
Letcher County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 21,548. Its county seat is Whitesburg. It was created in 1842 from Harlan and Perry counties, and named for Robert P. Letcher, Governor of Kentucky from 1840 to 1844.

Thomas Sowell is an American economist, social philosopher, and political commentator. He is a senior fellow at the Hoover Institution. With widely published commentary and books—and as a guest on TV and radio—he became a well-known voice in the American conservative movement as a prominent black conservative. He was a recipient of the National Humanities Medal from President George W. Bush in 2002.

The "Miracle of Chile" was a term used by economist Milton Friedman to describe the reorientation of the Chilean economy in the 1980s and the effects of the economic policies applied by a large group of Chilean economists who collectively came to be known as the Chicago Boys, having studied at the University of Chicago where Friedman taught. He said the "Chilean economy did very well, but more importantly, in the end the central government, the military junta, was replaced by a democratic society. So the really important thing about the Chilean business is that free markets did work their way in bringing about a free society." The junta to which Friedman refers was a military government that came to power in a 1973 coup d'état, which came to an end in 1990 after a democratic 1988 plebiscite removed Augusto Pinochet from the presidency.

Appalachia is a geographic region located in the central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern United States. Its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountains of New York into Pennsylvania, continuing on through the Blue Ridge Mountains and Great Smoky Mountains into northern Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi, with West Virginia being the only state in which the entire state is within the boundaries of Appalachia. In 2021, the region was home to an estimated 26.3 million people, of whom roughly 80% were white.

The Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) is a United States federal–state partnership that works with the people of Appalachia to create opportunities for self-sustaining economic development and improved quality of life. Congress established ARC to bring the region into socioeconomic parity with the rest of the nation.
Internal colonialism is the uneven effects of economic development on a regional basis, otherwise known as "uneven development" as a result of the exploitation of minority groups within a wider society which leads to political and economic inequalities between regions within a state. This is held to be similar to the relationship between a metropole and a colony, in colonialism proper. The phenomenon leads to the distinct separation of the dominant core from the periphery in an empire.
The settlement movement was a reformist social movement that began in the 1880s and peaked around the 1920s in the United Kingdom and the United States. Its goal was to bring the rich and the poor of society together in both physical proximity and social connection. Its main object was the establishment of "settlement houses" in poor urban areas, in which volunteer middle-class "settlement workers" would live, hoping to share knowledge and culture with, and alleviate the poverty of, their low-income neighbors. The settlement houses provided services such as daycare, English classes, and healthcare to improve the lives of the poor in these areas. The settlement movement also spawned educational/reform movements. Both in the UK and the US settlement workers worked to develop a unique activist form of sociology known as Settlement Sociology. This science of social reform movement is neglected in the history of sociology in favor of a teaching-, theory- and research university–based model.
Conservatism in the United States is based on a belief in individualism, traditionalism, republicanism, and limited federal governmental power in relation to U.S. states. It is one of two major political ideologies of the United States. Conservative and Christian media organizations and American conservative figures are influential, and American conservatism is a large and mainstream ideology in the Republican Party and nation. As of 2021, 36 percent of Americans consider themselves conservative, according to polling by Gallup, Inc.

Harry Monroe Caudill was an American author, historian, lawyer, legislator, and environmentalist from Letcher County, in the coalfields of southeastern Kentucky.

Harry S. Truman was the 33rd president of the United States, serving from 1945 to 1953. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as a United States senator from Missouri from 1935 to 1945 and briefly in 1945 as the 34th vice president under Franklin D. Roosevelt. Assuming the presidency after Roosevelt's death, Truman implemented the Marshall Plan in the wake of World War II to rebuild the economy of Western Europe and established both the Truman Doctrine and NATO to contain the expansion of Soviet communism. He proposed numerous liberal domestic reforms, but few were enacted by the conservative coalition that dominated Congress.
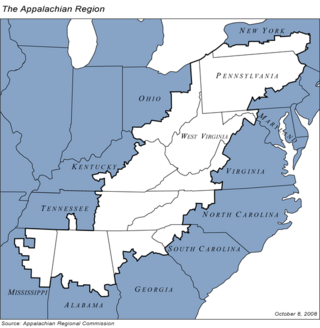
Appalachia is a geographic region of the Eastern United States. Home to over 25 million people, the region includes mountainous areas of 13 states: Mississippi, Alabama, Pennsylvania, New York, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Kentucky, Ohio, Maryland, as well as the entirety of West Virginia.

Appalachian Volunteers (AV) was a non-profit organization engaged in community development projects in central Appalachia that evolved into a controversial community organizing network, with a reputation that went "from self-help to sedition" as its staff developed from "reformers to radicals," teaching things from Marx, Lenin and Mao, in the words of one historian, in the brief period between 1964 and 1970 during the War on Poverty.
David Walls is an activist and academic who has made significant contributions to Appalachian studies and to the popular understanding of social movements. He is professor emeritus of sociology at Sonoma State University (SSU) in California, where he was dean of extended education from 1984 to 2000.

In the United States, poverty has both social and political implications. In 2020, there were 37.2 million people in poverty. Some of the many causes include income, inequality, inflation, unemployment, debt traps and poor education. The majority of adults living in poverty are employed and have at least a high school education. Although the US is a relatively wealthy country by international standards, it has a persistently high poverty rate compared to other developed countries due in part to a less generous welfare system.
Steven Pressman is an American economist. He is a former Professor of Economics and Finance at Monmouth University in West Long Branch, New Jersey. He has taught at the University of New Hampshire and Trinity College in Hartford, Connecticut.
Rebecca Caudill Ayars was an American writer of children's literature. More than twenty of her books were published. Tree of Freedom was a Newbery Honor Book in 1950. A Pocketful of Cricket, illustrated by Evaline Ness, was a Caldecott Honor Book.

This is a bibliography of works on Canada.

Poor White is a sociocultural classification used to describe economically disadvantaged Whites in the English-speaking world, especially White Americans with low incomes.

Cromona is a small unincorporated community located in the mountains of Eastern Kentucky in Letcher County, Kentucky, United States. The Cromona post office has operated since 1916. Cromona is actually known as Haymond by the local residents. However, for reasons that are obscure, the post office was given a different name, Cromona. It was built as a coal town in 1916, and was named for the president of the Elk Horn Coal Corporation, Thomas S. Haymond. The population of Haymond was 502 as of the 2010 census.

The Appalachian region and its people have historically been stereotyped by observers, with the basic perceptions of Appalachians painting them as backwards, rural, and anti-progressive. These widespread, limiting views of Appalachia and its people began to develop in the post-Civil War; Those who "discovered" Appalachia found it to be a very strange environment, and depicted its "otherness" in their writing. These depictions have persisted and are still present in common understandings of Appalachia today, with a particular increase of stereotypical imagery during the late 1950s and early 1960s in sitcoms. Common Appalachian stereotypes include those concerning economics, appearance, and the caricature of the "hillbilly."














