
Lambert–Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by muscle weakness of the limbs. It is also known as myasthenic syndrome, Eaton–Lambert syndrome, and when related to cancer, carcinomatous myopathy.

Neurology is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system, using various techniques of neurotherapy.

Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome usually has no known cause, but there are environmental and medical risk factors associated with the condition. CTS can affect both wrists.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists.

Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue that supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the first steps of the day or following a period of rest. Pain is also frequently brought on by bending the foot and toes up towards the shin. The pain typically comes on gradually, and it affects both feet in about one-third of cases.

Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In computer science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction.

Piriformis syndrome is a condition which is believed to result from nerve compression at the sciatic nerve by the piriformis muscle. It is a specific case of deep gluteal syndrome.

Neuropathology is the study of disease of nervous system tissue, usually in the form of either small surgical biopsies or whole-body autopsies. Neuropathologists usually work in a department of anatomic pathology, but work closely with the clinical disciplines of neurology, and neurosurgery, which often depend on neuropathology for a diagnosis. Neuropathology also relates to forensic pathology because brain disease or brain injury can be related to cause of death. Neuropathology should not be confused with neuropathy, which refers to disorders of the nerves themselves rather than the tissues. In neuropathology, the branches of the specializations of nervous system as well as the tissues come together into one field of study.

In neuroscience, nerve conduction velocity (CV) is the speed at which an electrochemical impulse propagates down a neural pathway. Conduction velocities are affected by a wide array of factors, which include age, sex, and various medical conditions. Studies allow for better diagnoses of various neuropathies, especially demyelinating diseases as these conditions result in reduced or non-existent conduction velocities. CV is an important aspect of nerve conduction studies.
Proximal diabetic neuropathy, also known as diabetic amyotrophy, is a complication of diabetes mellitus that affects the nerves that supply the thighs, hips, buttocks and/or lower legs. Proximal diabetic neuropathy is a type of diabetic neuropathy characterized by muscle wasting, weakness, pain, or changes in sensation/numbness of the leg. It is caused by damage to the nerves of the lumbosacral plexus.

The lateral pectoral nerve arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, and through it from the C5-7.

Fazio–Londe disease (FLD), also called progressive bulbar palsy of childhood, is a very rare inherited motor neuron disease of children and young adults and is characterized by progressive paralysis of muscles innervated by cranial nerves. FLD, along with Brown–Vialetto–Van Laere syndrome (BVVL), are the two forms of infantile progressive bulbar palsy, a type of progressive bulbar palsy in children.

Radiculopathy, also commonly referred to as pinched nerve, refers to a set of conditions in which one or more nerves are affected and do not work properly. Radiculopathy can result in pain, weakness, altered sensation (paresthesia) or difficulty controlling specific muscles. Pinched nerves arise when surrounding bone or tissue, such as cartilage, muscles or tendons, put pressure on the nerve and disrupt its function.
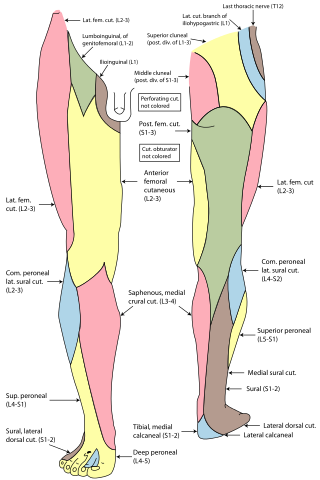
The superior cluneal nerves are pure sensory nerves that innervate the skin of the upper part of the buttocks. They are the terminal ends of the L1-L3 spinal nerve dorsal rami lateral branches. They are one of three different types of cluneal nerves. They travel inferiorly through multiple layers of muscles, then traverse osteofibrous tunnels between the thoracolumbar fascia and iliac crest.

Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a trapped nerve, though this may also refer to nerve root compression. Its symptoms include pain, tingling, numbness and muscle weakness. The symptoms affect just one particular part of the body, depending on which nerve is affected. The diagnosis is largely clinical and can be confirmed with diagnostic nerve blocks. Occasionally imaging and electrophysiology studies aid in the diagnosis. Timely diagnosis is important as untreated chronic nerve compression may cause permanent damage. A surgical nerve decompression can relieve pressure on the nerve but cannot always reverse the physiological changes that occurred before treatment. Nerve injury by a single episode of physical trauma is in one sense an acute compression neuropathy but is not usually included under this heading, as chronic compression takes a unique pathophysiological course.

Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in onset and improve with leaning forward. Severe symptoms may include loss of bladder control, loss of bowel control, or sexual dysfunction.
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli. The most widely used methods of recording spontaneous electrical activity are various forms of electrodiagnostic testing (electrography) such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG). Electrodiagnostic medicine is a medical subspecialty of neurology, clinical neurophysiology, cardiology, and physical medicine and rehabilitation. Electrodiagnostic physicians apply electrophysiologic techniques, including needle electromyography and nerve conduction studies to diagnose, evaluate, and treat people with impairments of the neurologic, neuromuscular, and/or muscular systems. The provision of a quality electrodiagnostic medical evaluation requires extensive scientific knowledge that includes anatomy and physiology of the peripheral nerves and muscles, the physics and biology of the electrical signals generated by muscle and nerve, the instrumentation used to process these signals, and techniques for clinical evaluation of diseases of the peripheral nerves and sensory pathways.
The American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine (AANEM) is a medical society for the medical subspecialty of neuromuscular and electrodiagnostic medicine based in the United States. Members are primarily neurologists and physiatrists—as well as allied health professionals and PhD researchers.
Femoral nerve dysfunction, also known as femoral neuropathy, is a rare type of peripheral nervous system disorder that arises from damage to nerves, specifically the femoral nerve. Given the location of the femoral nerve, indications of dysfunction are centered around the lack of mobility and sensation in lower parts of the legs. The causes of such neuropathy can stem from both direct and indirect injuries, pressures and diseases. Physical examinations are usually first carried out, depending on the high severity of the injury. In the cases of patients with hemorrhage, imaging techniques are used before any physical examination. Another diagnostic method, electrodiagnostic studies, are recognized as the gold standard that is used to confirm the injury of the femoral nerve. After diagnosis, different treatment methods are provided to the patients depending upon their symptoms in order to effectively target the underlying causes. Currently, femoral neuropathy is highly underdiagnosed and its precedent medical history is not well documented worldwide.

Iliocostal friction syndrome, also known as costoiliac impingement syndrome, is a condition in which the costal margin comes in contact with the iliac crest. The condition presents as low back pain which may radiate to other surrounding areas as a result of irritated nerve, tendon, and muscle structures. It may occur unilaterally due to conditions such as scoliosis, or bilaterally due to conditions such as osteoporosis and hyperkyphosis.














