed location on Earth at the same mean solar time, as that position varies over the course of a year. The diagram will resemble a figure eight. Globes of Earth often display an analemma as a two-dimensional figure of equation of time vs. declination of the Sun.

A gnomon is the part of a sundial that casts a shadow. The term is used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields.
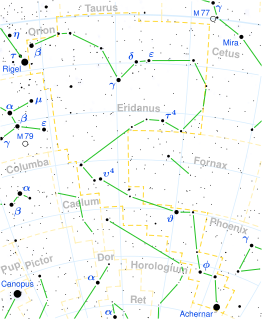
Achernar is the brightest star in the constellation of Eridanus, and the ninth-brightest in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Eridani, which is Latinized from α Eridani and abbreviated Alpha Eri or α Eri. The name Achernar applies to the primary component of a binary system. The two components are designated Alpha Eridani A and B, with the latter known informally as Achernar B. As determined by the Hipparcos astrometry satellite, this system is located at a distance of approximately 139 light-years from the Sun.
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49° north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.

Navicula is a genus of boat-shaped diatom algae, comprising over 1,200 species. Navicula is Latin for "small ship", and also a term in English for a boat-shaped incense-holder.
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. Muslim scholars made advances to the map-making traditions of earlier cultures, particularly the Hellenistic geographers Ptolemy and Marinus of Tyre, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Islamic geography had three major fields: exploration and navigation, physical geography, and cartography and mathematical geography. Islamic geography reached its apex with Muhammad al-Idrisi in the 12th century.

A quadrant is an instrument used to measure angles up to 90°. Different versions of this instrument could be used to calculate various readings, such as longitude, latitude, and time of day. It was originally proposed by Ptolemy as a better kind of astrolabe. Several different variations of the instrument were later produced by medieval Muslim astronomers. Mural quadrants were important astronomical instruments in 18th-century European observatories, establishing a use for positional astronomy.

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of the vertical due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape.

Astronomical rings, also known as Gemma's rings, are an early astronomical instrument. The instrument consists of three rings, representing the celestial equator, declination, and the meridian.

A sundial is a device that indicates time by using a light spot or shadow cast by the position of the Sun on a reference scale. As the Earth turns on its polar axis, the sun appears to cross the sky from east to west, rising at sun-rise from beneath the horizon to a zenith at mid-day and falling again behind the horizon at sunset. Both the azimuth (direction) and the altitude (height) can be used to create time measuring devices. Sundials have been invented independently in every major culture and became more accurate and sophisticated as the culture developed.

The Whitehurst & Son sundial was produced in Derby in 1812 by the nephew of John Whitehurst. It is a fine example of a precision sundial telling local apparent time with a scale to convert this to local mean time, and is accurate to the nearest minute. The sundial is now housed in the Derby Museum and Art Gallery.
2 Persei is a binary star system in the northern constellation Perseus, located around 500 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude is 5.70. The system is moving further away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 11 km/s.

Giovanni Francesco Zarbula was a mural painter and sundial designer from Piedmont Italy who created a hundred or more vertical and vertical declining sundials in the French and Italian Alpes between 1830 and 1881. He worked exclusively in Savoy, in Piémont, the Valley of the Ubaye, le Queyras and around Briançon.
Dialing scales are used to lay out the face of a sundial geometrically. They were proposed by Samuel Foster in 1638, and produced by George Serle and Anthony Thompson in 1658 on a ruler. There are two scales: the latitude scale and the hour scale. They can be used to draw all gnomonic dials – and reverse engineer existing dials to discover their original intended location.
A schema for horizontal dials is a set of instructions used to construct horizontal sundials using compass and straightedge construction techniques, which were widely used in Europe from the late fifteenth century to the late nineteenth century. The common horizontal sundial is a geometric projection of an equatorial sundial onto a horizontal plane.

Vertical declining dials are sundials that indicate local apparent time. Vertical south dials are a special case: as are vertical north, vertical east and vertical west dials. The word declining means that the wall is offset from one of these 4 cardinal points. There are dials that are not vertical, and these are called reclining dials.

A Butterfield dial is a portable horizontal sundial designed to be folded flat and used in latitudes between 35° and 60°. It was named after the English gnomonist Michael Butterfield, who was active in Paris around 1690.
The Columbia 22 is an American trailerable sailboat that was designed by William Crealock and first built in 1966.














