A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. Because minimum wages increase the cost of labor, many companies try to avoid minimum wage laws by using gig workers, moving labor to locations with lower or nonexistent minimum wages, or by automating job functions.
Economic interventionism, sometimes also called state interventionism, is an economic policy position favouring government intervention in the market process to correct market failures and promote the general welfare of the people. An economic intervention is an action taken by a government or international institution in a market economy in an effort to impact the economy beyond the basic regulation of fraud, enforcement of contracts, and provision of public goods and services. Economic intervention can be aimed at a variety of political or economic objectives, such as promoting economic growth, increasing employment, raising wages, raising or reducing prices, promoting income equality, managing the money supply and interest rates, increasing profits, or addressing market failures.

A living wage is defined as the minimum income necessary for a worker to meet their basic needs. This is not the same as a subsistence wage, which refers to a biological minimum. Needs are defined to include food, housing, and other essential needs such as clothing. The goal of a living wage is to allow a worker to afford a basic but decent standard of living through employment without government subsidies. Due to the flexible nature of the term "needs", there is not one universally accepted measure of what a living wage is and as such it varies by location and household type. A related concept is that of a family wage – one sufficient to not only support oneself, but also to raise a family.
Employment discrimination is a form of discrimination based on race, gender, religion, national origin, physical or mental disability, sexual orientation, and gender identity by employers. Earnings differentials or occupational differentiation—where differences in pay come from differences in qualifications or responsibilities—should not be confused with employment discrimination. Discrimination can be intended and involve disparate treatment of a group or be unintended, yet create disparate impact for a group.

Barack Obama has declared his position on many political issues through his public comments and legislative records. The Obama Administration stated that its general agenda was to "revive the economy, provide affordable and accessible health care to all, strengthen our public education and social security systems, define a clear path to energy independence and tackle climate change, end the War in Iraq responsibly and finish our mission in Afghanistan, and work with our allies to prevent Iran from developing a nuclear weapon."
Renewal Communities (RCs) and Empowerment Zones (EZs) are distressed urban and rural communities in the United States where qualifying businesses are eligible for billions of dollars in tax incentives. They were created in the Community Renewal Tax Relief Act of 2000, which was eventually passed as part of the Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2001.

The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 29 U.S.C. § 203 (FLSA) is a United States labor law that creates the right to a minimum wage, and "time-and-a-half" overtime pay when people work over forty hours a week. It also prohibits employment of minors in "oppressive child labor". It applies to employees engaged in interstate commerce or employed by an enterprise engaged in commerce or in the production of goods for commerce, unless the employer can claim an exemption from coverage.
A maximum wage, also often called a wage ceiling, is a legal limit on how much income an individual can earn. It is a prescribed limitation which can be used to affect change in an economic structure, but its effects are unrelated to those of minimum wage laws used currently by some states to enforce minimum earnings.

The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA), nicknamed the Recovery Act, was a stimulus package enacted by the 111th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Barack Obama in February 2009. Developed in response to the Great Recession, the primary objective of this federal statute was to save existing jobs and create new ones as soon as possible. Other objectives were to provide temporary relief programs for those most affected by the recession and invest in infrastructure, education, health, and renewable energy.
The economic policy of the Barack Obama administration was characterized by moderate tax increases on higher income Americans, designed to fund health care reform, reduce the federal budget deficit, and decrease income inequality. President Obama's first term (2009–2013) included measures designed to address the Great Recession and Subprime mortgage crisis, which began in 2007. These included a major stimulus package, banking regulation, and comprehensive healthcare reform. As the economy improved and job creation continued during his second term (2013–2017), the Bush tax cuts were allowed to expire for the highest income taxpayers and a spending sequester (cap) was implemented, to further reduce the deficit back to typical historical levels. The number of persons without health insurance was reduced by 20 million, reaching a record low level as a percent of the population. By the end of his second term, the number of persons with jobs, real median household income, stock market, and real household net worth were all at record levels, while the unemployment rate was well below historical average.

The Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment (HIRE) Act of 2010 is a law in the 111th United States Congress to provide payroll tax breaks and incentives for businesses to hire unemployed workers. Often characterized as a "jobs bill", certain Democrats in Congress state that it is only one piece of a broader job creation legislative agenda, along with the Travel Promotion Act and other bills.
99ers is a colloquial term for unemployed people in the United States, mostly citizens, who have exhausted all of their unemployment benefits, including all unemployment extensions. As a result of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act passed by Congress in February 2009, many unemployed people could receive up to 99 weeks of unemployment insurance benefits, hence the name "99ers". An estimated 7 million people are affected.
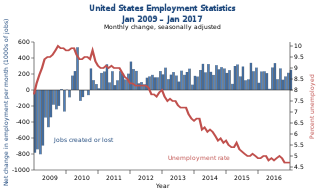
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.

The Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010, also known as the 2010 Tax Relief Act, was passed by the United States Congress on December 16, 2010, and signed into law by President Barack Obama on December 17, 2010.
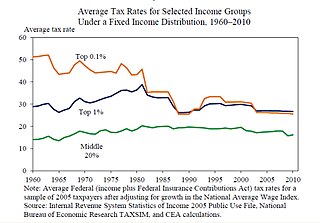
The Buffett Rule is part of a tax plan which would require millionaires and billionaires to pay the same tax rate as middle class families and working people. It was proposed by President Barack Obama in 2011. The tax plan proposed would apply a minimum tax rate of 30 percent on individuals making more than one million dollars a year. According to a White House official, the new tax rate would directly affect 0.3 percent of taxpayers.

We are the 99% is a political slogan widely used and coined during the 2011 Occupy movement from Gore Vidal's famous and original version "the one percent", meaning the nation's wealthiest 1%, to which the 99% reversely correspond.
Wage theft is the denial of wages or employee benefits rightfully owed to an employee. It can be conducted by employers in various ways, among them failing to pay overtime; violating minimum-wage laws; the misclassification of employees as independent contractors, illegal deductions in pay; forcing employees to work "off the clock", not paying annual leave or holiday entitlements, or simply not paying an employee at all.

The economic policy of the Donald Trump administration was characterized by the individual and corporate tax cuts, attempts to repeal the Affordable Care Act ("Obamacare"), trade protectionism, immigration restriction, deregulation focused on the energy and financial sectors, and responses to the COVID-19 pandemic.

The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Justin Trudeau.

The economic policy of the Joe Biden administration, or "Bidenomics" is characterized by goals to increase the national minimum wage and expand worker training, narrow income inequality, invest in clean energy and infrastructure, expand access to affordable healthcare, and forgive student loan debt. The March 2021 enactment of the American Rescue Plan to provide relief from the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic was the first major element of the policy.








