
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is most often used by the government of a single country to measure its economic health. Due to its complex and subjective nature, this measure is often revised before being considered a reliable indicator.
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns".

Happiness is a positive and pleasant emotion, ranging from contentment to intense joy. Moments of happiness may be triggered by positive life experiences or thoughts, but sometimes it may arise from no obvious cause. The level of happiness for longer periods of time is more strongly correlated with levels of life satisfaction, subjective well-being, flourishing and eudaimonia. In common usage, the word happy can be an appraisal of those measures themselves or as a shorthand for a "source" of happiness. As with any emotion, the precise definition of happiness has been a perennial debate in philosophy.
Positive psychology studies the conditions that contribute to the optimal functioning of people, groups, and institutions. It studies "positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions... it aims to improve quality of life."

The Index of Sustainable Economic Welfare (ISEW) is an economic indicator intended to replace the gross domestic product (GDP), which is the main macroeconomic indicator of System of National Accounts (SNA). Rather than simply adding together all expenditures like the GDP, consumer spending is balanced by such factors as income distribution and cost associated with pollution and other unsustainable costs. The calculation excludes defence expenditures and considers a wider range of harmful effects of economic growth. It is similar to the genuine progress indicator (GPI).

Gross National Happiness (GNH), sometimes called Gross Domestic Happiness (GDH), is a philosophy that guides the government of Bhutan. It includes an index which is used to measure the collective happiness and well-being of a population. Gross National Happiness Index is instituted as the goal of the government of Bhutan in the Constitution of Bhutan, enacted on 18 July 2008.

The New Economics Foundation (NEF) is a British think-tank that promotes "social, economic and environmental justice".

Andrew Oswald is a Professor of Economics and Behavioural Science at the University of Warwick, England. He is an ISI highly cited researcher and has been a professorial fellow of the ESRC. He is currently a member of the board of reviewing editors of Science. He held previous posts at Oxford, the London School of Economics, Princeton, Dartmouth and Harvard.

The Satisfaction with Life Index was created in 2007 by Adrian G. White, an analytic social psychologist at the University of Leicester, using data from a metastudy. It is an attempt to show life satisfaction in different nations.

The Happy Planet Index (HPI) is an index of human well-being and environmental impact that was introduced by the New Economics Foundation in 2006. Each country's HPI value is a function of its average subjective life satisfaction, life expectancy at birth, and ecological footprint per capita. The exact function is a little more complex, but conceptually it approximates multiplying life satisfaction and life expectancy and dividing that by the ecological footprint. The index is weighted to give progressively higher scores to nations with lower ecological footprints.
The economics of happiness or happiness economics is the theoretical, qualitative and quantitative study of happiness and quality of life, including positive and negative affects, well-being, life satisfaction and related concepts – typically tying economics more closely than usual with other social sciences, like sociology and psychology, as well as physical health. It typically treats subjective happiness-related measures, as well as more objective quality of life indices, rather than wealth, income or profit, as something to be maximized.
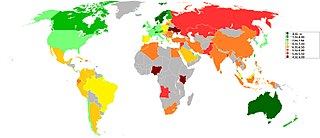
The Economist Intelligence Unit’s where-to-be-born index attempts to measure which country will provide the best opportunities for a healthy, safe and prosperous life in the years ahead.

Well-being, or wellbeing, also known as wellness, prudential value, prosperity or quality of life, refers to what is intrinsically valuable relative to someone. So the well-being of a person is what is ultimately good for this person, what is in the self-interest of this person. Well-being can refer to both positive and negative well-being. In its positive sense, it is sometimes contrasted with ill-being as its opposite. The term "subjective well-being" denotes how people experience and evaluate their lives, usually measured in relation to self-reported well-being obtained through questionnaires.
Action for Happiness (AfH) is a global movement and charity based in the United Kingdom. It aims to increase the happiness in the world by bringing together people and supporting them to take practical action to build a happier society. The patron of Action for Happiness is the Dalai Lama. The movement has over 270,000 members in 190 countries.
The OECD Better Life Index, created in May 2011 by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, is an initiative pioneering the development of economic indicators which better capture multiple dimensions of economic and social progress.
Although for many decades, it was customary to focus on GDP and other measures of national income, there has been growing interest in developing broad measures of economic well-being. National and international approaches include the Beyond GDP programme developed by the European Union, the Better Lives Compendium of Indicators developed by the OECD, as well as many alternative metrics of wellbeing or happiness. One of the earliest attempts to develop such an index at national level was Bhutan's Gross National Happiness Index and there are a now a number of similar projects ongoing around the world, including a project to develop for the UK an assessment of national well-being, commissioned by the Prime Minister David Cameron and led by the Office for National Statistics.
Subjective well-being (SWB) is a self-reported measure of well-being, typically obtained by questionnaire.

The World Happiness Report is a publication that contains articles and rankings of national happiness, based on respondent ratings of their own lives, which the report also correlates with various life factors. As of March 2023, Finland has been ranked the happiest country in the world six times in a row.
Gross National Well-being/Wellness (GNW) or Happiness (GNH) a socioeconomic development and measurement framework. The GNW/GNH Index consists of seven dimensions: economic, environmental, physical, mental, work, social, and political. Most wellness areas include both subjective results and objective data.
The World Happiness Council is a think tank of politicians and researchers based in the United Arab Emirates, intended to promote happiness and subjective well-being through the identification of public policy for policymakers worldwide and the standardization of happiness as a measure to guide governments.










