
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysics, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant or Stonehenge.

The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 member states for ground-based astronomy. Created in 1962, ESO has provided astronomers with state-of-the-art research facilities and access to the southern sky. The organisation employs over 750 staff members and receives annual member state contributions of approximately €162 million. Its observatories are located in northern Chile.

Yerkes Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in Williams Bay, Wisconsin, United States. The observatory was operated by the University of Chicago Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics from its founding in 1897 to 2018. Ownership was transferred to the non-profit Yerkes Future Foundation (YFF) in May 2020, which began restoration and renovation of the historic building and grounds. Re-opening for public tours and programming began May 27, 2022.

The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The observatory is managed by the University of California Observatories, with headquarters on the University of California, Santa Cruz campus, where its scientific staff moved in the mid-1960s. It is named after James Lick.

The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a 1,740-meter (5,710-foot) peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles.

La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is one of the largest in the Southern Hemisphere and was the first in Chile to be used by ESO.

The National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) is an astronomical research organisation comprising several facilities in Japan, as well as an observatory in Hawaii and Chile. It was established in 1988 as an amalgamation of three existing research organizations - the Tokyo Astronomical Observatory of the University of Tokyo, International Latitude Observatory of Mizusawa, and a part of Research Institute of Atmospherics of Nagoya University.
The Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) is a high-altitude astronomy station located in Hanle, India and operated by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. Situated in the Western Himalayas at an elevation of 4,500 meters (14,764 ft), the IAO is one of the world's highest located sites for optical, infrared and gamma-ray telescopes. It is currently the tenth (see List of highest astronomical observatories) highest optical telescope in the world. It is India's first dark-sky preserve.

The Calar Alto Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in Almería province in Spain on Calar Alto, a 2,168-meter-high (7,113 ft) mountain in the Sierra de Los Filabres range.

The Molėtai Astronomical Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by Vilnius University Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy. It is located on the Kaldiniai Hill next to Kulionys, Lithuania, 10 km from the town of Molėtai.

Hamburg Observatory is an astronomical observatory located in the Bergedorf borough of the city of Hamburg in northern Germany. It is owned and operated by the University of Hamburg, Germany since 1968, although it was founded in 1825 by the City of Hamburg and moved to its present location in 1912. It has operated telescopes at Bergedorf, at two previous locations in Hamburg, at other observatories around the world, and it has also supported space missions.
Anderson Mesa Station is an astronomical observatory established in 1959 as a dark-sky observing site for Lowell Observatory. It is located at Anderson Mesa in Coconino County, Arizona, about 12 miles (19 km) southeast of Lowell's main campus on Mars Hill in Flagstaff, Arizona.
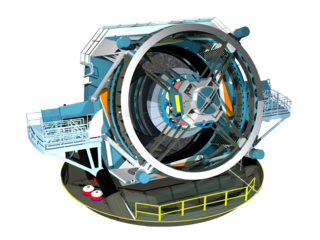
The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, previously referred to as the Large Synoptic Survey Telescope (LSST), is an astronomical observatory currently under construction in Chile. Its main task will be carrying out a synoptic astronomical survey, the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). The word synoptic is derived from the Greek words σύν and ὄψις, and describes observations that give a broad view of a subject at a particular time. The observatory is located on the El Peñón peak of Cerro Pachón, a 2,682-meter-high mountain in Coquimbo Region, in northern Chile, alongside the existing Gemini South and Southern Astrophysical Research Telescopes. The LSST Base Facility is located about 100 kilometres (62 mi) away by road, in the town of La Serena. The observatory is named for Vera Rubin, an American astronomer who pioneered discoveries about galaxy rotation rates.

An extremely large telescope (ELT) is an astronomical observatory featuring an optical telescope with an aperture for its primary mirror from 20 metres up to 100 metres across, when discussing reflecting telescopes of optical wavelengths including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and near infrared wavelengths. Among many planned capabilities, extremely large telescopes are planned to increase the chance of finding Earth-like planets around other stars. Telescopes for radio wavelengths can be much bigger physically, such as the 300 metres aperture fixed focus radio telescope of the Arecibo Observatory. Freely steerable radio telescopes with diameters up to 100 metres have been in operation since the 1970s.

The Tottori Expressway is an expressway connecting Sayō in Hyōgo Prefecture and Tottori, the capital and largest city in Tottori Prefecture. It is owned and operated partly by the West Nippon Expressway Company and the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. The expressway is signed as an auxiliary route of National Route 373 as well as E29 under the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism's "2016 Proposal for Realization of Expressway Numbering."

GroundBIRD is an experiment to observe the cosmic microwave background at 145 and 220GHz. It aims to observe the B-mode polarisation signal from inflation in the early universe. It is located at Teide Observatory, on the island of Tenerife in the Canary Islands.














