
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation for the problems of mathematical analysis. Numerical analysis naturally finds application in all fields of engineering and the physical sciences, but in the 21st century also the life sciences, social sciences, medicine, business and even the arts have adopted elements of scientific computations. The growth in computing power has revolutionized the use of realistic mathematical models in science and engineering, and subtle numerical analysis is required to implement these detailed models of the world. For example, ordinary differential equations appear in celestial mechanics ; numerical linear algebra is important for data analysis; stochastic differential equations and Markov chains are essential in simulating living cells for medicine and biology.

In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface. The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an objective, and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it.

Computational physics is the study and implementation of numerical analysis to solve problems in physics for which a quantitative theory already exists. Historically, computational physics was the first application of modern computers in science, and is now a subset of computational science.
ISO 3166-1 is part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and defines codes for the names of countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. The official name of the standard is Codes for the representation of names of countries and their subdivisions – Part 1: Country codes. It defines three sets of country codes:
In the mathematical subfield of numerical analysis, numerical stability is a generally desirable property of numerical algorithms. The precise definition of stability depends on the context. One is numerical linear algebra and the other is algorithms for solving ordinary and partial differential equations by discrete approximation.
James Hardy Wilkinson FRS was a prominent figure in the field of numerical analysis, a field at the boundary of applied mathematics and computer science particularly useful to physics and engineering.
"How High the Moon" is a jazz standard with lyrics by Nancy Hamilton and music by Morgan Lewis. It was first featured in the 1940 Broadway revue Two for the Show, where it was sung by Alfred Drake and Frances Comstock. In Two for the Show, this was a rare serious moment in an otherwise humorous revue.

Num Lock or Numeric Lock (⇭) is a key on the numeric keypad of most computer keyboards. It is a lock key, like Caps Lock and Scroll Lock. Its state affects the function of the numeric keypad commonly located to the right of the main keyboard, and is commonly displayed by an LED built into the keyboard.
ISO 3166-1 numeric codes are three-digit country codes defined in ISO 3166-1, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), to represent countries, dependent territories, and special areas of geographical interest. They are similar to the three-digit country codes developed and maintained by the United Nations Statistics Division, from which they originate in its UN M.49 standard. They were first included as part of the ISO 3166 standard in its second edition in 1981, but they were released by the United Nations Statistics Division since as early as 1970.
A numeric character reference (NCR) is a common markup construct used in SGML and SGML-derived markup languages such as HTML and XML. It consists of a short sequence of characters that, in turn, represents a single character. Since WebSgml, XML and HTML 4, the code points of the Universal Character Set (UCS) of Unicode are used. NCRs are typically used in order to represent characters that are not directly encodable in a particular document. When the document is interpreted by a markup-aware reader, each NCR is treated as if it were the character it represents.
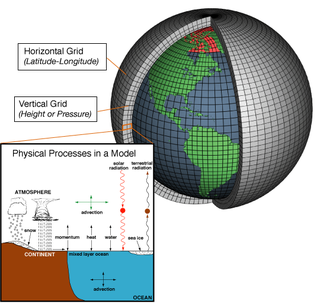
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and other European languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words, such as unicycle – bicycle – tricycle, dyad – triad – decade, biped – quadruped, September – October – November – December, decimal – hexadecimal, sexagenarian – octogenarian, centipede – millipede, etc. There are two principal systems, taken from Latin and Greek, each with several subsystems; in addition, Sanskrit occupies a marginal position. There is also an international set of metric prefixes, which are used in the metric system and which for the most part are either distorted from the forms below or not based on actual number words.
ISO 31-0 is the introductory part of international standard ISO 31 on quantities and units. It provides guidelines for using physical quantities, quantity and unit symbols, and coherent unit systems, especially the SI. It is intended for use in all fields of science and technology and is augmented by more specialized conventions defined in other parts of the ISO 31 standard. ISO 31-0 was withdrawn on 17 November 2009. It is superseded by ISO 80000-1. Other parts of ISO 31 have also been withdrawn and replaced by parts of ISO 80000.

The Abjad numerals, also called Hisab al-Jummal, are a decimal alphabetic numeral system/alphanumeric code, in which the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet are assigned numerical values. They have been used in the Arabic-speaking world since before the eighth century when positional Arabic numerals were adopted. In modern Arabic, the word ʾabjadīyah (أَبْجَدِيَّة) means 'alphabet' in general.

The Apple Keyboard is a keyboard designed by Apple Inc. first for the Apple line, then the Macintosh line of computers. Dozens of models have been released over time, including the Apple Extended Keyboard. Currently, Apple offers only three keyboards via Bluetooth: Magic Keyboard, and Magic Keyboard with Numeric Keypad. The space gray model is also included with the iMac Pro.
ISO/IEC 10967, Language independent arithmetic (LIA), is a series of standards on computer arithmetic. It is compatible with ISO/IEC/IEEE 60559:2011, more known as IEEE 754-2008, and much of the specifications are for IEEE 754 special values (though such values are not required by LIA itself, unless the parameter iec559 is true). It was developed by the working group ISO/IEC JTC1/SC22/WG11, which was disbanded in 2011.
Numerical linear algebra is the study of how matrix operations can be used to create computer algorithms which efficiently and accurately provide approximate answers to mathematical questions. It is a subfield of numerical analysis, and a type of linear algebra. Because computers use floating-point arithmetic, they cannot exactly represent irrational data, and many algorithms increase that imprecision when implemented by a computer. Numerical linear algebra uses properties of vectors and matrices to develop computer algorithms that minimize computer error while retaining efficiency and precision.

Computational mathematics may refer to two different aspects of the relation between computing and mathematics.

A numeric keypad, number pad, numpad, or ten key, is the palm-sized, 17-key section of a standard computer keyboard, usually on the far right. It provides calculator-style efficiency for entering numbers. The idea of a 10-key number pad cluster was originally introduced by Tadao Kashio, the developer of Casio electronic calculators.







