Related Research Articles

The Norwegian Institute of Technology was a science institute in Trondheim, Norway. It was established in 1910, and existed as an independent technical university for 58 years, after which it was merged into the University of Trondheim as an independent college.
Baker Hughes Company is an American international industrial service company and one of the world's largest oil field services companies. The company provides the oil and gas industry with products and services for oil drilling, formation evaluation, completion, production and reservoir consulting. Baker Hughes is organized in Delaware and headquartered in Houston. The company was originally known as Baker Hughes Incorporated until 2017 when it was merged with GE Oil and Gas to become Baker Hughes, a GE Company (BHGE), then in 2019 the company divested from General Electric and became Baker Hughes Company. As of December 2020, GE is no longer majority owner of Baker Hughes, owning 30% and intending to completely divest its ownership stake over the next few years.

A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.

In fluid mechanics, multiphase flow is the simultaneous flow of materials with two or more thermodynamic phases. Virtually all processing technologies from cavitating pumps and turbines to paper-making and the construction of plastics involve some form of multiphase flow. It is also prevalent in many natural phenomena.
Geosteering is the optimal placement of a wellbore based on the results of realtime downhole geological and geophysical logging measurements rather than three-dimensional targets in space. The objective is usually to keep a directional wellbore within a hydrocarbon pay zone defined in terms of its resistivity, density or even biostratigraphy. In mature areas, geosteering may be used to keep a wellbore in a particular section of a reservoir to minimize gas or water breakthrough and maximize economic production from the well. In the process of drilling a borehole, geosteering is the act of adjusting the borehole position on the fly to reach one or more geological targets. These changes are based on geological information gathered while drilling. Originally only a projected target would be aimed for with crude directional tools. Now the advent of rotary steerable tools and an ever-increasing arsenal of geophysical tools enables well placement with ever-increasing accuracy. Typically a basic tool configuration will have directional and inclination sensors, along with a gamma ray tool. Other options are neutron density, look ahead seismic, downhole pressure readings et al. Due to the vast volume of data generated, especially by imaging tools, the data transmitted to surface is a carefully selected fraction of what is available. Data is collected in memory for a data dump when back on surface with the tool.
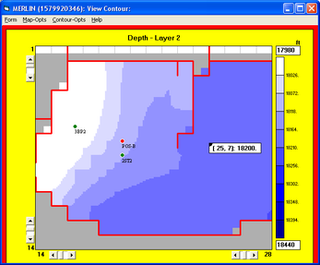
Reservoir simulation is an area of reservoir engineering in which computer models are used to predict the flow of fluids through porous media.
A multiphase flow meter is a device used to measure the individual phase flow rates of constituent phases in a given flow where oil, water and gas mixtures are initially co-mingled together during the oil production processes.
In 2017 the department was merged with the Department of Geology and Mineral Resources Engineering, forming the new Department of Geoscience and Petroleum.

Equinor ASA is a Norwegian state-owned multinational energy company headquartered in Stavanger. It is primarily a petroleum company, operating in 36 countries with additional investments in renewable energy. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Equinor was ranked as the 169th-largest public company in the world. As of 2021, the company has 21,126 employees.
Roxar AS was a provider of products and associated services for reservoir management and production optimisation in the upstream oil and gas industry. Roxar was headquartered in Stavanger, Norway and operated in 19 countries with around 900 employees. Roxar offered software for reservoir interpretation, modelling and simulation, as well as instrumentation for well planning, monitoring, metering and production optimisation. Roxar was acquired by Emerson Electric Company in April 2009.
POSC Caesar Association (PCA) is an international, open, not-for-profit, member organization that promotes the development of open specifications to be used as standards for enabling the interoperability of data, software and related matters.

Gjøa oilfield is an oilfield in the Norwegian section of the North Sea. It lies about 70 kilometres (43 mi) off the Troll field.

Cameron International Corporation though now operating under Schlumberger, is a global provider of pressure control, production, processing, and flow control systems as well as project management and aftermarket services for the oil and gas and process industries. Cameron was acquired by Schlumberger (SLB) in 2016, and now operates as 'Cameron, a Schlumberger Company.' At the start of the SLB acquisition in 2015, Cameron employed approximately 23,000 people and delivered $9.8 billion in revenue.
Cybernetica is a Norwegian technology company with headquarters in Trondheim, Norway. Cybernetica delivers systems for model predictive control (MPC) and soft-sensing, as well as performing research and problem-solving for hire within the field of process control, for customers within polymer, metal and petroleum industry.
In the petroleum industry, a well test is the execution of a set of planned data acquisition activities. The acquired data is analyzed to broaden the knowledge and increase the understanding of the hydrocarbon properties therein and characteristics of the underground reservoir where the hydrocarbons are trapped.
In the petroleum industry, allocation refers to practices of breaking down measures of quantities of extracted hydrocarbons across various contributing sources. Allocation aids the attribution of ownerships of hydrocarbons as each contributing element to a commingled flow or to a storage of petroleum may have a unique ownership. Contributing sources in this context are typically producing petroleum wells delivering flows of petroleum or flows of natural gas to a commingled flow or storage.
FLACS is a commercial Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) software used extensively for explosion modeling and atmospheric dispersion modeling within the field of industrial safety and risk assessment. Main application areas of FLACS are in petrochemical, process manufacturing, food processing, wood processing, metallurgical, and nuclear safety industries.
In petroleum science, reservoir fluids are the fluids mixture contained within the petroleum reservoir which technically are placed in the reservoir rock. Reservoir fluids normally include liquid hydrocarbon, aqueous solutions with dissolved salt, hydrocarbon and non-hydrocarbon gases such as methane and hydrogen sulfide respectively.

GE Oil & Gas was the division of General Electric that owned its investments in the petroleum industry. In July 2017, this division was merged with Baker Hughes.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-02-26. Retrieved 2010-07-01.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-10-13. Retrieved 2010-07-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ http://www.sintef.no/cgi-bin/MsmGo.exe?grab_id=0&page_id=2822&query=olga&hiword=OLGAS%20olga%20%5B%5D