Related Research Articles
Hemiparesis, or unilateral paresis, is weakness of one entire side of the body. Hemiplegia is, in its most severe form, complete paralysis of half of the body. Hemiparesis and hemiplegia can be caused by different medical conditions, including congenital causes, trauma, tumors, or stroke.

Auckland University of Technology is a university in New Zealand, formed on 1 January 2000 when a former technical college was granted university status. AUT is New Zealand's third largest university in terms of total student enrolment, with approximately 29,100 students enrolled across three campuses in Auckland. It has five faculties, and an additional three specialist locations: AUT Millennium, Warkworth Radio Astronomical Observatory and AUT Centre for Refugee Education.
Rehabilitation of sensory and cognitive function typically involves methods for retraining neural pathways or training new neural pathways to regain or improve neurocognitive functioning that have been diminished by disease or trauma. The main objective outcome for rehabilitation is to assist in regaining physical abilities and improving performance. Three common neuropsychological problems treatable with rehabilitation are attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), concussion, and spinal cord injury. Rehabilitation research and practices are a fertile area for clinical neuropsychologists, rehabilitation psychologists, and others.
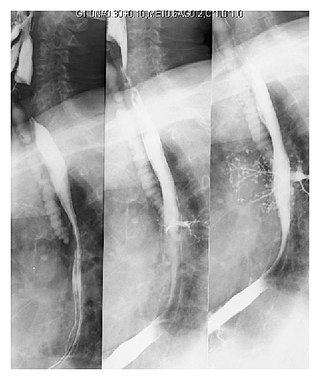
Pulmonary aspiration is the entry of material such as pharyngeal secretions, food or drink, or stomach contents from the oropharynx or gastrointestinal tract, into the larynx and lower respiratory tract, the portions of the respiratory system from the trachea (windpipe) to the lungs. A person may inhale the material, or it may be delivered into the tracheobronchial tree during positive pressure ventilation. When pulmonary aspiration occurs during eating and drinking, the aspirated material is often colloquially referred to as "going down the wrong pipe".

Cerebral edema is excess accumulation of fluid (edema) in the intracellular or extracellular spaces of the brain. This typically causes impaired nerve function, increased pressure within the skull, and can eventually lead to direct compression of brain tissue and blood vessels. Symptoms vary based on the location and extent of edema and generally include headaches, nausea, vomiting, seizures, drowsiness, visual disturbances, dizziness, and in severe cases, death.

Acquired brain injury (ABI) is brain damage caused by events after birth, rather than as part of a genetic or congenital disorder such as fetal alcohol syndrome, perinatal illness or perinatal hypoxia. ABI can result in cognitive, physical, emotional, or behavioural impairments that lead to permanent or temporary changes in functioning. These impairments result from either traumatic brain injury or nontraumatic injury derived from either an internal or external source. ABI does not include damage to the brain resulting from neurodegenerative disorders.
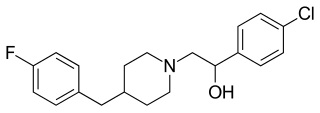
Eliprodil is an NMDA antagonist drug candidate which selectively inhibits the NR2B (GLUN2B) subtype NMDA receptor at submicromolar concentrations. Eliprodil failed a Phase III clinical trial for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in 1996, sponsored by Synthélabo Recherche.

Repinotan (BAYx3702), an aminomethylchroman derivative, is a selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist with high potency and efficacy. It has neuroprotective effects in animal studies, and was trialed in humans for reducing brain injury following head trauma. It was subsequently trialed up to phase II for treatment of stroke, but while side effects were mild and consisted mainly of nausea, repinotan failed to demonstrate sufficient efficacy to justify further clinical trials. However, repinotan continues to be investigated for other applications, and was found to be effective at counteracting the respiratory depression produced by morphine, though with slight reduction in analgesic effects.

Segun Toyin Dawodu is a Nigerian Physiatrist and lawyer with the WellSpan Health, he served as an Associate Professor of Pain Medicine at Albany Medical College.
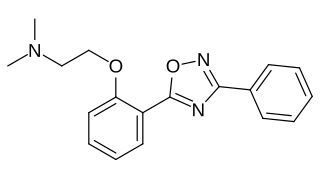
Irampanel is a drug which acts as a dual noncompetitive antagonist of the AMPA receptor and neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel blocker. It was under development by Boehringer Ingelheim for the treatment of acute stroke/cerebral ischemia but never completed clinical trials for this indication. Irampanel was also trialed, originally, for the treatment of epilepsy and pain, but these indications, too, were abandoned, and the drug was ultimately never marketed.
Cerebrolysin is a mixture of enzymatically treated peptides derived from pig brain whose constituents can include brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF).

Janet Marion Leathem is a New Zealand psychology academic specializing in traumatic brain injury. She is currently a full professor at Massey University.
Kathryn Margaret McPherson is a New Zealand medical researcher and administrator. As of 2018 she is a full professor at the Auckland University of Technology and chief executive of the Health Research Council of New Zealand.
Patria Anne Hume is a New Zealand sports biomechanics academic. She is currently a full-time Professor of Human Performance at the Auckland University of Technology Sport Performance Research Institute New Zealand (SPRINZ) at AUT Millennium.
Shanthi Neranjana Ameratunga is a New Zealand public health academic. As of September 2018 she is currently a full professor at the University of Auckland.
Alice Theadom is an English-born New Zealand psychologist and academic. As of 2020 she is a full professor and Rutherford Discovery Fellow at Auckland University of Technology (AUT).

Priscilla M. Wehi is a New Zealand ethnobiologist and conservation biologist. As at July 2021 she is an associate professor at the University of Otago and on the first of that month officially undertook the role of director of Te Pūnaha Matatini, a centre of research excellence in complex systems and data analytics. During the COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand Te Pūnaha Matatini scientists have developed mathematical models of the spread of the virus across the country that influence the New Zealand government's response to the outbreak. In 2021 Wehi was awarded the Hill Tinsley Medal.
Makarena Diana Dudley, also known as Margaret Dudley, is a New Zealand clinical psychologist, neuropsychologist and academic, specialising in neuropsychology, dementia and Māori health psychology research. She is currently one of the co-directors of the clinical psychology programme at the University of Auckland. In 2016, Dudley became the first permanent Māori clinical psychology lecturer employed at the University of Auckland. Dudley's iwi include Te Rarawa, Te Aupōuri and Ngāti Kahu.

Lynette Joy Tippett is a New Zealand professor of psychology at the University of Auckland, specialising in neurodegenerative diseases.
Rita V. Krishnamurthi is a New Zealand academic, and since 2023 is a full professor at the Auckland University of Technology, specialising in the epidemiology of stroke and dementia.
References
- 1 2 "Nicola Starkey – Staff Profiles: University of Waikato". www.waikato.ac.nz.
- ↑ "Nicola Starkey – NISAN – AUT". nisan.aut.ac.nz.
- ↑ "Assoc. Prof. Nicola Starkey".
- ↑ "The sobering science of drinking and driving". 12 December 2017.
- ↑ "Concussion issues can linger for years, New Zealand study finds – Horsetalk.co.nz". 4 February 2018.
- ↑ Keogh, Brittany (10 March 2018). "Driverless shuttles take to the tarmac as gridlock baffles city planners". The New Zealand Herald .