| Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis | |
|---|---|
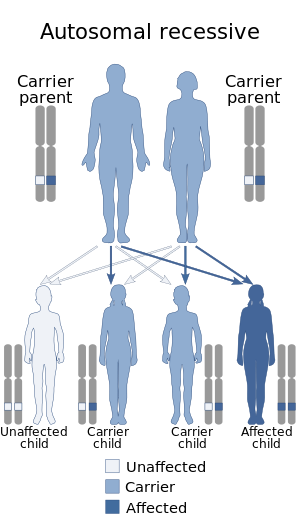 | |
| Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner |
Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis (NCPF) is a chronic liver disease [1] and type of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (NCPH).
| Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner |
Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis (NCPF) is a chronic liver disease [1] and type of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (NCPH).
It is characterized by 'obliterative portovenopathy', which leads to various problems such as portal hypertension, massive splenomegaly, and variceal bleeding. It is estimated that about 85% of people with NCPF have repeated episodes of variceal bleeding. [2]
Hallmark of the disease is thrombosis/sclerosis of branches of portal vein. Vessels formed are often termed as mesangiosinusoids or periportal cavernoma.[ citation needed ]
| | This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (March 2022) |

Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8-10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severe cases may be treated with glucocorticoids. The condition often comes on suddenly and may progress in severity very rapidly.

Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop severe bleeding which left untreated can be fatal. Esophageal varices are typically diagnosed through an esophagogastroduodenoscopy.

Portal hypertension is abnormally increased portal venous pressure – blood pressure in the portal vein and its branches, that drain from most of the intestine to the liver. Portal hypertension is defined as a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Cirrhosis is the most common cause of portal hypertension; other, less frequent causes are therefore grouped as non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. When it becomes severe enough to cause symptoms or complications, treatment may be given to decrease portal hypertension itself or to manage its complications.
Gastrointestinal bleeding, also called gastrointestinal hemorrhage (GIB), is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may include vomiting red blood, vomiting black blood, bloody stool, or black stool. Small amounts of bleeding over a long time may cause iron-deficiency anemia resulting in feeling tired or heart-related chest pain. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, shortness of breath, pale skin, or passing out. Sometimes in those with small amounts of bleeding no symptoms may be present.

Liver biopsy is the biopsy from the liver. It is a medical test that is done to aid diagnosis of liver disease, to assess the severity of known liver disease, and to monitor the progress of treatment.

Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is an artificial channel within the liver that establishes communication between the inflow portal vein and the outflow hepatic vein. It is used to treat portal hypertension which frequently leads to intestinal bleeding, life-threatening esophageal bleeding and the buildup of fluid within the abdomen (ascites).

Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a vascular disease of the liver that occurs when a blood clot occurs in the hepatic portal vein, which can lead to increased pressure in the portal vein system and reduced blood supply to the liver. The mortality rate is approximately 1 in 10.

Gastric antral vascular ectasia (GAVE) is an uncommon cause of chronic gastrointestinal bleeding or iron deficiency anemia. The condition is associated with dilated small blood vessels in the pyloric antrum, which is a distal part of the stomach. The dilated vessels result in intestinal bleeding. It is also called watermelon stomach because streaky long red areas that are present in the stomach may resemble the markings on watermelon.

In medicine, a distal splenorenal shunt procedure (DSRS), also splenorenal shunt procedure and Warren shunt, is a surgical procedure in which the distal splenic vein is attached to the left renal vein. It is used to treat portal hypertension and its main complication. It was developed by W. Dean Warren.
Portopulmonary hypertension (PPH) is defined by the coexistence of portal and pulmonary hypertension. PPH is a serious complication of liver disease, present in 0.25 to 4% of all patients with cirrhosis. Once an absolute contraindication to liver transplantation, it is no longer, thanks to rapid advances in the treatment of this condition. Today, PPH is comorbid in 4-6% of those referred for a liver transplant.

Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), with the latter also including liver inflammation. Non-alcoholic fatty liver is less dangerous than NASH and usually does not progress to NASH. When NAFL does progress to NASH, it may eventually lead to complications such as cirrhosis, liver cancer, liver failure, or cardiovascular disease.
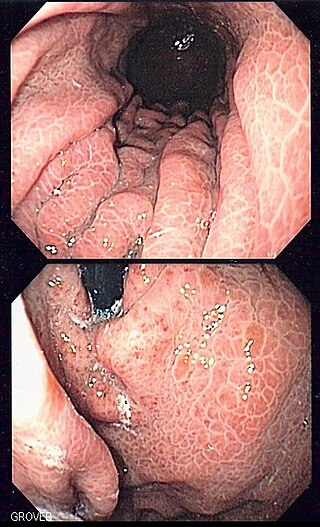
Portal hypertensive gastropathy refers to changes in the mucosa of the stomach in patients with portal hypertension; by far the most common cause of this is cirrhosis of the liver. These changes in the mucosa include friability of the mucosa and the presence of ectatic blood vessels at the surface. Patients with portal hypertensive gastropathy may experience bleeding from the stomach, which may uncommonly manifest itself in vomiting blood or melena; however, portal hypertension may cause several other more common sources of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, such as esophageal varices and gastric varices. On endoscopic evaluation of the stomach, this condition shows a characteristic mosaic or "snake-skin" appearance to the mucosa of the stomach.
Portal venous pressure is the blood pressure in the hepatic portal vein, and is normally between 5-10 mmHg. Raised portal venous pressure is termed portal hypertension, and has numerous sequelae such as ascites and hepatic encephalopathy.
Nodular regenerative hyperplasia (NRH) is a rare liver disease, characterised by the growth of nodules within the liver, resulting in liver hyperplasia. While in many cases it is asymptomatic and thus goes undetected – or is only discovered incidentally while investigating some other medical condition – in some people it results in non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (NCPH). NCPH is generally less severe than the much more common portal hypertension due to cirrhosis. Complications of NCPH can include jaundice, ascites, splenomegaly, and bleeding esophageal varices. Most people with NRH retain normal liver function – even among the subset who go on to develop NCPH – and liver failure in NRH is uncommon. Only a small proportion of NRH patients will ever require liver transplantation.

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repair and subsequent formation of scar tissue, which over time can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may become spontaneously infected. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins in the esophagus, stomach, or intestines, and liver cancer.
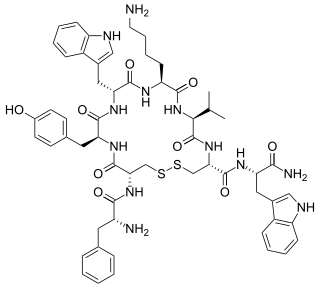
Vapreotide (Sanvar) is a synthetic somatostatin analog. It is used in the treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding in patients with cirrhotic liver disease and AIDS-related diarrhea.
Anorectal varices are the dilation of collateral submucosal vessels due to backflow in the veins of the rectum. Typically this occurs due to portal hypertension which shunts venous blood from the portal system through the portosystemic anastomosis present at this site into the systemic venous system. This can also occur in the esophagus, causing esophageal varices, and at the level of the umbilicus, causing caput medusae. Between 44% and 78% of patients with portal hypertension get anorectal varices.
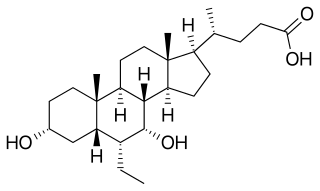
Obeticholic acid (OCA), sold under the brand name Ocaliva, is a semi-synthetic bile acid analogue which has the chemical structure 6α-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid. It is used as a medication used to treat primary biliary cholangitis. Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc. hold the worldwide rights to develop OCA outside Japan and China, where it is licensed to Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma.
Surinder Kumar Sama is an Indian gastroenterologist, known for his expertise in endocrinology and diabetology. He is considered by many as the Father of Gastroenterology in India. The discovery of Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis, an idiopathic chronic liver disease is attributed to him, which he described in a 1962 medical paper, co-authored with Ramalingaswami and Wig. The Government of India awarded him the civilian honour of the Padma Shri in 2004 for his pioneering research on liver diseases including Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis and Hepatitis B. Sama also received the highest Indian medical honour of Dr. B. C. Roy Award in 2004.