
Hellas Planitia is a plain located within the huge, roughly circular impact basin Hellas located in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. Hellas is the third- or fourth-largest known impact crater in the Solar System. The basin floor is about 7,152 m (23,465 ft) deep, 3,000 m (9,800 ft) deeper than the Moon's South Pole-Aitken basin, and extends about 2,300 km (1,400 mi) east to west. It is centered at 42.4°S 70.5°E. It features the lowest point on Mars, serves as a known source of global dust storms, and may have contained lakes and glaciers. Hellas Planitia spans the boundary between the Hellas quadrangle and the Noachis quadrangle.

Argyre Planitia is a plain located within the impact basin Argyre in the southern highlands of Mars. Its name comes from a map produced by Giovanni Schiaparelli in 1877; it refers to Argyre, a mythical island of silver in Greek mythology.

Chryse Planitia is a smooth circular plain in the northern equatorial region of Mars close to the Tharsis region to the west, centered at 28.4°N 319.7°E. Chryse Planitia lies partially in the Lunae Palus quadrangle, partially in the Oxia Palus quadrangle, partially in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle. It is 1600 km or 994 mi in diameter and with a floor 2.5 km below the average planetary surface altitude, and has been suggested to be an ancient buried impact basin, though this is contested. It has several features in common with lunar maria, such as wrinkle ridges. The density of impact craters in the 100 to 2,000 metres range is close to half the average for lunar maria.

Uzboi Vallis is a valley lying situated within the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region on Mars. It is named after the Uzboy dry channel, now in Turkmenistan, which repeatedly served as the main channel of the Amu Darya river. The valley begins on the northern rim of the Argyre basin, and cuts through several craters, before ending at Holden crater.
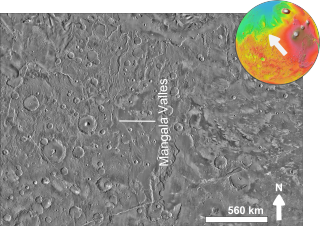
The Mangala Valles are a complex system of criss-crossing channels on Mars, located in the Tharsis region and in the Memnonia quadrangle. They originated in the Hesperian and Amazonian epochs. They are thought to be an outflow channel system, carved by catastrophic floods, and the release of vast quantities of water across the Martian surface. This flooding was probably initiated by tectonic stretching and the formation of a graben, Mangala Fossa, at the channels' head, perhaps breaching a pressurized aquifer trapped beneath a thick "cryosphere" beneath the surface. The Mangala Valles contain several basins; after they filled, the overflow went through a series of spillways. One source of waters for the system was the Memonia Fossae, but water also probably came from a large basin centered at 40 degrees S.

Elysium, located in the Elysium and Cebrenia quadrangles, is the second largest volcanic region on Mars, after Tharsis. The region includes the volcanoes Hecates Tholus, Elysium Mons and Albor Tholus. The province is centered roughly on Elysium Mons at 24.7°N 150°E. Elysium Planitia is a broad plain to the south of Elysium, centered at 3.0°N 154.7°E. Another large volcano, Apollinaris Mons, lies south of Elysium Planitia and is not part of the province. Besides having large volcanoes, Elysium has several areas with long trenches, called fossa or fossae (plural) on Mars. They include the Cerberus Fossae, Elysium Fossae, Galaxias Fossae, Hephaestus Fossae, Hyblaeus Fossae, Stygis Fossae and Zephyrus Fossae.
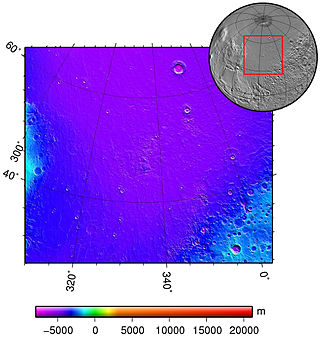
Acidalia Planitia is a plain on Mars, between the Tharsis volcanic province and Arabia Terra to the north of Valles Marineris, centered at 49.8°N 339.3°E. Most of this region is found in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle, but a small part is in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle. The plain contains the famous Cydonia region at the contact with the heavily cratered highland terrain.

The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The quadrangle is located in the northeastern portion of Mars' western hemisphere and covers 300° to 360° east longitude and 30° to 65° north latitude. The quadrangle uses a Lambert conformal conic projection at a nominal scale of 1:5,000,000 (1:5M). The Mare Acidalium quadrangle is also referred to as MC-4.

The Iapygia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Iapygia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-21. It was named after the heel of the boot of Italy. That name was given by the Greeks It is part of a region of Italy named Apulia. The name Iapygia was approved in 1958.

The Coprates quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Coprates quadrangle is also referred to as MC-18. The Coprates quadrangle contains parts of many of the old classical regions of Mars: Sinai Planum, Solis Planum, Thaumasia Planum, Lunae Planum, Noachis Terra, and Xanthe Terra.

The Hellas quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Hellas quadrangle is also referred to as MC-28 . The Hellas quadrangle covers the area from 240° to 300° west longitude and 30° to 65° south latitude on the planet Mars. Within the Hellas quadrangle lies the classic features Hellas Planitia and Promethei Terra. Many interesting and mysterious features have been discovered in the Hellas quadrangle, including the giant river valleys Dao Vallis, Niger Vallis, Harmakhis, and Reull Vallis—all of which may have contributed water to a lake in the Hellas basin in the distant past. Many places in the Hellas quadrangle show signs of ice in the ground, especially places with glacier-like flow features.

Nirgal Vallis is a long river channel bordering the Coprates quadrangle and Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle of Mars at 28.4° south latitude and 42° west longitude. It is 610 km long and is named after Nergal, the Babylonian god of war and counterpart to the Roman god of war Mars. Nirgal Vallis had a discharge of 4800 cubic meters/second. The western half of Nirgal Valles is a branched system, but the eastern half is a tightly sinuous, deeply entrenched valley. Nirgal Valles ends at Uzboi Vallis. Tributaries are very short and end in steep-walled valley heads, often called "amphitheater-headed valleys." The shape of these valley heads is like cirques on the Earth.
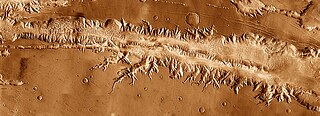
Ius Chasma is a large canyon in the Coprates quadrangle of Mars at 7° south latitude and 85.8° west longitude. It is about 938 km long and was named after a classical albedo feature name.
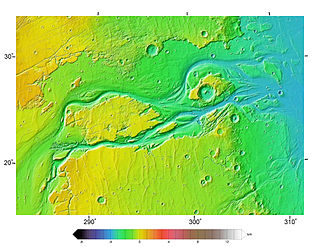
Outflow channels are extremely long, wide swathes of scoured ground on Mars. They extend many hundreds of kilometers in length and are typically greater than one kilometer in width. They are thought to have been carved by huge outburst floods.

Naktong Vallis is an ancient river valley in the Arabia quadrangle of Mars, located at 5.3 degrees north latitude and 327.1 degrees west longitude. It is 670 km long and was named after the Nakdong River in Korea.

Enipeus Vallis is a valley in the northern hemisphere of the planet Mars. It is centered at lat. 37°N, long. 267°E in the Arcadia quadrangle (MC-3) between the large volcano Alba Mons and the Tempe Terra plateau. The valley follows a gently sinuous, north–south path for a distance of about 357 km (222 mi). It is likely an ancient watercourse that formed during the early Hesperian period, around 3.7 billion years ago.

The Paraná Valles are a set of channels in a valley in the Margaritifer Sinus quadrangle (MC-19) region of Mars, located at approximately 23.1° South and 10.2° West. They are 350 kilometres (220 mi) long and were named after an ancient and modern name for a South American river. A low area between the Paraná Valles and Loire Valles is believed to have once held a lake.

Ausonia Mensa is a mensa in the Hellas quadrangle of Mars, located at 30.3° S and 262.3° W. It is 103 km (64 mi) across and was named after an albedo feature name. The term "mensa" is used for a flat-topped prominence with cliff-like edges. Ausonia Mensa has many small channels. Some features look like alluvial fans. These channels add to the mass of evidence that water once flowed on Mars. Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9 orbiter.
Eridania Planitia is a plain located in the southern highlands of Mars. It borders the Hellas basin to the west, Promethei Terra to the south, and the massive shield volcano Hesperia Planum to the north. The name Eridania Planitia was approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 22 September 2010; it is named after the closest classical albedo feature.

In summer 1965, the first close-up images from Mars showed a cratered desert with no signs of water. However, over the decades, as more parts of the planet were imaged with better cameras on more sophisticated satellites, Mars showed evidence of past river valleys, lakes and present ice in glaciers and in the ground. It was discovered that the climate of Mars displays huge changes over geologic time because its axis is not stabilized by a large moon, as Earth's is. Also, some researchers maintain that surface liquid water could have existed for periods of time due to geothermal effects, chemical composition, or asteroid impacts. This article describes some of the places that could have held large lakes.


















