
Java applets are small applications written in the Java programming language, or another programming language that compiles to Java bytecode, and delivered to users in the form of Java bytecode.

Internet Explorer is a retired series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were used in the Windows line of operating systems. While IE has been discontinued on most Windows editions, it remains supported on certain editions of Windows, such as Windows 10 LTSB/LTSC. Starting in 1995, it was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year. Later versions were available as free downloads or in-service packs and included in the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) service releases of Windows 95 and later versions of Windows. Microsoft spent over US$100 million per year on Internet Explorer in the late 1990s, with over 1,000 people involved in the project by 1999. New feature development for the browser was discontinued in 2016 and ended support on June 15, 2022 for Windows 10 Semi-Annual Channel (SAC), in favor of its successor, Microsoft Edge.
Netscape Communications Corporation was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California, and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was once dominant but lost to Internet Explorer and other competitors in the first browser war, with its market share falling from more than 90 percent in the mid-1990s to less than one percent in 2006. An early Netscape employee, Brendan Eich, created the JavaScript programming language, the most widely used language for client-side scripting of web pages. A founding engineer of Netscape, Lou Montulli, created HTTP cookies. The company also developed SSL which was used for securing online communications before its successor TLS took over.

Sun Microsystems, Inc. was an American technology company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, the Network File System (NFS), and SPARC microprocessors. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. Notable Sun acquisitions include Cray Business Systems Division, Storagetek, and Innotek GmbH, creators of VirtualBox. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California, on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center.

The World Wide Web is an information system that enables content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond IT specialists and hobbyists. It allows documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to specific rules of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource. It improves privacy, security, and possibly performance in the process.

ActiveX is a deprecated software framework created by Microsoft that adapts its earlier Component Object Model (COM) and Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) technologies for content downloaded from a network, particularly from the World Wide Web. Microsoft introduced ActiveX in 1996. In principle, ActiveX is not dependent on Microsoft Windows operating systems, but in practice, most ActiveX controls only run on Windows. Most also require the client to be running on an x86-based computer because ActiveX controls contain compiled code.

Squid is a caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy. It has a wide variety of uses, including speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests, caching World Wide Web (WWW), Domain Name System (DNS), and other network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources, and aiding security by filtering traffic. Although used for mainly HTTP and File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Squid includes limited support for several other protocols including Internet Gopher, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), Transport Layer Security (TLS), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). Squid does not support the SOCKS protocol, unlike Privoxy, with which Squid can be used in order to provide SOCKS support.
Link prefetching allows web browsers to pre-load resources. This speeds up both the loading and rendering of web pages. Prefetching was first introduced in HTML5.
A web accelerator is a proxy server that reduces website access time. They can be a self-contained hardware appliance or installable software.
Google Web Accelerator was a web accelerator produced by Google. It used client software installed on the user's computer, as well as data caching on Google's servers, to speed up page load times by means of data compression, prefetching of content, and sharing cached data between users. The beta, released on May 4, 2005, works with Mozilla Firefox 1.0+ and Internet Explorer 5.5+ on Windows 2000 SP3+, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista and Windows 7 machines. It was discontinued in October 2008.
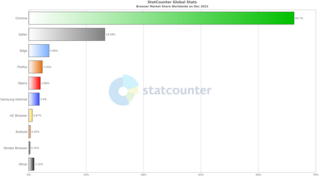
The usage share of web browsers is the portion, often expressed as a percentage, of visitors to a group of web sites that use a particular web browser.
In computing, Java Web Start is a deprecated framework developed by Sun Microsystems that allows users to start application software for the Java Platform directly from the Internet using a web browser. The technology enables seamless version updating for globally distributed applications and greater control of memory allocation to the Java virtual machine.

HTTP cookies are small blocks of data created by a web server while a user is browsing a website and placed on the user's computer or other device by the user's web browser. Cookies are placed on the device used to access a website, and more than one cookie may be placed on a user's device during a session.
A web desktop or webtop is a desktop environment embedded in a web browser or similar client application. A webtop integrates web applications, web services, client–server applications, application servers, and applications on the local client into a desktop environment using the desktop metaphor. Web desktops provide an environment similar to that of Windows, Mac, or a graphical user interface on Unix and Linux systems. It is a virtual desktop running in a web browser. In a webtop the applications, data, files, configuration, settings, and access privileges reside remotely over the network. Much of the computing takes place remotely. The browser is primarily used for display and input purposes.
The Microsoft Java Virtual Machine (MSJVM) is a discontinued proprietary Java virtual machine from Microsoft. It was first made available for Internet Explorer 3 so that users could run Java applets when browsing on the World Wide Web. It was the fastest Windows-based implementation of a Java virtual machine for the first two years after its release. Sun Microsystems, the creator of Java, sued Microsoft in October 1997 for incompletely implementing the Java 1.1 standard. It was also named in the United States v. Microsoft Corp. antitrust civil actions, as an implementation of Microsoft's "Embrace, extend and extinguish" strategy. In 2001, Microsoft settled the lawsuit with Sun and discontinued its Java implementation.
Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995.

Internet Explorer 11 (IE11) is the eleventh and final version of the Internet Explorer web browser. It was initially included in the release of Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 on October 17, 2013, and was later released for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 on November 7, 2013. It is the successor to Internet Explorer 10, released the previous year, and was the original, default browser in Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, before Microsoft Edge was introduced. Internet Explorer 11 was also included in the release of Windows 10 on July 29, 2015, as well as in Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019. On April 16, 2019, Internet Explorer 11 was made available to Windows Server 2012 and Windows Embedded 8 Standard, the only still supported edition of Windows 8 as the final expansion of Internet Explorer 11 availability. Internet Explorer 11, like its predecessor, is not available for Windows 8, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and earlier versions of Windows and Windows Server.
Kiva Software was the leading provider and pioneer of internet application server software. Kiva Software released the industry's first application server in January 1996, offering companies a robust platform on which to develop and deploy transaction-oriented business applications on the Web. Kiva's customers included Bank of America, E-Trade, Travelocity, Internet Shopping Network, Hong Kong Telecom and Pacific Bell Internet.










