North Coast Line (NCL) opening dates chronologically [1] [2]

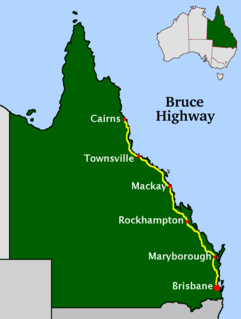
The North Coast railway line is a narrow gauge railway line in Queensland, Australia. It commences at Roma Street station, Brisbane, and largely parallels the Queensland coast to Cairns in Far North Queensland. The line is electrified between Brisbane and Rockhampton. Along the way, the 1680 km railway passes through the numerous towns and cities of eastern Queensland including Nambour, Bundaberg, Gladstone, Rockhampton, Mackay and Townsville. The line though the centre of Rockhampton runs down the middle of Denison Street.
This is a list of the NCL opening dates in chronological order. This list shows the known opening dates for all line construction, including deviations, plus the known dates of other significant NCL related events. A list of the NCL opening dates by section is here.
North Coast Line (NCL) opening dates by section
- 20 Dec 1880 Townsville-Stuart opens
- 6 Aug 1881 Maryborough-Gympie opens
- 11 May 1882 Roma Street-Sandgate (via Normanby) opens
- 30 Mar 1883 Baddow-Howard opens
- 1 April 1886 First section of duplicated track in Queensland, Albion-Eagle Junction, opens
- 22 Dec 1886 Mayne-Albion duplication opened
- 15 Aug 1887 Howard-Goodwood opens
- 20 Feb 1888 Goodwood-Bundaberg opens, links Bundaberg to Maryborough and Gympie
- 11 June 1888 Petrie-Caboolture opens
- 10 June 1889 Gympie-Cooran opens
- 18 Aug 1889 Roma Street-Central opens, first section in Queensland constructed as dual track
- 1 Feb 1890 Caboolture-Landsborough opens
- 1 May 1890 Bowen-Guthalungra opens, creating the 11th isolated system
- 17 Aug 1890 Eagle Junction-Northgate duplication opens
- 1 Nov 1890 Central-Mayne opens as dual track, completing the 'City Railway'
- 1 Jan 1891 Landsborough-Yandina opens
- 1 April 1891 Cooran-Cooroy opens
- 15 June 1891 Bundaberg-North Bundaberg, over Burnett River opens, links Mount Perry line to North Coast line
- 17 July 1891 Yandina-Cooroy opens, links Bundaberg, Maryborough and Gympie to Brisbane, Chrleville and Wallangarra
- 1 Oct 1891 Guthalungra-Bobawaba opens
- 1 July 1892 North Bundaberg-Rosedale opens
- 1 Aug 1896 Gladstone-Iveragh opens
- 1 Oct 1897 Rosedale-Iveragh opens, links Gladstone to Bundaberg and Brisbane
- 1897 Cairns-Gordonvale opens as Cairns Shire Tramway
- 1898 Steamer service between Gladstone-Rockhampton and Gladstone-Mackay-Townsville commenced
- 6 Nov 1899 Rockhampton-North Rockhampton over Fitzroy River opens as dual track, links Emu Park and Broadmount to Rockhampton and Longreach
- 1901 Stuart-Ayr tramway opened by Ayr Tramway Joint Board (ATJB)
- 1903 Bowen-Bobawaba line closed as public railway, leased to Bowen abattoir
- 18 Dec 1903 Gladstone-Rockhampton opens, links Longreach, Springsure and Clermont to Brisbane and beyond
- 1904 QR resumes operation of Bowen-Bobawaba line as a public railway
- 1910 Gordonvale-Babinda tramway opens
- 1910 Don (Bowen)-Proserpine tramway opened by Bowen Proserpine Joint Tramway Board (BPJTB)
- 1 Jan 1911 Stuart-Ayr Tramway purchased from ATJB by Queensland Railways
- 1 July 1911 Cairns-Babinda Tramway purchased from Cairns Shire Council by Queensland Railways
- 18 Oct 1911 Glenmore Junction (North Rockhampton)-Milman opens
- 9 Dec 1912 Babinda-Pawngilly opens
- 30 June 1913 Ayr-Carstairs opens
- 1 July 1913 Paget-Sarina opens
- 3 July 1913 Bobawaba-Home Hill opens
- 1 Sept 1913 Home Hill-Carstairs, including low level Burdekin Bridge opens, links Bowen to Townsville
- 1 Oct 1913 Milman-Yaamba opens
- 14 April 1914 Townsville-Kurukan opens
- 5 April 1915 Kurukan-Rollingstone opens
- 20 July 1915 Sarina-Koumala opens
- 3 Aug 1915 Yaamba-Kunwarara opens
- 1917 Duplication to Caboolture completed
- 31 March 1917 Kunwarara-Marlborough opens
- 2 May 1917 Rollingstone-Moongobulla opens
- 1 July 1917 Don-Proserpine purchased from BPJTB by Queensland Railways
- 19 April 1918 Mackay-Farleigh opens
- 29 July 1918 Moongobulla-Coolbie opens
- 26 Dec 1918 Coolbie-Bambaroo opens
- 5 June 1919 Marlborough-Styx opens
- 21 July 1919 Bambaroo-Toobanna opens
- 13 Sept 1919 Daradgee-Pawngilly opens
- 1 Dec 1919 Toobana-Ingham opens
- 9 August 1920 Styx-Wumalgi opens
- 10 Aug 1920 Koumala-Carmila opens
- 10 Jan 1921 Ingham-Lily Pond opens
- 4 June 1921 Wumalgi-St Lawrence opens
- 24 Sept 1921 St Lawrence-Carmila opens, linking Mackay to Rockhampton and beyond
- 1 March 1922 Gargett-Pakula opened
- 28 Aug 1922 Pakula-Owens Creek opened
- 18 Dec 1922 Innisfail-El Arish opens
- 1 Dec 1923 Farleigh-Proserpine opens, linking Townsville and Ingham with Mackay and beyond
- 3 Dec 1923 El Arish-Feluga opens
- 10 Dec 1924 Lily Pond-Feluga, Innisfail-Daradgee opens, linking Cairns to Townsville and rest of Queensland Railways system
- 1936 Townsville-Stuart duplication opens
- 1957 Burdekin High level bridge opens
- 1963 Stuart-Nome duplication opens
- 17 Nov 1979 Roma Street-Bowen Hills (via Central) section electrified
- 1979 Brunswick Street-Northgate third line completed
- 24 Nov 1980 Midgee-Rocklands-Gracemere opens
- 3 March 1982 Roma Street-Bowen Hills (via Normanby) section electrified
- 18 Sep 1982 Bowen Hills-Northgate electrified
- 23 April 1983 Northgate-Petrie electrified
- 26 May 1986 Rocklands-Port Curtis Junction opens, Gracemere-Port Curtis Junction and Midgee-Port Curtis Junction sections closed
- 28 June 1986 Petrie-Caboolture electrified
- 6 Sept 1986 Gladstone-Rockhampton electrification commissioned
- 28 April 1988 Caboolture-Nambour electrification commissioned
- 23 May 1988 Maryborough bypass opens
- 9 Dec 1988 Gympie bypass opens
- 4 Feb 1989 Nambour-Gympie North electrification commissioned
- 1989 Gympie North-Gladstone electrification commissioned
- 2 May 1993 Mackay realignment opens
- 1 Sep 1993 Bowen realignment opens
- 1995 Gladstone-Rocklands duplication completed
- 2009 Caboolture-Beerburrum duplicated

Townsville railway station is located on the North Coast line in Queensland, Australia. It serves the city of Townsville. The station has one platform. Opposite the platform lies a passing loop. It is also the starting point for the Great Northern line.

Stuart is a rural coastal suburb of the City of Townsville, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Stuart had a population of 1,386 people.

Maryborough railway station is a heritage-listed railway station at Lennox Street, Maryborough, Fraser Coast Region, Queensland, Australia. It is on the North Coast line serving the city of Maryborough. It was designed by Chief Engineer of the Queensland Railways Department and built from 1878 to 1890 by John Roddam & John Walker. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992.