Related Research Articles

Ab urbe condita, or anno urbis conditae, abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is an expression used in antiquity and by classical historians to refer to a given year in Ancient Rome. In reference to the traditional year of the foundation of Rome, the year 1 BC would be written AUC 753, whereas AD 1 would be AUC 754. The foundation of the Roman Empire in 27 BC would be AUC 727. The current year AD 2024 would be AUC 2777.

The Antigonid dynasty was a Macedonian Greek royal house which ruled the kingdom of Macedon during the Hellenistic period. Founded by Antigonus I Monophthalmus, a general and successor of Alexander the Great, the dynasty first came to power after the Battle of Salamis in 306 BC and ruled much of Hellenistic Greece from 294 until their defeat at the Battle of Pydna in 168 BC, after which Macedon came under the control of the Roman Republic.

Classics or classical studies is the study of classical antiquity. In the Western world, classics traditionally refers to the study of Classical Greek and Roman literature and their related original languages, Ancient Greek and Latin. Classics also includes Greco-Roman philosophy, history, archaeology, anthropology, art, mythology and society as secondary subjects.

Thucydides was an Athenian historian and general. His History of the Peloponnesian War recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of "scientific history" by those who accept his claims to have applied strict standards of impartiality and evidence-gathering and analysis of cause and effect, without reference to intervention by the gods, as outlined in his introduction to his work.

Ancient Greece was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity, that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period.

Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and ancient Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia.

Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in Northern Italy.

Colonies in antiquity were post-Iron Age city-states founded from a mother-city or metropolis rather than a territory-at-large. Bonds between a colony and its metropolis often remained close, and took specific forms during the period of classical antiquity. Generally, colonies founded by the ancient Phoenicians, Carthage, Rome, Alexander the Great and his successors remained tied to their metropolis, though Greek colonies of the Archaic and Classical eras were sovereign and self-governing from their inception. While Greek colonies were often founded to solve social unrest in the mother-city by expelling a part of the population, Hellenistic, Roman, Carthaginian, and Han Chinese colonies were used for trade, expansion and empire-building.
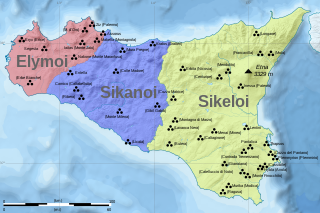
The Sicels were an Indo-European tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily, their namesake, during the Iron Age. They spoke the Siculian language. After the defeat of the Sicels at the Battle of Nomae in 450 BCE and the death of Sicel leader Ducetius in 440 BCE, the Sicel state broke down and the Sicel culture merged into Magna Graecia.

Roman commerce was a major sector of the Roman economy during the later generations of the Republic and throughout most of the imperial period. Fashions and trends in historiography and in popular culture have tended to neglect the economic basis of the empire in favor of the lingua franca of Latin and the exploits of the Roman legions. The language and the legions were supported by trade and were part of its backbone. The Romans were businessmen, and the longevity of their empire was caused by their commercial trade.

The Macedonians were an ancient tribe that lived on the alluvial plain around the rivers Haliacmon and lower Axios in the northeastern part of mainland Greece. Essentially an ancient Greek people, they gradually expanded from their homeland along the Haliacmon valley on the northern edge of the Greek world, absorbing or driving out neighbouring non-Greek tribes, primarily Thracian and Illyrian. They spoke Ancient Macedonian, which is usually classified by scholars as a dialect of Northwest Doric Greek, and occasionally as a distinct sister language of Greek or an Aeolic Greek dialect. However, the prestige language of the region during the Classical era was Attic Greek, replaced by Koine Greek during the Hellenistic era. Their religious beliefs mirrored those of other Greeks, following the main deities of the Greek pantheon, although the Macedonians continued Archaic burial practices that had ceased in other parts of Greece after the 6th century BC. Aside from the monarchy, the core of Macedonian society was its nobility. Similar to the aristocracy of neighboring Thessaly, their wealth was largely built on herding horses and cattle.
Richard John Alexander Talbert is a British-American contemporary ancient historian and classicist on the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, where he was William Rand Kenan, Jr., Professor of History and is currently Research Professor in charge of the Ancient World Mapping Center. Talbert is a leading scholar of ancient geography and ideas of space in the ancient Mediterranean world.

Classical demography refers to the study of human demography in the Classical period. It often focuses on the absolute number of people who were alive in civilizations around the Mediterranean Sea between the Bronze Age and the fall of the Western Roman Empire, but in recent decades historians have been more interested in trying to analyse demographic processes such as the birth and death rates or the sex ratio of ancient populations. The period was characterized by an explosion in population with the rise of the Greek and Roman civilizations followed by a steep decline caused by economic and social disruption, migrations, and a return to primarily subsistence agriculture. Demographic questions play an important role in determining the size and structure of the economy of Ancient Greece and the Roman economy.
Hellenic historiography involves efforts made by Greeks to track and record historical events. By the 5th century BC, it became an integral part of ancient Greek literature and held a prestigious place in later Roman historiography and Byzantine literature.

Epirus was an ancient Greek kingdom, and later republic, located in the geographical region of Epirus, in parts of north-western Greece and southern Albania. Home to the ancient Epirotes, the state was bordered by the Aetolian League to the south, Ancient Thessaly and Ancient Macedonia to the east, and Illyrian tribes to the north. The Greek king Pyrrhus is known to have made Epirus a powerful state in the Greek realm that was comparable to the likes of Ancient Macedonia and Ancient Rome. Pyrrhus' armies also attempted an assault against the state of Ancient Rome during their unsuccessful campaign in what is now modern-day Italy.

Walter Scheidel is an Austrian historian who teaches ancient history at Stanford University, California. Scheidel's main research interests are ancient social and economic history, pre-modern historical demography, and comparative and transdisciplinary approaches to world history.

Roman mythology is the body of myths of ancient Rome as represented in the literature and visual arts of the Romans, and is a form of Roman folklore. "Roman mythology" may also refer to the modern study of these representations, and to the subject matter as represented in the literature and art of other cultures in any period. Roman mythology draws from the mythology of the Italic peoples and shares mythemes with Proto-Indo-European mythology.

Caulonia or Caulon was an ancient city on the shore of the Ionian Sea near Monasterace, Italy.
References
- ↑ Morley, Neville Daniel Gregory (1994). Metropolis and hinterland : the city of Rome and the Italian economy 200 B.C. - A.D. 200 (Thesis). Apollo - University of Cambridge Repository. doi:10.17863/CAM.19766.
- ↑ "Neville Morley". Freie Universität Berlin (in German). 2016-04-15. Retrieved 2020-11-03.