Related Research Articles

Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. DDT was first synthesized in 1874 by the Austrian chemist Othmar Zeidler. DDT's insecticidal action was discovered by the Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller in 1939. DDT was used in the second half of World War II to limit the spread of the insect-borne diseases malaria and typhus among civilians and troops. Müller was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1948 "for his discovery of the high efficiency of DDT as a contact poison against several arthropods". The WHO's anti-malaria campaign of the 1950s and 1960s relied heavily on DDT and the results were promising, though there was a resurgence in developing countries afterwards.

Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other vertebrates. Human malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected Anopheles mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria.

Anopheles or Marsh Mosquitoes is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognized; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which cause malaria in humans in endemic areas. Anopheles gambiae is one of the best known, because of its predominant role in the transmission of the most dangerous malaria parasite species – Plasmodium falciparum.

Plasmodium falciparum is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. It is responsible for around 50% of all malaria cases. P. falciparum is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer and is classified as a Group 2A (probable) carcinogen.

Vector control is any method to limit or eradicate the mammals, birds, insects or other arthropods which transmit disease pathogens. The most frequent type of vector control is mosquito control using a variety of strategies. Several of the "neglected tropical diseases" are spread by such vectors.

A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area, to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus against the diseases they may carry. Examples of such preventable insect-borne diseases include malaria, dengue fever, yellow fever, zika virus, Chagas disease and various forms of encephalitis, including the West Nile virus.
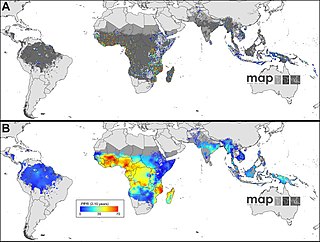
The Malaria Atlas Project (MAP) is a nonprofit academic group led by Peter Gething, Kerry M Stokes Chair in Child Health, at the Telethon Kids Institute, Perth, Western Australia. The group is funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, with previous funding also coming from the Medical Research Council and the Wellcome Trust. MAP aims to disseminate free, accurate, and up-to-date information on malaria and associated topics, organised on a geographical basis. The work of MAP falls into three areas:

Indoor residual spraying or IRS is the process of spraying the inside of dwellings with an insecticide to kill mosquitoes that spread malaria. A dilute solution of insecticide is sprayed on the inside walls of certain types of dwellings—those with walls made from porous materials such as mud or wood but not plaster as in city dwellings. Mosquitoes are killed or repelled by the spray, preventing the transmission of the disease. In 2008, 44 countries employed IRS as a malaria control strategy. Several pesticides have historically been used for IRS, the first and most well-known being DDT.
Rajpal Singh Yadav is an Indian scientist in the field of vector ecology and management at World Health Organization headquarters, Geneva, Switzerland. He has been working with various countries and international organizations to formulate and promote policies for public health pesticide management and vector control.
The mainstay of malaria diagnosis has been the microscopic examination of blood, utilizing blood films. Although blood is the sample most frequently used to make a diagnosis, both saliva and urine have been investigated as alternative, less invasive specimens. More recently, modern techniques utilizing antigen tests or polymerase chain reaction have been discovered, though these are not widely implemented in malaria endemic regions. Areas that cannot afford laboratory diagnostic tests often use only a history of subjective fever as the indication to treat for malaria.

Anopheles darlingi, the American malaria mosquito, is a species of mosquito in the family Culicidae. A. darlingi is one of the major species of mosquito known to be responsible for malaria in the Amazonian regions. It has a wide range of geographic distribution that stretches from Mexico and Argentina but it has also been found to populate in areas affected by deforestation and environment changes due to humans.

Attractive toxic sugar baits (ATSBs) are oral insecticides designed to reduce malaria infections by killing the host vector – the mosquito – rather than the parasite itself.
The Society for Family Health (SFH) is a pan-African non governmental organisation (NGO), founded in 1983 and incorporated in 1985.
Zhou Yiqing is a professor of medicine at the Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology of the People's Liberation Army Academy of Military Medical Sciences. He was one of the scientists who participated in the Project 523 of the Chinese Government under Chairman Mao Zedong. The project resulted in the discovery of artemisinins, a class of antimalarial drugs, from the medicinal plant Artemisia annua.
Anopheles nili is a species of mosquito in the Culicidae family. It comprises the following elements: An. carnevalei, An. nili, An. ovengensis and An. somalicus. The scientific name of this species was first published in 1904 by Theobald. It is the main mosquito species found in the south Cameroon forest zone which bites humans. It is known as a problematic carrier of malaria, although newly discovered, closely related species in the same genus have also been found to interact with A. nili as a disease vector. In that, they both have similar feeding habits on local targets in the Cameroon region.
Sarah Ssali, is a Ugandan social scientist, researcher, academic and academic administrator, who is an associate professor and dean of the School of Gender Studies at Makerere University, Uganda's oldest and largest public university.

Quartan fever is one of the four types of malaria which can be contracted by humans.
The African Health Economics and Policy Association (AfHEA) (French: Association Africaine d'Economie et Politique de la Santé) is a professional association for health economists and policy makers in Africa established in 2009 in Accra. The Association aims to strengthen the use of health economics and health policy analysis in Africa to improve efficiency in health systems. AfHEA is a bilingual organisation operating in English and French.
Emelda Aluoch Okiro is a Kenyan public health researcher who is lead of the Population Health Unit at the Kenya Medical Research Institute–Wellcome Trust program in Kenya. She looks to understand the determinants of health transitions and to evaluate access to health information. She is a Fellow of the African Academy of Sciences.
References
- ↑ "Obinna Onwujekwe" . Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- 1 2 "Obinna Onwujekwe". University of Nigeria. Archived from the original on November 11, 2016. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- 1 2 "The African Advisory Committee on Health Research and Development". WHO | Regional Office for Africa. Retrieved 2022-05-23.
- ↑ "Search". www.ajrh.info. Retrieved 2022-05-23.
- ↑ Onwujekwe, Obinna (April 21, 2016). "How stigma can stymie Nigeria's efforts to extend HIV treatment". Bhekisisa. Archived from the original on January 26, 2018. Retrieved January 25, 2018.
- ↑ Obinna E. Onwujekwe; Kara Hanson; Julia Fox-Rushby (2004). "Inequalities in purchase of mosquito nets and willingness to pay for insecticide-treated nets in Nigeria: Challenges for malaria control interventions". Malaria Journal . 3 (1): 6. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-3-6 . PMC 395839 . PMID 15023234.
- ↑ African Advisory Committee for Research and Development World Health Organization (WHO).
- ↑ Board of Directors Network for Health Equity and Development (NHED).