
Dresden is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area, and the third most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants.

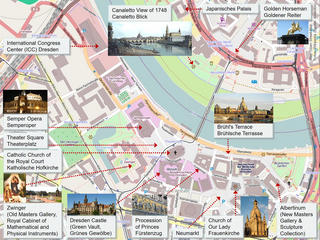
The Zwinger is a palatial complex with gardens in Dresden, Germany. Designed by architect Matthäus Daniel Pöppelmann, it is one of the most important buildings of the Baroque period in Germany. Along with the Frauenkirche, the Zwinger is the most famous architectural monument of Dresden.

The bombing of Dresden was a joint British and American aerial bombing attack on the city of Dresden, the capital of the German state of Saxony, during World War II. In four raids between 13 and 15 February 1945, 772 heavy bombers of the Royal Air Force (RAF) and 527 of the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF) dropped more than 3,900 tons of high-explosive bombs and incendiary devices on the city. The bombing and the resulting firestorm destroyed more than 1,600 acres (6.5 km2) of the city centre. Up to 25,000 people were killed. Three more USAAF air raids followed, two occurring on 2 March aimed at the city's railway marshalling yard and one smaller raid on 17 April aimed at industrial areas.

The Frauenkirche is a Lutheran church in Dresden, the capital of the German state of Saxony. Destroyed during the Allied firebombing of Dresden towards the end of World War II, the church was reconstructed between 1994 and 2005.

A firestorm is a conflagration which attains such intensity that it creates and sustains its own wind system. It is most commonly a natural phenomenon, created during some of the largest bushfires and wildfires. Although the term has been used to describe certain large fires, the phenomenon's determining characteristic is a fire with its own storm-force winds from every point of the compass towards the storm's center, where the air is heated and then ascends.
The year 1945 in architecture involved some significant events.

The Altstadt is a quarter of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. It is part of the Ortsbezirk Innenstadt I and is located on the northern Main river bank. It is completely surrounded by the Innenstadt district, Frankfurt's present-day city centre. On the opposite side of the Main is the district of Sachsenhausen.

Brühl's Terrace is a historic architectural ensemble in Dresden, Germany. Nicknamed "The Balcony of Europe", the terrace stretches high above the bank of the river Elbe, and is located north of the recently rebuilt Neumarkt Square and the Frauenkirche.

The Potsdam City Palace is a building in Potsdam, Germany, located on the Old Market Square, next to the St. Nicholas' Church (Nikolaikirche). It was the second official residence of the margraves and electors of Brandenburg, later kings in Prussia, kings of Prussia and German emperors.

Altstadt is the German language word for "old town", and generally refers to the historical town or city centre within the old town or city wall, in contrast to younger suburbs outside. Neustadt, the logical opposite of Altstadt, mostly stands for a part of the "Altstadt" in modern sense, sometimes only a few years younger than the oldest part, e. g. a late medieval enlargement.

The New Synagogue is a Jewish congregation and synagogue, located at Hasenberg 1, in the old town of Dresden, Germany. The edifice was completed in 2001 and designed by architects Rena Wandel-Hoefer and Wolfgang Lorch. It was built on the same location as the Semper Synagogue (1839–1840) designed by Gottfried Semper, which was destroyed in 1938, during the Kristallnacht.

The architecture of Germany has a long, rich and diverse history. Every major European style from Roman to Postmodern is represented, including renowned examples of Carolingian, Romanesque, Gothic, Renaissance, Baroque, Classical, Modern and International Style architecture.
Dresden is a cultural centre in Germany which has influenced the development of European culture. "It is [...] outstanding as a cultural landscape, an ensemble that integrates the celebrated Baroque setting and suburban garden city into an artistic whole within the river valley, and as an example of land use, representing an exceptional development of a major Central-European city."

The Wackerbarth Palace, also known as the Dresdener Ritterakademie, was a palace in Dresden, Germany, built between 1723 and 1729, under the supervision of architect Johann Christoph Knöffel (1686-1752). It was one of the several Baroque palaces in Dresden which were destroyed during the allied bombing raids on February 13, 1945. It was named for Count August Christoph von Wackerbarth (1662-1734), a Saxon minister and Field Marshal. The palace was situated in the city, north of the Elbe river, at the former Beaumontplatz near Neustädter Markt.

Reconstruction in architectural conservation is the returning of a place to a known earlier state by the introduction of new materials. It is related to the architectural concepts of restoration and preservation, wherein the most extensive form of reconstruction is creating a replica of a destroyed building.

The Kulturpalast Dresden is a modernist building built by Wolfgang Hänsch during the era of the German Democratic Republic. It was the largest multi-purpose hall in Dresden when it opened in 1969, and was used for concerts, dances, conferences and other events. The building underwent several years of reconstruction beginning in 2012 and opened with a new concert hall in April 2017.

The Dresden Historical Neumarkt Society e. V. (GHND) is an association founded in 1999, which is committed to reconstructing the historic city centre of the German city of Dresden as much as possible.

The Dreikönigskirche is a Lutheran church located in the Innere Neustadt of Dresden, Germany. It is the centre of a parish, and a community venue called Haus der Kirche. The church is a listed cultural monument of Dresden.
The Loschwitz Church is a baroque church in the Loschwitz district of Dresden. It was the first church built by the architect of the Dresden Frauenkirche, George Bähr. The churchyard, which was used as a cemetery until 1907, is one of the few 18th-century churchyards in Saxony that is still in its original state and is the smallest cemetery in the city at about 400 square meters. The Loschwitz church and cemetery are under monument protection.

The Frauenkirchhof was the oldest known cemetery in Dresden. It had existed since the first building of the Frauenkirche, which is dated to the 10th or 11th century. Until the 16th century, the Frauenkirchhof was the main burial place for the inhabitants of Dresden, who often buried their dead in the cemetery for several generations due to large family graves. The richly decorated and painted Schwibbogengräber were of particular art-historical value. Due to new buildings at the Frauenkirche, the cemetery was initially reduced in size several times and finally secularized by 1727 despite protests from the population in the course of the construction of the new Frauenkirche built by George Bähr. Epitaphs and gravestones have been preserved from the cemetery. Archaeological excavations since the 1980s have unearthed grave goods, including several funeral crowns.



















