Related Research Articles
Observational learning is learning that occurs through observing the behavior of others. It is a form of social learning which takes various forms, based on various processes. In humans, this form of learning seems to not need reinforcement to occur, but instead, requires a social model such as a parent, sibling, friend, or teacher with surroundings. Particularly in childhood, a model is someone of authority or higher status in an environment. In animals, observational learning is often based on classical conditioning, in which an instinctive behavior is elicited by observing the behavior of another, but other processes may be involved as well.

Physical education, often abbreviated to Phys. Ed. or PE, and sometimes informally referred to as gym class or simply just gym, is a subject taught in schools around the world. PE is taught during primary and secondary education and encourages psychomotor, cognitive, and effective learning through physical activity and movement exploration to promote health and physical fitness. When taught correctly and in a positive manner, children and teens can receive a storm of health benefits. These include reduced metabolic disease risk, improved cardiorespiratory fitness, and better mental health. In addition, PE classes can produce positive effects on students' behavior and academic performance. Research has shown that there is a positive correlation between brain development and exercising. Researchers in 2007 found a profound gain in English Arts standardized test scores among students who had 56 hours of physical education in a year, compared to those who had 28 hours of physical education a year.

Albert Bandura was a Canadian-American psychologist. He was a professor of social science in psychology at Stanford University.
Applied psychology is the use of psychological methods and findings of scientific psychology to solve practical problems of human and animal behavior and experience. Educational and organizational psychology, business management, law, health, product design, ergonomics, behavioural psychology, psychology of motivation, psychoanalysis, neuropsychology, psychiatry and mental health are just a few of the areas that have been influenced by the application of psychological principles and scientific findings. Some of the areas of applied psychology include counseling psychology, industrial and organizational psychology, engineering psychology, occupational health psychology, legal psychology, school psychology, sports psychology, community psychology, neuropsychology, medical psychology and clinical psychology, evolutionary psychology, human factors, forensic psychology and traffic psychology. In addition, a number of specialized areas in the general area of psychology have applied branches. However, the lines between sub-branch specializations and major applied psychology categories are often mixed or in some cases blurred. For example, a human factors psychologist might use a cognitive psychology theory. This could be described as human factor psychology or as applied cognitive psychology. When applied psychology is used in the treatment of behavioral disorders there are many experimental approaches to try and treat an individual. This type of psychology can be found in many of the subbranches in other fields of psychology.
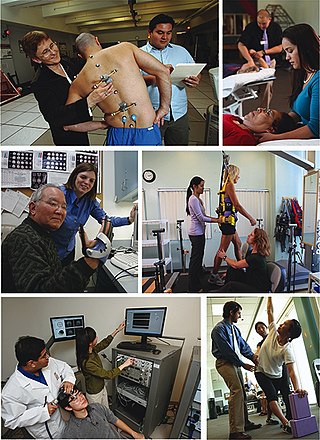
Kinesiology is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses physiological, anatomical, biomechanical, pathological, neuropsychological principles and mechanisms of movement. Applications of kinesiology to human health include biomechanics and orthopedics; strength and conditioning; sport psychology; motor control; skill acquisition and motor learning; methods of rehabilitation, such as physical and occupational therapy; and sport and exercise physiology. Studies of human and animal motion include measures from motion tracking systems, electrophysiology of muscle and brain activity, various methods for monitoring physiological function, and other behavioral and cognitive research techniques.

Sports science is a discipline that studies how the healthy human body works during exercise, and how sports and physical activity promote health and performance from cellular to whole body perspectives. The study of sports science traditionally incorporates areas of physiology, psychology, anatomy, biomechanics, biochemistry, and kinesiology.
Mathematical psychology is an approach to psychological research that is based on mathematical modeling of perceptual, thought, cognitive and motor processes, and on the establishment of law-like rules that relate quantifiable stimulus characteristics with quantifiable behavior. The mathematical approach is used with the goal of deriving hypotheses that are more exact and thus yield stricter empirical validations. There are five major research areas in mathematical psychology: learning and memory, perception and psychophysics, choice and decision-making, language and thinking, and measurement and scaling.
J. A. Scott Kelso is an American neuroscientist, and Professor of Complex Systems and Brain Sciences, Professor of Psychology, Biological Sciences and Biomedical Science at Florida Atlantic University (FAU) in Boca Raton, Florida and The University of Ulster in Derry, N. Ireland.
Evolutionary educational psychology is the study of the relation between inherent folk knowledge and abilities and accompanying inferential and attributional biases as these influence academic learning in evolutionarily novel cultural contexts, such as schools and the industrial workplace. The fundamental premises and principles of this discipline are presented below.
Social cognitive theory (SCT), used in psychology, education, and communication, holds that portions of an individual's knowledge acquisition can be directly related to observing others within the context of social interactions, experiences, and outside media influences. This theory was advanced by Albert Bandura as an extension of his social learning theory. The theory states that when people observe a model performing a behavior and the consequences of that behavior, they remember the sequence of events and use this information to guide subsequent behaviors. Observing a model can also prompt the viewer to engage in behavior they already learned. Depending on whether people are rewarded or punished for their behavior and the outcome of the behavior, the observer may choose to replicate behavior modeled. Media provides models for a vast array of people in many different environmental settings.

Play is a range of intrinsically motivated activities done for recreational pleasure and enjoyment. Play is commonly associated with children and juvenile-level activities, but may be engaged in at any life stage, and among other higher-functioning animals as well, most notably mammals and birds.

Bowling Green State University College of Education and Human Development is the School of education at Bowling Green State University in Bowling Green, Ohio, United States. The college offers curriculum for both undergraduate and graduate students.
Some of the research that is conducted in the field of psychology is more "fundamental" than the research conducted in the applied psychological disciplines, and does not necessarily have a direct application. The subdisciplines within psychology that can be thought to reflect a basic-science orientation include biological psychology, cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and so on. Research in these subdisciplines is characterized by methodological rigor. The concern of psychology as a basic science is in understanding the laws and processes that underlie behavior, cognition, and emotion. Psychology as a basic science provides a foundation for applied psychology. Applied psychology, by contrast, involves the application of psychological principles and theories yielded up by the basic psychological sciences; these applications are aimed at overcoming problems or promoting well-being in areas such as mental and physical health and education.
Sport psychology was defined by the European Federation of Sport Psychology (FEPSAC) in 1996, as the study of the psychological basis, processes, and effects of sport. Otherwise, sport is considered as any physical activity where the individuals engage for competition and health. Sport psychology is recognized as an interdisciplinary science that draws on knowledge from many related fields including biomechanics, physiology, kinesiology and psychology. It involves the study of how psychological factors affect performance and how participation in sport and exercise affect psychological and physical factors. Sport psychologists teach cognitive and behavioral strategies to athletes in order to improve their experience and performance in sports.
Psychology encompasses a vast domain, and includes many different approaches to the study of mental processes and behavior. Below are the major areas of inquiry that taken together constitute psychology. A comprehensive list of the sub-fields and areas within psychology can be found at the list of psychology topics and list of psychology disciplines.
Michelle L. Segar is an American behavioral sustainability scientist, author, and speaker. She is known for her research on how to create autonomous and sustained motivation for self-care behaviors. This work integrates ideas from marketing, persuasion, executive functioning, learning, goal pursuit, positive psychology, organizational change, behavioral economics, and socialization to understand and leverage the unconscious influences on the daily decision making that underlies sustained health, fitness, and well-being. She has written two books. One book is about the science behind lasting exercise motivation, No Sweat: How the Simple Science of Motivation Can Bring You a Lifetime of Fitness. The other, The Joy Choice: How to Finally Achieve Lasting Changes in Eating and Exercise, explains the new science and method for breaking down all-or-nothing thinking and cultivating the in-the-moment decisions that support sustainable self-care, health, and well-being. Reviewing this book for The Washington Post in 2022, health columnist Gretchen Reynolds wrote: “It offers gentle, practical guidance about how to stop setting and then backsliding on ambitious exercise and eating goals and instead find the ‘perfect imperfect option’ that motivates us … now.”
Coaching psychology is a field of applied psychology that applies psychological theories and concepts to the practice of coaching. Its aim is to increase performance, self-actualization, achievement and well-being in individuals, teams and organisations by utilising evidence-based methods grounded in scientific research. Coaching psychology is influenced by theories in various psychological fields, such as humanistic psychology, positive psychology, learning theory and social psychology.
The International Society of Sport Psychology (ISSP) is an international and multidisciplinary organization of researchers, psychologists, educators, coaches, administrators, and national organizations in sport and exercise psychology. The organization is founded in 1965. ISSP promotes research, practice, and development of sport and exercise psychology.
The Canadian Society for Psychomotor Learning and Sport Psychology (SCAPPS) is a multidisciplinary association that promotes psychomotor learning and sport psychology in Canada. It was founded as a society in Banff, Alberta, in 1977. The organization encourages the exchange of ideas and scientific knowledge.
References
- ↑ "North American Society for the Psychology of Sport and Physical Activity". APA Dictionary of Psychology. 2023-09-12. Retrieved 2023-09-12.
- ↑ Weinberg, Robert S.; Gould, Daniel. Foundations of Sport and Exercise Psychology. Human Kinetics. p. 34. ISBN 978-1-7182-1656-3.