
Action Against Hunger is a global humanitarian organization which originated in France and is committed to ending world hunger. The organization helps malnourished children and provides communities with access to safe water and sustainable solutions to hunger.

Kwashiorkor is a form of severe protein malnutrition characterized by edema and an enlarged liver with fatty infiltrates. It is thought to be caused by sufficient calorie intake, but with insufficient protein consumption, which distinguishes it from marasmus. Recent studies have found that a lack of antioxidant micronutrients such as Vitamin C, β- carotene, lycopene, and carotenoids as well as the presence of aflatoxins may play a role in the development of the disease. However, the exact cause of kwashiorkor is still unknown. Inadequate food supply is correlated with occurrences of kwashiorkor; occurrences in high income countries are rare. It occurs amongst weaning children to ages of about five years old.

Human nutrition deals with the provision of essential nutrients in food that are necessary to support human life and good health. Poor nutrition is a chronic problem often linked to poverty, food security, or a poor understanding of nutritional requirements. Malnutrition and its consequences are large contributors to deaths, physical deformities, and disabilities worldwide. Good nutrition is necessary for children to grow physically and mentally, and for normal human biological development.

Malnutrition is a condition that results from eating a diet which does not supply a healthy amount of one or more nutrients. This includes diets that have too little nutrients or so many that the diet causes health problems. The nutrients involved can include calories, protein, carbohydrates, fat, vitamins or minerals. A lack of nutrients is called undernutrition or undernourishment while a surplus of nutrients cases overnutrition. Malnutrition is most often used to refer to undernutrition - when an individual is not getting enough calories, protein, or micronutrients. If undernutrition occurs during pregnancy, or before two years of age, it may result in permanent problems with physical and mental development. Extreme undernourishment, known as starvation or chronic hunger, may have symptoms that include: a short height, thin body, very poor energy levels, and swollen legs and abdomen. Those who are malnourished often get infections and are frequently cold. The symptoms of micronutrient deficiencies depend on the micronutrient that is lacking.

Marasmus is a form of severe malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency. It can occur in anyone with severe malnutrition but usually occurs in children. Body weight is reduced to less than 62% of the normal (expected) body weight for the age. Marasmus occurrence increases prior to age 1, whereas kwashiorkor occurrence increases after 18 months. It can be distinguished from kwashiorkor in that kwashiorkor is protein deficiency with adequate energy intake whereas marasmus is inadequate energy intake in all forms, including protein. This clear-cut separation of marasmus and kwashiorkor is however not always clinically evident as kwashiorkor is often seen in a context of insufficient caloric intake, and mixed clinical pictures, called marasmic kwashiorkor, are possible. Protein wasting in kwashiorkor generally leads to edema and ascites, while muscular wasting and loss of subcutaneous fat are the main clinical signs of marasmus.
Therapeutic foods are foods designed for specific, usually nutritional, therapeutic purposes as a form of dietary supplement. The primary examples of therapeutic foods are used for emergency feeding of malnourished children or to supplement the diets of persons with special nutrition requirements, such as the elderly. For liquid nutrition products fed via tube feeding see Medical foods.

Helen Keller International combats the causes and consequences of blindness and malnutrition by establishing programs based on evidence and research in vision, health and nutrition. Founded in 1915 by Helen Keller and George A. Kessler, the organization's mission is to save the sight and lives of the most vulnerable and disadvantaged.
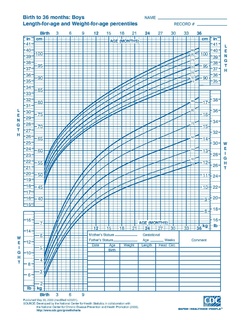
Failure to thrive (FTT) indicates insufficient weight gain or inappropriate weight loss in pediatric patients unless the term is more precisely defined. In children, it is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low weight for the child's age, or by a low rate of increase in the weight.
India's population in 2020 as per world bank is 1.38 billion. Being world’s second-most-populous country and one of its fastest-growing economies, India experiences both challenges and opportunities in context of public health. India is hub for pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries; world-class scientists, clinical trials and hospitals yet country faces daunting public health challenges like child undernutrition, high rates of neonatal and maternal mortality, growth in noncommunicable diseases, high rates of road traffic accidents and other health related issues.
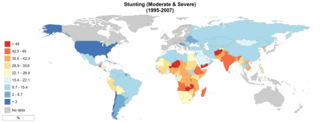
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth, due to malnutrition during fetal development brought on by a malnourished mother. The definition of stunting according to the World Health Organization (WHO) is for the "height for age" value to be less than two standard deviations of the WHO Child Growth Standards median.

Protein–energy malnutrition (PEM), sometimes called protein-energy undernutrition (PEU), is a form of malnutrition that is defined as a range of conditions arising from coincident lack of dietary protein and/or energy (calories) in varying proportions. The condition has mild, moderate, and severe degrees.

"nutritionDay worldwide" is a large scale, worldwide action project designed to reduce disease related malnutrition among hospitalised patients and nursing home residents. The aim of this project is to increase awareness and knowledge regarding disease related malnutrition in hospitalised patients and the elderly.

The Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) is an independent non-profit foundation based in Geneva, Switzerland. GAIN was developed at the UN 2002 Special Session of the General Assembly on Children.

Despite India's 50% increase in GDP since 2013, more than one third of the world's malnourished children live in India. Among these, half of the children under three years old are underweight.
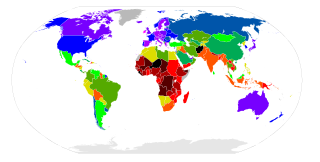
The Save the Children State of the World's Mothers report is an annual report by the Save the Children USA, which compiles statistics on the health of mothers and children and uses them to produce rankings of more than 170 countries, showing where mothers fare best and where they face the greatest hardships. The rankings are presented in the Mothers’ Index, which has been produced annually since the year 2000.
Clinical nutrition centers on the prevention, diagnosis, and management of nutritional changes in patients linked to chronic diseases and conditions primarily in health care. Clinical in this sense refers to the management of patients, including not only outpatients at clinics and in private practice, but also inpatients in hospitals. It incorporates primarily the scientific fields of nutrition and dietetics. Furthermore, clinical nutrition aims to maintain a healthy energy balance, while also providing sufficient amounts of nutrients such as protein, vitamins, and minerals to patients.
Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) is a government program in India which provides nutritional meals, preschool education, primary healthcare, immunization, health check-up and referral services to children under 6 years of age and their mothers. The scheme was launched in 1975, discontinued in 1978 by the government of Morarji Desai, and then relaunched by the Tenth Five Year Plan.

There were 795 million undernourished people in the world in 2014, a decrease of 216 million since 1990, despite the fact that the world already produces enough food to feed everyone—7 billion people—and could feed more than that—12 billion people.
Malnutrition continues to be a problem in the Republic of South Africa, although it is not as endemic as in other countries of Sub-Saharan Africa.

Undernutrition in children, occurs when children do not consume enough calories, protein, or micronutrients to maintain good health. It is common globally and may result in both short and long term irreversible adverse health outcomes. Undernutrition is sometimes used synonymously with malnutrition, however, malnutrition could mean both undernutrition or overnutrition. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that malnutrition accounts for 54 percent of child mortality worldwide, which is about 1 million children. Another estimate, also by WHO, states that childhood underweight is the cause for about 35% of all deaths of children under the age of five worldwide.














