
In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each element is the sum of the two elements that precede it. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn . Many writers begin the sequence with 0 and 1, although some authors start it from 1 and 1 and some from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the sequence begins

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase or receive ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.

Oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is the most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium.
The number π is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159, that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. It appears in many formulae across mathematics and physics, and some of these formulae are commonly used for defining π, to avoid relying on the definition of the length of a curve.
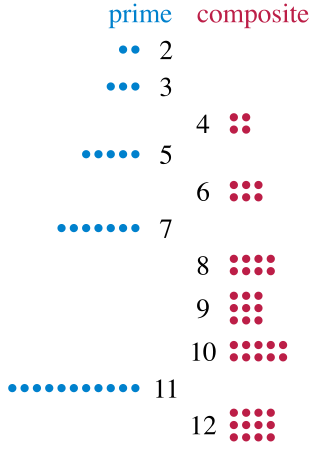
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.

Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation.

Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), that allows data exchange and delivery of power between many types of electronics. It specifies its architecture, in particular its physical interface, and communication protocols for data transfer and power delivery to and from hosts, such as personal computers, to and from peripheral devices, e.g. displays, keyboards, and mass storage devices, and to and from intermediate hubs, which multiply the number of a host's ports.

Zeus is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.

Wayne Mark Rooney is an English professional football manager and former player who was most recently the head coach of EFL Championship club Plymouth Argyle. Widely considered one of the best players of his generation and one of the greatest British players of all time, Rooney is the record goalscorer for Manchester United, and was the record goalscorer for the England national team from 2015 to 2023. He has also made more appearances for England than any other outfield player. Rooney spent most of his playing career as a forward, but was also used in various midfield roles.
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies.
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is a square number, the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.

R is a programming language for statistical computing and data visualization. It has been adopted in the fields of data mining, bioinformatics and data analysis.

The Monty Hall problem is a brain teaser, in the form of a probability puzzle, based nominally on the American television game show Let's Make a Deal and named after its original host, Monty Hall. The problem was originally posed in a letter by Steve Selvin to the American Statistician in 1975. It became famous as a question from reader Craig F. Whitaker's letter quoted in Marilyn vos Savant's "Ask Marilyn" column in Parade magazine in 1990:
Suppose you're on a game show, and you're given the choice of three doors: Behind one door is a car; behind the others, goats. You pick a door, say No. 1, and the host, who knows what's behind the doors, opens another door, say No. 3, which has a goat. He then says to you, "Do you want to pick door No. 2?" Is it to your advantage to switch your choice?
Call of Duty is a military first-person shooter video game series and media franchise published by Activision, starting in 2003. The games were first developed by Infinity Ward, then by Treyarch and Sledgehammer Games. Several spin-off and handheld games were made by other developers. The most recent, Call of Duty: Black Ops 6, was released on October 25, 2024.

The PlayStation 2 (PS2) is a home video game console developed and marketed by Sony Computer Entertainment. It was first released in Japan on 4 March 2000, in North America on 26 October 2000, in Europe on 24 November 2000, in Australia on 30 November 2000, and other regions thereafter. It is the successor to the original PlayStation console, as well as the second installment in the PlayStation brand of consoles. As a sixth-generation console, it competed with Nintendo's GameCube, Sega's Dreamcast, and Microsoft's Xbox. It is the best-selling video game console of all time, having sold over 160 million units worldwide, nearly triple the combined sales of its competing consoles.

Christopher Grant Wood is a New Zealand professional footballer who plays as a forward for Premier League club Nottingham Forest and captains the New Zealand national team.
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of its first beta on November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released on September 23, 2008. The operating system has been developed by Google on a yearly schedule since at least 2011. New major releases are announced at Google I/O in May along with beta testing with the stable version usually released to the public between August and October.

Mohamed Salah Hamed Mahrous Ghaly, known as Mohamed Salah or Mo Salah, is an Egyptian professional footballer who plays as a right winger or forward for Liverpool and captains the Egypt national team. Widely regarded as one of the best players of his generation, one of the greatest African players of all time and one of the greatest wingers in the history of the sport, he is known for his clinical finishing, dribbling, speed, and playmaking abilities.

Ted Lasso is an American sports comedy-drama television series developed by Jason Sudeikis, Bill Lawrence, Brendan Hunt, and Joe Kelly, based on a character Sudeikis portrayed in a series of promotional media for NBC Sports's coverage of England's Premier League.














