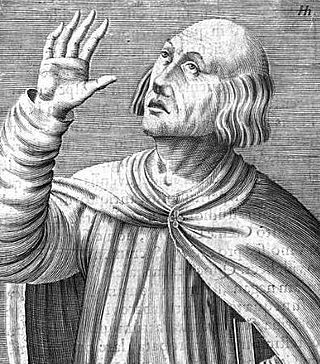
Berengar of Tours, in Latin Berengarius Turonensis, was an 11th-century French Christian theologian and archdeacon of Angers, a scholar whose leadership of the cathedral school at Chartres set an example of intellectual inquiry through the revived tools of dialectic that was soon followed at cathedral schools of Laon and Paris. Berengar of Tours was distinguished from mainline Catholic theology by two views: his assertion of the supremacy of Scripture and his denial of transubstantiation.

Neath Port Talbot is a county borough in the south-west of Wales. Its principal towns are Neath, Port Talbot, Briton Ferry and Pontardawe. The county borough borders Bridgend County Borough and Rhondda Cynon Taf to the east, Powys and Carmarthenshire to the north; and Swansea to the west.

The Church of God , also called the Church of God Ministries, is an international holiness Christian denomination with roots in Wesleyan-Arminianism and also in the restorationist traditions. The organization grew out of the evangelistic efforts of several Holiness evangelists in Indiana and Michigan in the early 1880s, most notably Daniel Sidney Warner.

The Evangelical Presbyterian Church (EPC) is an American church body holding to presbyterian governance and Reformed theology. It is a conservative Calvinist denomination. It is most distinctive for its approach to the way it balances certain liberties across congregations on "non-essential" doctrines, such as egalitarianism /complementarianism in marriage or the ordination of women, alongside an affirmation of core "essential" doctrinal standards.

Bernard Joseph Francis Lonergan was a Canadian Jesuit priest, philosopher, and theologian, regarded by many as one of the most important thinkers of the 20th century.

The Christian Apologetics and Research Ministry (CARM) is a nonprofit, nondenominational Protestant apologetics ministry with an internet and radio outreach. It is involved in evangelism, including full-time support for several foreign missionaries. It is based in the United States and was founded in 1995. Matthew Slick currently serves as president of the ministry. The ministry is registered as a 501(c)(3) organization and is headquartered in Nampa, Idaho.

John Fullerton MacArthur Jr. is an American pastor and author who hosts the national Christian radio and television program Grace to You. He has been the pastor of Grace Community Church, a non-denominational church in Sun Valley, California since February 9, 1969. He is currently the chancellor emeritus of The Master's University in Santa Clarita and The Master's Seminary.

Wolfhart Pannenberg was a German Lutheran theologian. He made a number of significant contributions to modern theology, including his concept of history as a form of revelation centered on the resurrection of Christ, which has been widely debated in both Protestant and Catholic theology, as well as by non-Christian thinkers.

Protestant denominations arrived in the Philippines in 1898, after the United States took control of the Philippines from Spain, first with United States Army chaplains and then within months civilian missionaries.
Barry W. Lynn is an American activist who was the executive director of Americans United for Separation of Church and State from 1992 to November 2017, when he retired. He was ordained as a minister in the United Church of Christ and a prominent leader of the religious left in the United States. Lynn was formerly a member of the District of Columbia Bar Association. He has been known as a strong advocate of separation of church and state.

Talbot School of Theology is an evangelical Christian theological seminary located near Los Angeles. Talbot is one of the nine schools of Biola University, located in La Mirada, California. Talbot is nondenominational and known for its conservative theological positions, particularly its historical adherence to biblical inerrancy.
Free will in theology is an important part of the debate on free will in general. Religions vary greatly in their response to the standard argument against free will and thus might appeal to any number of responses to the paradox of free will, the claim that omniscience and free will are incompatible.
Leith Anderson is an American evangelical Christian leader, author, and retired pastor. Anderson served as senior pastor of Wooddale Church in Eden Prairie, Minnesota from 1977 to 2011. He is pastor emeritus of Wooddale Church and president emeritus of the National Association of Evangelicals.
R. Kent Hughes is the former senior pastor of College Church in Wheaton, Illinois, United States. Hughes is the author of numerous books, including the best-selling Disciplines of a Godly Man. He is also editor and contributor for the projected 50-volume Preaching the Word series, including Mark: Jesus, Servant and Savior, which received the ECPA Gold Medallion Book Award for best commentary in 1990. Hughes served as senior pastor of College Church for 27 years and retired at the end of 2006. He moved to Wheaton from California, where he pastored two churches. He holds a BA from Whittier College, an M.Div. from Talbot School of Theology, a D.Min. from Trinity Evangelical Divinity School and a DD from Biola University. He lives in Pennsylvania state with his wife, Barbara, and he is the father of 4, grandfather of 26 and great grandfather of 14.
Free grace theology is a Christian soteriological view which holds that the only condition of salvation is faith, excluding good works and perseverance, holding to eternal security. Free grace advocates believe that good works are not necessary to merit, to maintain or to prove salvation, but rather are part of discipleship and the basis for receiving eternal rewards. This soteriological view distinguishes between salvation and discipleship – the call to believe in Christ as Savior and to receive the gift of eternal life, and the call to follow Christ and become an obedient disciple, respectively. Free grace theologians emphasize the absolute freeness of salvation and the possibility of full assurance that is not grounded upon personal performance. Thus, Free Grace theology allows for the salvation of an individual despite moral failings, although the disobedient Christian will face divine discipline. Norman Geisler has divided this view into a moderate form and a more radical form. The moderate form being associated with Charles Ryrie and the strong form with Zane Hodges.

Ethelbert Talbot was the fifteenth presiding bishop of the Episcopal Church. He is credited with inspiring Pierre de Coubertin to coin the phrase, "The important thing in the Olympic Games is not so much the winning but taking part, for the essential thing in life is not conquering but fighting well."
Robert Lloyd Saucy was an American biblical scholar and professor of systematic theology.

John Nicol Farquhar was a Scottish educational missionary to Calcutta, and an Orientalist. He is one of the pioneers who popularised the Fulfilment theology in India that Christ is the crown of Hinduism, though, Fulfilment thesis in Bengal was built on foundation originally laid in Madras by William Miller.

Joseph Estlin Carpenter was an English Unitarian minister, the principal of Manchester College, Oxford. He was an expert in Sanskrit and a pioneer in the study of comparative religion.

Mary Shawn Copeland, known professionally as M. Shawn Copeland, is a retired American womanist and Black Catholic theologian, and a former religious sister. She is professor emerita of systematic theology at Boston College and is known for her work in theological anthropology, political theology, and African American Catholicism.













