
Married... with Children is an American sitcom created by Michael G. Moye and Ron Leavitt for the Fox Broadcasting Company, broadcast from April 5, 1987, to June 9, 1997. It is the longest-running live-action sitcom ever aired on Fox. Married... with Children was the first primetime series broadcast on the new Fox network. The series' run ended with the episode broadcast on May 5, 1997. Two previously unaired episodes were broadcast on June 9, 1997, and June 18, 2002.

Asperger syndrome (AS), also known as Asperger's syndrome or Asperger's, is a term formerly used to describe a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significant difficulties in social interaction and nonverbal communication, along with restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior and interests. Asperger syndrome has been merged with other disorders into autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and is no longer considered a stand-alone diagnosis. It was considered milder than other diagnoses which were merged into ASD due to relatively unimpaired spoken language and intelligence.

Sesame Street is an American educational children's television series that combines live-action, sketch comedy, animation and puppetry. It is produced by Sesame Workshop and was created by Joan Ganz Cooney and Lloyd Morrisett. It is known for its images communicated through the use of Jim Henson's Muppets, and includes short films, with humor and cultural references. It premiered on November 10, 1969, to positive reviews, some controversy, and high viewership. It has aired on the United States national public television provider PBS since its debut, with its first run moving to premium channel HBO on January 16, 2016, then its sister streaming service Max in 2020.

Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable.

Children's literature or juvenile literature includes stories, books, magazines, and poems that are created for children. Modern children's literature is classified in two different ways: genre or the intended age of the reader, from picture books for the very young to young adult fiction.

Roald Dahl was a British author of popular children's literature and short stories, a poet, screenwriter and a wartime fighter ace. His books have sold more than 300 million copies worldwide. He has been called "one of the greatest storytellers for children of the 20th century".

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by executive dysfunction occasioning symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate.

Child labour is the exploitation of children through any form of work that interferes with their ability to attend regular school, or is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful. Such exploitation is prohibited by legislation worldwide, although these laws do not consider all work by children as child labour; exceptions include work by child artists, family duties, supervised training, and some forms of work undertaken by Amish children, as well as by Indigenous children in the Americas.

A child (pl. children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. It may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking countries, the legal definition of child generally refers to a minor, in this case as a person younger than the local age of majority, regardless of their physical, mental and sexual development as biological adults. Children generally have fewer rights and responsibilities than adults. They are generally classed as unable to make serious decisions.

Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th century in Germany, Bavaria and Alsace to serve children whose parents both worked outside home. The term was coined by German pedagogue Friedrich Fröbel, whose approach globally influenced early-years education. Today, the term is used in many countries to describe a variety of educational institutions and learning spaces for children ranging from two to six years of age, based on a variety of teaching methods.

The Montessori method of education is a type of educational method that involves children's natural interests and activities rather than formal teaching methods. A Montessori classroom places an emphasis on hands-on learning and developing real-world skills. It emphasizes independence and it views children as naturally eager for knowledge and capable of initiating learning in a sufficiently supportive and well-prepared learning environment. It discourages some conventional measures of achievement, such as grades and tests.

Children's Day is a commemorative date celebrated annually in honour of children, whose date of observance varies by country. In 1925, International Children's Day was first proclaimed in Geneva during the World Conference on Child Welfare. Since 1950, it is celebrated on 1 June in many countries, which follow the suggestion from Women's International Democratic Federation. World Children's Day is celebrated on 20 November to commemorate the Declaration of the Rights of the Child by the UN General Assembly on 20 November 1959. In some countries, it is Children's Week and not Children's Day. The Sikhs celebrate Children Day on 20 December to 27 December.

Child abuse is physical, sexual, emotional and/or psychological maltreatment or neglect of a child, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to act by a parent or a caregiver that results in actual or potential wrongful harm to a child and can occur in a child's home, or in organizations, schools, or communities the child interacts with.
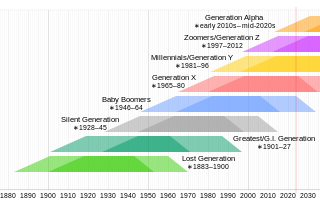
Generation Z, colloquially known as Zoomers, is the demographic cohort succeeding Millennials and preceding Generation Alpha. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1990s as starting birth years and the early 2010s as ending birth years. Most members of Generation Z are the children of Generation X or older Millennials.
Pedophilia is a psychiatric disorder in which an adult or older adolescent experiences a primary or exclusive sexual attraction to prepubescent children. Although girls typically begin the process of puberty at age 10 or 11, and boys at age 11 or 12, psychiatric diagnostic criteria for pedophilia extend the cut-off point for prepubescence to age 13. People with the disorder are often referred to as pedophiles.
Child sexual abuse (CSA), also called child molestation, is a form of child abuse in which an adult or older adolescent uses a child for sexual stimulation. Forms of child sexual abuse include engaging in sexual activities with a child, indecent exposure, child grooming, and child sexual exploitation, such as using a child to produce child pornography.
UNICEF, originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to children worldwide. The organization is one of the most widely known and visible social welfare entities globally, operating in 192 countries and territories. UNICEF's activities include providing immunizations and disease prevention, administering treatment for children and mothers with HIV, enhancing childhood and maternal nutrition, improving sanitation, promoting education, and providing emergency relief in response to disasters.
Child pornography is erotic material that depicts persons under the age of 18. The precise characteristics of what constitutes child pornography varies by criminal jurisdiction.
Autism, also called autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or autism spectrum condition (ASC), is a neurodevelopmental disorder marked by restricted and repetitive patterns of behavior and deficits in reciprocal social communication. Other common signs include perseverative interests, stereotypic body movements (stimming), rigid routines, hyper- or hyporeactivity to sensory input, and difficulty with social interaction and verbal and nonverbal communication. Autism is clinically regarded as a spectrum disorder, meaning that it can manifest very differently in each person. For example, some are nonspeaking, while others have proficient spoken language. Because of this, there is wide variation in the support needs of people across the autism spectrum.

YouTube Kids is a video app and website for children developed by YouTube, a subsidiary of Google. The app provides a version of the service oriented solely towards children, with curated selections of content, parental control features, and filtering of videos deemed inappropriate for viewing by children under the age of 13, in accordance with the Children's Online Privacy Protection Act, which prohibits the regular YouTube app from profiling children under the age of 13 for advertising purposes.
















