Operators
 Denmark
Denmark
- Danish Army (Royal Danish Army Air Corps)
 Norway
Norway
| Type AA | |
|---|---|
| Role | Single-seat fighter |
| National origin | Denmark |
| Manufacturer | Nielsen and Winther A/S |
| First flight | 21 January 1917 |
| Introduction | 1917 |
| Retired | 1919 |
| Primary user | Danish Army |
| Number built | 6 |
The Nielsen & Winther Type AA, also known as the Type AA, was a Danish fighter aircraft of the 1910s manufactured by Nielsen & Winther in Copenhagen.
The first Danish fighter aircraft to be conceived and built, the single seat Type AA was of wooden construction and powered by a 90 hp Thulin rotary engine. It was armed with one 8 mm Madsen machine gun.
The first flight took place on 21 January 1917. The plane was tested again in 1918, this time with synchronising gear for its single Madsen machine gun. During 1917 six Type AA aircraft were delivered to the Danish Army, though they saw little service and were retired in 1919 owing to engine unreliability.
Data from Green [2]
General characteristics
Performance
Armament

The Sopwith Pup is a British single-seater biplane fighter aircraft built by the Sopwith Aviation Company. It entered service with the Royal Naval Air Service and the Royal Flying Corps in the autumn of 1916. With pleasant flying characteristics and good manoeuvrability, the aircraft proved very successful. The Pup was eventually outclassed by newer German fighters, but it was not completely replaced on the Western Front until the end of 1917. The remaining Pups were relegated to Home Defence and training units. The Pup's docile flying characteristics also made it ideal for use in aircraft carrier deck landing and takeoff experiments and training.

The Republic XP-69 was an American fighter aircraft proposed by Republic Aviation in 1941 in response to a requirement by the United States Army Air Corps for a high-speed fighter. Manufacturers were encouraged to consider unorthodox designs; although the design was ordered as a prototype it was canceled because of delays with the engine that was to power it.

The Hawker Woodcock was a British single-seat fighter built by the Hawker Engineering Company as the first fighter to be produced by Hawker Engineering. It was used by the RAF as a night fighter in the 1920s.

The Hawker Danecock biplane was developed from the Hawker Woodcock for the Danish air force and naval service.

The Thulin LA was a Swedish two-seat, single-engine biplane designed by Enoch Thulin in 1917 and made by his company AB Thulinverken in Landskrona. It was based on the earlier Thulin L and E aircraft, with a new engine, fuselage and empennage. The L and E types were in turn based on the German Albatros B.II aircraft, like the NAB Albatros. The Thulin LA was used in Sweden, the Netherlands (10) and Finland (1). This type also made the first passenger transport flights between Sweden and Denmark in 1919. Altogether there were 15 Thulin LAs built.

The Nakajima Ki-49Donryu was a twin-engine Japanese World War II heavy bomber. It was designed to carry out daylight bombing missions, without the protection of escort fighters. Consequently, while its official designation, Army Type 100 Heavy Bomber, was accurate in regard to its formidable defensive armament and armor, these features restricted the Ki-49 to payloads comparable to those of lighter medium bombers – the initial production variant could carry only 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) of bombs.

The Nakajima Army Type 91 Fighter was a Japanese fighter of the 1930s. It was a single-engine, single-seat parasol monoplane with a fixed, tailskid undercarriage.

The Pfalz D.VIII was a German World War I fighter aircraft.

The Fokker D.VI was a German fighter aircraft built in limited numbers at the end of World War I. The D.VI served in the German and Austro-Hungarian air services.

The Nakajima Ki-8 was an unsuccessful attempt by the Nakajima Aircraft Company to interest the Imperial Japanese Army Air Force in a two-seat modern monoplane fighter.

The Sikorsky S-16, or RBVZ S-XVI, was a Russian equi-span single-bay two-seat biplane designed by Igor Sikorsky in 1914-15. Conceived in response to demand for an escort fighter for the Ilya Muromets bombers, it was noteworthy in that it was one of the first aircraft to possess synchronisation gear for its 7.7 mm machine gun. The first S-XVI was completed on 6 February 1915 with an 80 hp engine instead of the intended 100 hp because of supply problems. On 17 December 1915, the Russian government placed an order for 18 aircraft, these being delivered in early 1916.

The Thulin K was a Swedish naval fighter aircraft in the 1910s. It was operated by both the Swedish and Dutch armed forces.
The Armstrong Whitworth Armadillo was a British single-seat biplane fighter aircraft built by Armstrong Whitworth.

The Orenco D was an American biplane fighter aircraft, designed by Orenco and built by Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. It was the first fighter type of completely indigenous design to enter US military service.

The Orenco B was a prototype American fighter aircraft of World War I. It was a single-engined, single-seat biplane that flew in 1918. Although it demonstrated good performance, it did not enter large scale service.

The LFG Roland D.IX was a World War I German single seat fighter aircraft, a biplane powered by one of a new generation of powerful rotary engines. Three slightly different prototypes were built but there was no series production.
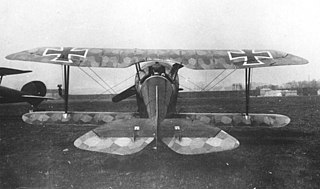
The Kondor D 1, given the unofficial name Kondorlaus, was a German single seat, biplane fighter aircraft designed and built close to the end of WWI.

The Friedrichshafen D.I was a German single-seat fighter plane developed by the Flugzeugbau Friedrichshafen during the First World War. Two prototypes were flown in 1917, but it was judged inferior to the Albatros D.III then in production and no further production ensued.

The Thulin FA was a Swedish reconnaissance aircraft built in the late 1910s.

Nielsen & Winther was a Danish machine factory and aeroplane manufacturer based in Copenhagen, Denmark.