Related Research Articles

The Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution established the prohibition of alcohol in the United States. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 18, 1917, and ratified by the requisite number of states on January 16, 1919. The Eighteenth Amendment was repealed by the Twenty-first Amendment on December 5, 1933—it is the only constitutional amendment in American history to be repealed.

The National Prohibition Act, known informally as the Volstead Act, was an act of the 66th United States Congress designed to execute the 18th Amendment which established the prohibition of alcoholic drinks. The Anti-Saloon League's Wayne Wheeler conceived and drafted the bill, which was named after Andrew Volstead, chairman of the House Judiciary Committee, who managed the legislation.

The Anti-Saloon League, now known the American Council on Addiction and Alcohol Problems, is an organization of the temperance movement in the United States.
A local option is the ability of local political jurisdictions, typically counties or municipalities, to allow decisions on certain controversial issues within their borders, usually referring to a popular vote. It usually relates to the issue of alcoholic beverage, marijuana sales, and now mask wearing.

Ernest Hurst Cherrington was a leading temperance journalist. He became active in the Anti-Saloon League and was appointed editor of the organization's publishing house, the American Issue Publishing Company. He edited and contributed to the writing of The Standard Encyclopedia of the Alcohol Problem, a comprehensive six-volume work. In addition, he was active in establishing the World League Against Alcoholism.

Howard Hyde Russell was an American lawyer and clergyman, the founder of the Anti-Saloon League.
Pressure politics generally refers to political action which relies heavily on the use of mass media and mass communications to persuade politicians that the public wants or demands a particular action. However, it can also refer to intimidation, threats, and other covert techniques as well.

The World League Against Alcoholism was organized by the Anti-Saloon League, whose goal became establishing prohibition not only in the United States but throughout the entire world.

James Cannon Jr. was an American bishop of the Methodist Episcopal Church, South, elected in 1918. He was a prominent leader in the temperance movement in the United States in the 1920s, until derailed by scandal. H. L. Mencken said in 1934: "Six years ago he was the undisputed boss of the United States. Congress was his troop of Boy Scouts, and Presidents trembled whenever his name was mentioned.... But since that time there has been a violent revolution, and his whole world is in collapse."

William David Upshaw served eight years in Congress (1919–1927), where he was such a strong proponent of the temperance movement that he became known as the "driest of the drys." In Congress, Upshaw was a staunch defender of the Ku Klux Klan, which was founded in his congressional district, and lost reelection because of major KKK scandals in the mid-1920s. In 1932, he ran for President of the United States on the Prohibition Party ticket, finishing the race in fifth place.

William Hamilton Anderson was the superintendent of the New York Anti-Saloon League. He worked toward the prohibition of alcohol and the closing of saloons. In 1924 a jury convicted him of skimming contributions to the league.

A Western saloon is a kind of bar particular to the Old West. Saloons served customers such as fur trappers, cowboys, soldiers, lumberjacks, businessmen, lawmen, outlaws, miners, and gamblers. A saloon might also be known as a "watering trough, bughouse, shebang, cantina, grogshop, and gin mill". The first saloon was established at Brown's Hole, Wyoming, in 1822, to serve fur trappers.
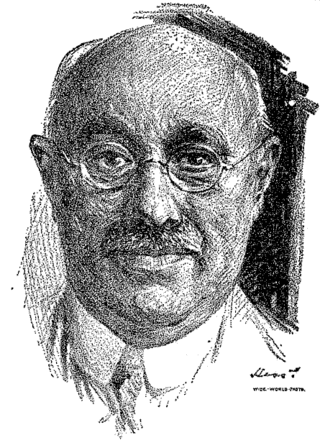
William Eugene "Pussyfoot" Johnson was an American Prohibition advocate and law enforcement officer. In pursuit of his campaign to outlaw intoxicating beverages, he went undercover, posing as an habitué of saloons and collecting information against their owners.

Wayne Bidwell Wheeler was an American attorney and longtime leader of the Anti-Saloon League. The leading advocate of the prohibitionist movement in the late 1800s and early 1900s, he played a major role in the passage of the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which outlawed the manufacture, distribution, and sale of alcoholic beverages.
The LaMontages brothers -- Rene, Montaigu, William and Morgan—were high society bootleggers who made $2,000,000 annually through their illegal business during the early years of alcohol Prohibition in the United States.

The Prohibition era was a period in the United States from 1920 to 1933 during which a nationwide constitutional law prohibiting the production, importation, transportation, and sale of alcoholic beverages was enacted. The alcohol industry was curtailed by a succession of state legislatures, and finally ended nationwide under the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified on January 16, 1919. Prohibition ended with the ratification of the Twenty-first Amendment, which repealed the Eighteenth Amendment on December 5, 1933.

In the United States, the temperance movement, which sought to curb the consumption of alcohol, had a large influence on American politics and American society in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, culminating in the prohibition of alcohol, through the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, from 1920 to 1933. Today, there are organizations that continue to promote the cause of temperance.

The 1925 New Jersey gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1925. Democratic Jersey City Commissioner A. Harry Moore defeated Republican State Senator Arthur Whitney with 51.87% of the vote.

The 1924 United States Senate election in New Jersey was held on November 4, 1924. Incumbent Republican Senator Walter Evans Edge was re-elected to a second term in office. He would not complete the term, resigning from office in 1929 to be sworn in as the U.S. Ambassador to France.

The 1922 United States Senate election in New York was held on November 7, 1922. Incumbent Republican Senator William Calder ran for re-election to a second term, but was defeated by Democrat Royal Copeland.
References
- David Kyvig; Repealing National Prohibition