Related Research Articles

The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about 85,133,000 km2 (32,870,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia.

North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) is a deep water mass formed in the North Atlantic Ocean. Thermohaline circulation of the world's oceans involves the flow of warm surface waters from the southern hemisphere into the North Atlantic. Water flowing northward becomes modified through evaporation and mixing with other water masses, leading to increased salinity. When this water reaches the North Atlantic, it cools and sinks through convection, due to its decreased temperature and increased salinity resulting in increased density. NADW is the outflow of this thick deep layer, which can be detected by its high salinity, high oxygen content, nutrient minima, high 14C/12C, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
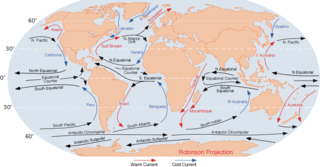
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.

The Labrador Sea is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay through the Davis Strait. It is a marginal sea of the Atlantic.
The capelin or caplin is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the North Atlantic, North Pacific and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat a great deal of krill and other crustaceans. Among others, whales, seals, Atlantic cod, Atlantic mackerel, squid and seabirds prey on capelin, in particular during the spawning season while the capelin migrate south. Capelin spawn on sand and gravel bottoms or sandy beaches at the age of two to six years. When spawning on beaches, capelin have an extremely high post-spawning mortality rate which, for males, is close to 100%. Males reach 20 cm (8 in) in length, while females are up to 25.2 cm (10 in) long. They are olive-coloured dorsally, shading to silver on sides. Males have a translucent ridge on both sides of their bodies. The ventral aspects of the males iridesce reddish at the time of spawn.

The East Greenland Current (EGC) is a cold, low-salinity current that extends from Fram Strait (~80N) to Cape Farewell (~60N). The current is located off the eastern coast of Greenland along the Greenland continental margin. The current cuts through the Nordic Seas and through the Denmark Strait. The current is of major importance because it directly connects the Arctic to the Northern Atlantic, it is a major contributor to sea ice export out of the Arctic, and it is a major freshwater sink for the Arctic.

The Greenland Sea is a body of water that borders Greenland to the west, the Svalbard archipelago to the east, Fram Strait and the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Norwegian Sea and Iceland to the south. The Greenland Sea is often defined as part of the Arctic Ocean, sometimes as part of the Atlantic Ocean. However, definitions of the Arctic Ocean and its seas tend to be imprecise or arbitrary. In general usage the term "Arctic Ocean" would exclude the Greenland Sea. In oceanographic studies the Greenland Sea is considered part of the Nordic Seas, along with the Norwegian Sea. The Nordic Seas are the main connection between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans and, as such, could be of great significance in a possible shutdown of thermohaline circulation. In oceanography the Arctic Ocean and Nordic Seas are often referred to collectively as the "Arctic Mediterranean Sea", a marginal sea of the Atlantic.

The North Atlantic Gyre of the Atlantic Ocean is one of five great oceanic gyres. It is a circular ocean current, with offshoot eddies and sub-gyres, across the North Atlantic from the Intertropical Convergence Zone to the part south of Iceland, and from the east coasts of North America to the west coasts of Europe and Africa.

Lincoln Sea is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from Cape Columbia, Canada, in the west to Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland, in the east. The northern limit is defined as the great circle line between those two headlands. It is covered with sea ice throughout the year, the thickest sea ice in the Arctic Ocean, which can be up to 15 m (49 ft) thick. Water depths range from 100 m (330 ft) to 300 m (980 ft). Water and ice from Lincoln Sea empty into Robeson Channel, the northernmost part of Nares Strait, most of the time.

The Greenland halibut or Greenland turbot belongs to the family Pleuronectidae, and is the only species of the genus Reinhardtius. It is a predatory fish that mostly ranges at depths between 500 and 1,000 m (1,600–3,300 ft), and is found in the cold northern Atlantic, northern Pacific, and Arctic Oceans.

The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately 14,060,000 km2 (5,430,000 sq mi) and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing world ocean.

The Fram Strait is the passage between Greenland and Svalbard, located roughly between 77°N and 81°N latitudes and centered on the prime meridian. The Greenland and Norwegian Seas lie south of Fram Strait, while the Nansen Basin of the Arctic Ocean lies to the north. Fram Strait is noted for being the only deep connection between the Arctic Ocean and the World Oceans. The dominant oceanographic features of the region are the West Spitsbergen Current on the east side of the strait and the East Greenland Current on the west.
The East Iceland Current (EIC) is a cold water ocean current that forms east of Greenland at 72°N, 11°W as a branch of the East Greenland Current that merges with the Irminger Current flowing southward until it meets the northeast part of Iceland. It quickly rotates in a counterclockwise direction and flows eastward along the Iceland-Faeroe Ridge before turning north and flowing into the Norwegian Sea. The EIC flows at an average rate of 6 centimeters per second, with a maximum velocity of 10 centimeters per second occurring as the current turns eastward.
The Denmark Strait overflow is an undersea overflow located in the Denmark Strait between Greenland and Iceland. The overflow transports around 3.2 million m3 (110 million cu ft) of water per second, greatly eclipsing the discharge of the Amazon River into the Atlantic Ocean and the flow rate of the former Guaíra Falls. The descending column of water is approximately 200 m (660 ft) wide and 200 m (660 ft) thick and descends over a length of around 1,000 km (620 mi). It is formed by the density difference of the water masses either side of the Denmark Strait; the southward-flowing water originating from the Nordic Seas is colder and consequently more dense than the Irminger Sea to the south of the strait. At the Greenland–Iceland Rise – an elevated ridge forming the overflow's apex – the colder water cascades along the seafloor to a depth of around 3,000 m (10,000 ft). Due to the Coriolis effect, the downward flow of water is deflected to the right, resulting in the descending water on the Greenland side of the channel being roughly 1 km (0.62 mi) higher than the opposite side of the channel.
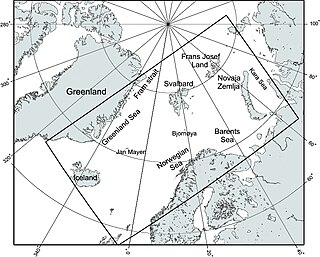
The Nordic Seas are located north of Iceland and south of Svalbard. They have also been defined as the region located north of the Greenland-Scotland Ridge and south of the Fram Strait-Spitsbergen-Norway intersection. Known to connect the North Pacific and the North Atlantic waters, this region is also known as having some of the densest waters, creating the densest region found in the North Atlantic Deep Water. The deepest waters of the Arctic Ocean are connected to the worlds other oceans through Nordic Seas and Fram Strait. There are three seas within the Nordic Sea: Greenland Sea, Norwegian Sea, and Iceland Sea. The Nordic Seas only make up about 0.75% of the world's oceans. This region is known as having diverse features in such a small topographic area, such as the mid oceanic ridge systems. Some locations have shallow shelves, while others have deep slopes and basins. This region, because of the atmosphere-ocean transfer of energy and gases, has varying seasonal climate. During the winter, sea ice is formed in the western and northern regions of the Nordic Seas, whereas during the summer months, the majority of the region remains free of ice.
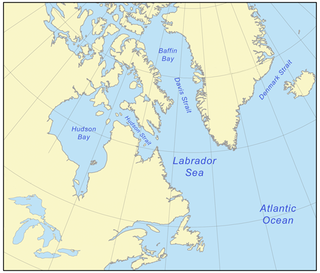
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.
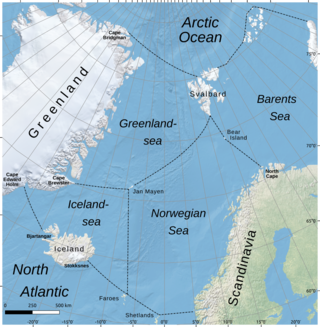
The Iceland Sea, a relatively small body of water, is bounded by Iceland. It is characterized by its proximity to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which transforms into the Kolbeinsey Ridge, and the Greenland-Scotland Ridge, and it lies just south of the Arctic Circle. This region is typically delineated by Greenland to the west, the Denmark Strait, and the continental shelf break south of Iceland to the south. Next in the boundary line are Jan Mayen, being a small Norwegian volcanic island, and the Jan Mayen Fracture Zone to the north, with the Jan Mayen Ridge to the east of the sea. This ridge serves as the northern boundary of the Iceland Sea, acting as the dividing line from the Greenland Sea. To the immediate south of Jan Mayen, the Iceland-Jan Mayen Ridge stretches towards the Iceland-Faroe Ridge, creating a boundary between the Iceland Sea and the Norwegian Sea to the east.

Cold and dense water from the Nordic Seas is transported southwards as Faroe-Bank Channel overflow. This water flows from the Arctic Ocean into the North Atlantic through the Faroe-Bank Channel between the Faroe Islands and Scotland. The overflow transport is estimated to contribute to one-third of the total overflow over the Greenland-Scotland Ridge. The remaining two-third of overflow water passes through Denmark Strait, the Wyville Thomson Ridge (0.3 Sv), and the Iceland-Faroe Ridge (1.1 Sv).
Reykjavík was one of the multi-member constituencies of the Althing, the national legislature of Iceland. The constituency was established in 1844 when the Althing was converted into a consultative assembly. It was abolished in 2003 when the constituency was split into two constituencies following the re-organisation of constituencies across Iceland. Reykjavík was conterminous with the municipality of Reykjavík.
References
- Kjetil Våge, Robert S. Pickart, Michael A. Spall, Héðinn Valdimarsson, Steingrímur Jónsson, Daniel J. Torres, Svein Østerhus & Tor Eldevik, Significant role of the North Icelandic Jet in the formation of Denmark Strait overflow water, Nature Geoscience 4, 723–727 (2011) doi:10.1038/ngeo1234
- Steingrimur Jonsson and Hedinn Valdimarsson, A new path for the Denmark Strait overflow water from the Iceland, GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L03305, doi:10.1029/2003GL019214
- Stefanie Semper, Kjetil Våge, Robert S. Pickart, Héðinn Valdimarsson, Daniel J. Torres & Steingrímur Jónsson, The emergence of the North Icelandic Jet and its evolution from Northeast Iceland to Denmark Strait, Journal of Physical Oceanography, 49, 2499-2521, doi:10.1175/JPO-D-19-0088.1
- North Icelandic Jet: New Ocean Current Could Change Climate Picture