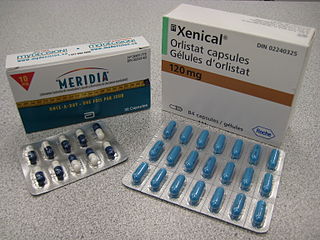
Anti-obesity medication or weight loss medications are pharmacological agents that reduce or control weight. These medications alter one of the fundamental processes of the human body, weight regulation, by altering either appetite, or absorption of calories. The main treatment modalities for overweight and obese individuals remain dieting and physical exercise.

Idebenone is a drug that was initially developed by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and other cognitive defects. This has been met with limited success. The Swiss company Santhera Pharmaceuticals has started to investigate it for the treatment of neuromuscular diseases. In 2010, early clinical trials for the treatment of Friedreich's ataxia and Duchenne muscular dystrophy have been completed. As of December 2013 the drug is not approved for these indications in North America or Europe. It is approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for use in Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) and was designated an orphan drug in 2007.

Sunitinib, sold under the brand name Sutent, is a medication used to treat cancer. It is a small-molecule, multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that was approved by the FDA for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) on January 26, 2006. Sunitinib was the first cancer drug simultaneously approved for two different indications.

Latrepirdine, is an antihistamine drug which has been used clinically in Russia since 1983.

Laquinimod is an experimental immunomodulator developed by Active Biotech and Teva. It is being investigated as an oral treatment for multiple sclerosis (MS).

Tesofensine (NS2330) is a serotonin–noradrenaline–dopamine reuptake inhibitor from the phenyltropane family of drugs, which is being developed for the treatment of obesity. Tesofensine was originally developed by a Danish biotechnology company, NeuroSearch, who transferred the rights to Saniona in 2014.
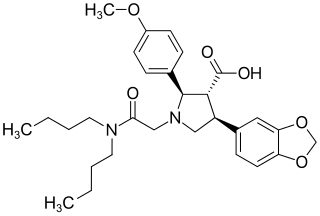
Atrasentan is an experimental drug that is being studied for the treatment of various types of cancer, including non-small cell lung cancer. It is also being investigated as a therapy for diabetic kidney disease.
Ramucirumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (IgG1) developed for the treatment of solid tumors. This drug was developed by ImClone Systems Inc. It was isolated from a native phage display library from Dyax.
Polycap is a specific five-in-one fixed dose combination polypill created by Cadila Pharmaceuticals Limited of Ahmedabad, India that combines moderate levels of five different medications in a single, one-a-day pill aimed at reducing/preventing heart attacks and strokes.

Preladenant was a drug that was developed by Schering-Plough which acted as a potent and selective antagonist at the adenosine A2A receptor. It was being researched as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease. Positive results were reported in Phase II clinical trials in humans, but it did not prove itself to be more effective than a placebo during Phase III trials, and so was discontinued in May 2013.

NS-2359 (GSK-372,475) is a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor. It was under development by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) as an antidepressant, but was discontinued in 2009 when phase II clinical trials showed the drug was not effective and not well tolerated. The results did not support further effort by the company. NS-2359 was also in clinical trials for the treatment of ADHD, phase II having been completed in 2007. A phase I clinical trial exploring the effect of NS-2359 on cocaine-dependent individuals was completed in 2002.
Pridopidine is an orally administrated small molecule investigational drug. Pridopidine is a selective and potent Sigma-1 Receptor (S1R) agonist 1,2 in late-stage clinical development for Huntington’s disease (HD) and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) by Prilenia Therapeutics.

Losmapimod (GW856553X) is an investigational drug being developed by Fulcrum Therapeutics for the treatment of facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) and COVID-19. It selectively inhibits enzymes p38α/β mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which are modulators of DUX4 expression and mediators of inflammation.

PBT2 is a safe-for-human-use Zinc ionophore and an experimental drug candidate. It is a second-generation 8-hydroxyquinoline analog intended to be a successor to clioquinol and a potential treatment of Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's disease.

Motesanib is an experimental drug candidate originally developed by Amgen but later investigated by the Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. It is an orally administered small molecule belonging to angiokinase inhibitor class which acts as an antagonist of VEGF receptors, platelet-derived growth factor receptors, and stem cell factor receptors. It is used as the phosphate salt motesanib diphosphate. After clinical trials in thyroid cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, gastrointestinal stromal cancer, colorectal cancer, and breast cancer, the drug was not found to show sufficient efficacy for further development, and development was abandoned by Takeda.
The European Huntington's Disease Network is a Europe-wide network of professionals and people affected by Huntington's disease, who collaborate to organise and perform research into the condition, and improve the care of HD-affected individuals.
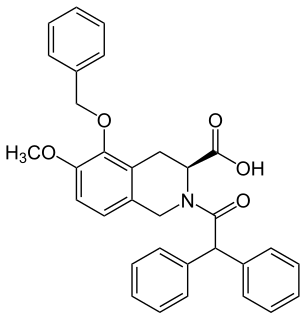
EMA401 is a drug under development for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain. Trials were discontinued in 2015, with new trials scheduled to begin March, 2018. It was initially established as a potential drug option for patients suffering pain caused by postherpetic neuralgia. It may also be useful for treating various types of chronic neuropathic pain EMA401 has shown efficacy in preclinical models of shingles, diabetes, osteoarthritis, HIV and chemotherapy. EMA401 is a competitive antagonist of angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R) being developed by the Australian biotechnology company Spinifex Pharmaceuticals. EMA401 target angiotensin II type 2 receptors, which may have importance for painful sensitisation.

Durvalumab is an FDA-approved immunotherapy for cancer, developed by Medimmune/AstraZeneca. It is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1κ) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) with the PD-1 (CD279).
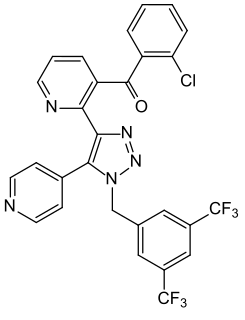
Tradipitant is an experimental drug that is a neurokinin 1 antagonist. It works by blocking substance P, a small signaling molecule. Originally, this compound was owned by Eli Lilly and named LY686017. VLY-686 was purchased by Vanda Pharmaceuticals from Eli Lilly and Company in 2012. Vanda Pharmaceuticals is a U.S. pharmaceutical company that as of November 2015 only has three drugs in their product pipeline: tasimelteon, VLY-686, and iloperidone.
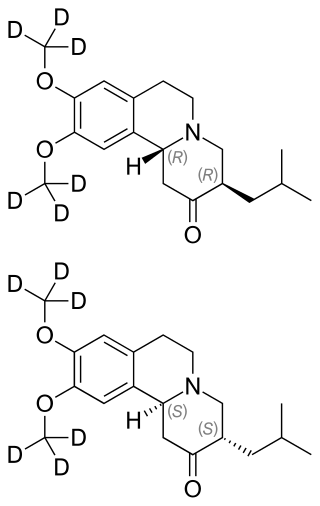
Deutetrabenazine is a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitor which is used for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and tardive dyskinesia.















