
A college is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offering vocational education or a secondary school.

The House of Habsburg, also called the House of Austria, was one of the most influential and distinguished royal houses of Europe. The throne of the Holy Roman Empire was continuously occupied by the Habsburgs from 1438 until their extinction in the male line in 1740. The house also produced emperors and kings of the Kingdom of Bohemia, Kingdom of England, Kingdom of Germany, Kingdom of Hungary, Kingdom of Croatia, Kingdom of Illyria, Second Mexican Empire, Kingdom of Ireland, Kingdom of Portugal, and Kingdom of Spain, as well as rulers of several Dutch and Italian principalities. From the 16th century, following the reign of Charles V, the dynasty was split between its Austrian and Spanish branches. Although they ruled distinct territories, they nevertheless maintained close relations and frequently intermarried.

Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or postsecondary education, is the educational level following the completion of a school providing a secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including universities as well as trade schools and colleges. Higher education is taken to include undergraduate and postgraduate education, while vocational education beyond secondary education is known as further education in the United Kingdom, or continuing education in the United States.

Macedonia, also called Macedon, was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula, and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south.

Cleopatra VII Philopator was the last active ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, nominally survived as pharaoh by her son Caesarion. As a member of the Ptolemaic dynasty, she was a descendant of its founder Ptolemy I Soter, a Macedonian Greek general and companion of Alexander the Great. After the death of Cleopatra, Egypt became a province of the Roman Empire, marking the end of the Hellenistic period that had lasted since the reign of Alexander. While her native language was Koine Greek, she was the first Ptolemaic ruler to learn the Egyptian language.
Hematology, also spelled haematology, is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots, other bleeding disorders and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory work that goes into the study of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist.

Brighton & Hove Albion Football Club, commonly referred to as Brighton, is a professional football club from Brighton where they play in the edge of the city in Falmer, England. They compete in the Premier League, the top tier of the English football league system. Brighton's home ground is the 30,750-capacity Falmer Stadium.
Further education in the United Kingdom and Ireland is education in addition to that received at secondary school, that is distinct from the higher education (HE) offered in universities and other academic institutions. It may be at any level in compulsory secondary education, from entry to higher level qualifications such as awards, certificates, diplomas and other vocational, competency-based qualifications through awarding organisations including City and Guilds, Edexcel (BTEC) and OCR. FE colleges may also offer HE qualifications such as HNC, HND, Foundation Degree or PGCE. The colleges are also a large provider of apprenticeships, where most of the training takes place in the apprentices' workplace with some day release into college.

Psychological projection is a defence mechanism in which the human ego defends itself against unconscious impulses or qualities by denying their existence in themselves while attributing them to others. For example, a person who is habitually rude may constantly accuse other people of being rude. It incorporates blame shifting.
Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their own combatants at the hands of hostile forces. The United States Department of Defense, for example, says that those declared KIA need not have fired their weapons but have been killed due to hostile attack. KIAs do not come from incidents such as accidental vehicle crashes and other "non-hostile" events or terrorism. KIA can be applied both to front-line combat troops and to naval, air and support troops. Someone who is killed in action during a particular event is denoted with a † (dagger) beside their name to signify their death in that event or events.
A mahram is an unmarriageable kin with whom marriage or sexual intercourse would be considered haram, illegal in Islam, or people from whom purdah is not obligatory or legal escorts of a woman during journey longer than a day and night, 24 hours.
Law 41 of the Laws of Cricket covers unfair play. This law has developed and expanded over time as various incidents of real life unfair play have been legislated against.
A Master of Arts is a person who was admitted to a type of master's degree awarded by universities in many countries, and the degree is also named Master of Arts in colloquial speech. The degree is usually contrasted with the Master of Science. Those admitted to the degree typically study linguistics, history, communication studies, diplomacy, public administration, political science, or other subjects within the scope of the humanities and social sciences; however, different universities have different conventions and may also offer the degree for fields typically considered within the natural sciences and mathematics. The degree can be conferred in respect of completing courses and passing examinations, research, or a combination of the two.

East Africa Time, or EAT, is a time zone used in eastern Africa. The time zone is three hours ahead of UTC (UTC+03:00), which is the same as Arabia Standard Time, Further-eastern European Time, Moscow Time and Eastern European Summer Time.
Drugs controlled by the United Kingdom (UK) Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 are listed in this article. These drugs are known in the UK as controlled drugs, because this is the term by which the act itself refers to them. In more general terms, however, many of these drugs are also controlled by the Medicines Act 1969, there are many other drugs which are controlled by the Medicines Act but not by the Misuse of Drugs Act, and other substances which may be considered drugs are controlled by other laws.

The Department for Education (DfE) is a department of Her Majesty's Government responsible for child protection, education, apprenticeships and wider skills in England.

The 74 regional units are administrative units of Greece. They are subdivisions of the country's 13 regions, further subdivided into municipalities. They were introduced as part of the "Kallikratis" administrative reform on 1 January 2011 and are comparable in area and, in the mainland, coterminous with the pre-"Kallikratis" prefectures of Greece.
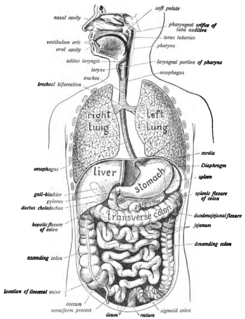
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion. Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has many stages. The first stage is the cephalic phase of digestion which begins with gastric secretions in response to the sight and smell of food. The next stage starts in the mouth.











